-
Couldn't load subscription status.
- Fork 0
Registering Middleware
The middleware.add() method allows you to add a middleware to the middleware stack.
container.middleware.add(key, middleware, options);Arguments:
-
key: Unique key for the new middleware, which should match the service name. -
middleware: Callback function with the signature(next, context, args) => {}-
next(): Function that accepts args as a parameter, and is responsible for calling the next middleware in the stack, and return the result of calling the next middleware. -
context:{ serviceName: string, methodName: string, container: Container } -
args: The parameters array passed to the operation performed by the called method or function.
-
-
options:{ priority: number, name: string }
See the Middleware API for more details.
The most basic example of a middleware, without any modifications, is as follows:
container.middleware.add('Service', (next, context, args) => {
return next(args);
});The
next()function receives the arguments from the middleware. You can modify these arguments before calling the next middleware if needed.Internally, if the
next()function is called with empty arguments, it will use the default arguments from the service method instead.
See Service Middleware Considerations for more information about using the container inside a middleware.
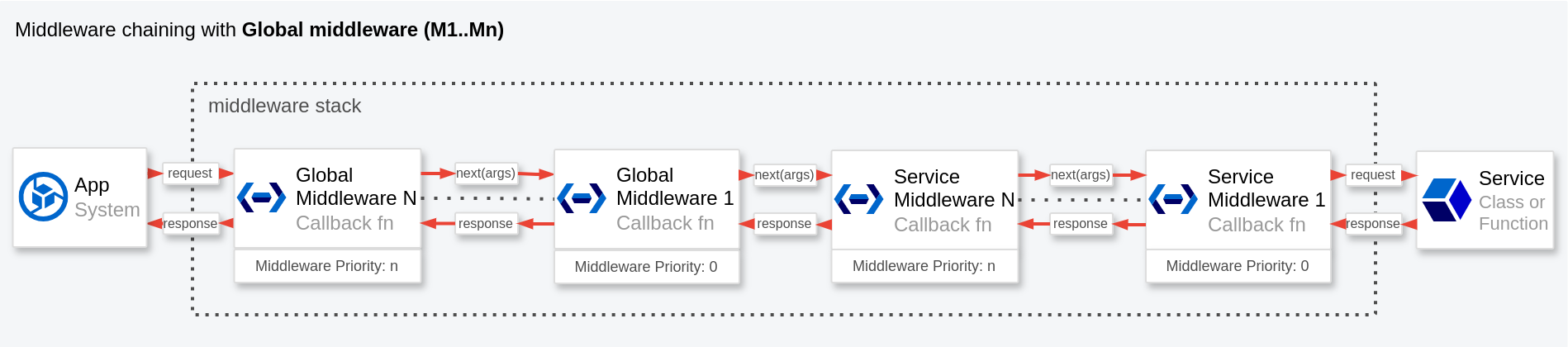
Global middleware are similar to service middleware, but they are applied to all the services in the container.
The signature of addGlobal() method is similar to add() method, without the key parameter:
container.middleware.addGlobal(middleware, options);See the Middleware API for more details.
The most basic example of a global middleware, without any modifications, is as follows:
container.middleware.addGlobal((next, context, args) => {
return next(args);
});Global middleware, which have higher priority than service middleware, are always executed first.
See Global Middleware Considerations for more information about using the container inside a global middleware.
We welcome contributions from the community! Whether it's reporting a bug, suggesting a feature, or contributing code, your involvement is key to making Packet.js better. Please check out this section for more details.
If you encounter any issues or bugs while using packetjs, or if you have any feature requests, please feel free to
open an issue in our GitHub repository. You can report issues, track progress, and engage in discussions with the
community via the following link:
If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to reach out via the discussion board.