-
Couldn't load subscription status.
- Fork 0
Middleware
The concept of middleware remains similar to other frameworks like Express, but it is adapted to intercept and modify the requests and responses of each of the container's services, instead of handling HTTP requests.
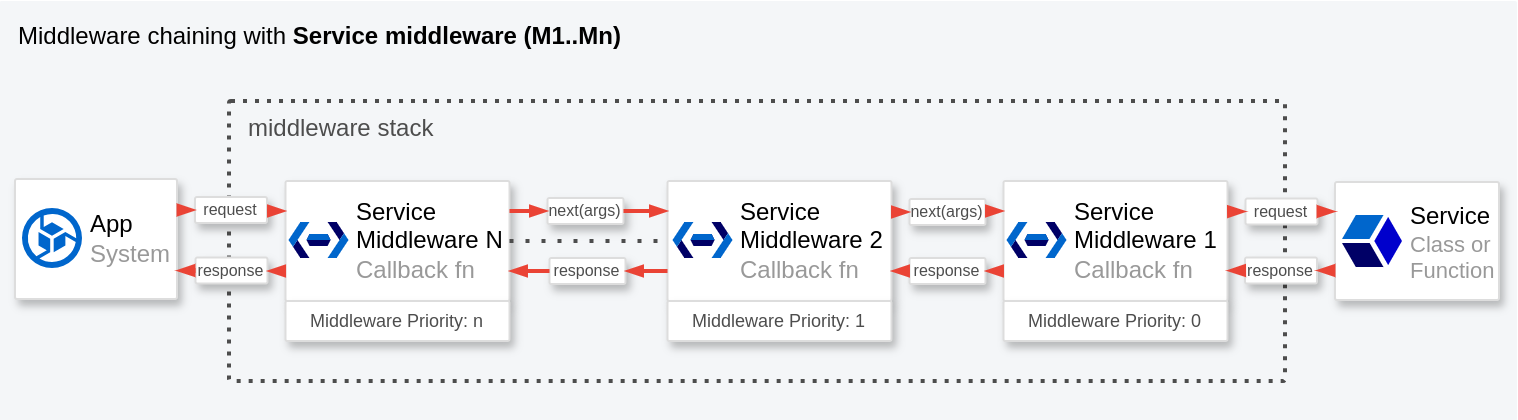
The middleware stack is a chain of functions that execute in sequence when an operation is performed on a particular service.
Each middleware can modify the request, perform additional operations and/or modify the response.
The next function is used to pass control to the next middleware in the chain and execute the underlying operation.
next returns the response, which can be synchronous or a promise, and which resolves with the result of the operation
or rejects with an error.
The middleware can intercept the request before it is sent to the service, modify the request parameters, add additional logic and manipulate the response after it is received.
The middleware only intercept calls to methods or functions of previously instantiated services. But, they do not intercept service instantiation.
The middleware with a higher priority value runs first. Conversely, if you need to create a middleware that runs closer to the service execution, assign it a lower priority value. Note that the priority value must be an integer. Negative values are also allowed.
We welcome contributions from the community! Whether it's reporting a bug, suggesting a feature, or contributing code, your involvement is key to making Packet.js better. Please check out this section for more details.
If you encounter any issues or bugs while using packetjs, or if you have any feature requests, please feel free to
open an issue in our GitHub repository. You can report issues, track progress, and engage in discussions with the
community via the following link:
If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to reach out via the discussion board.