Streamlit component for displaying and interacting with graph data using yFiles - the Graph Visualization SDK. This component allows you to display and interact with graph data directly within your Streamlit apps. It supports full customization of nodes, edges, layouts, and behaviors, making it suitable for a wide range of graph-based use cases.
The component is available in the Python Package Index.
pip install yfiles_graphs_for_streamlitSee also basic-example.py.
import streamlit as st
from yfiles_graphs_for_streamlit import StreamlitGraphWidget
nodes = [
{"id": 0, "properties": {"firstName": "Alpha", "label": "Person A"}},
{"id": 1, "properties": {"firstName": "Bravo", "label": "Person B"}},
{"id": 2, "properties": {"firstName": "Charlie", "label": "Person C", "has_hat": False}},
{"id": 3, "properties": {"firstName": "Delta", "label": "Person D", "likes_pizza": True}}
]
edges = [
{"id": 0, "start": 0, "end": 1, "properties": {"since": "1992", "label": "knows"}},
{"id": 1, "start": 1, "end": 3, "properties": {"label": "knows", "since": "1992"}},
{"id": 2, "start": 2, "end": 3, "properties": {"label": "knows", "since": "1992"}},
{"id": 3, "start": 0, "end": 2, "properties": {"label": "knows", "since": 234}}
]
StreamlitGraphWidget(nodes, edges).show()
Automatic graph layouts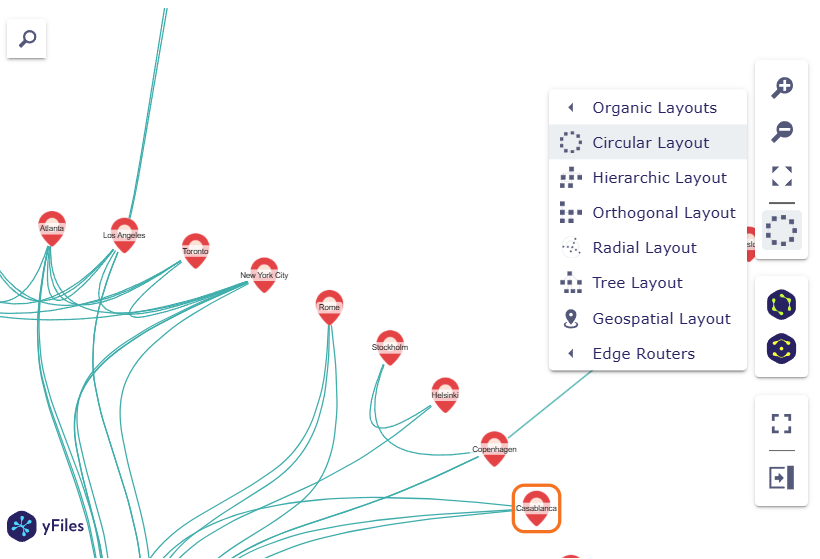
|
Item neighborhood
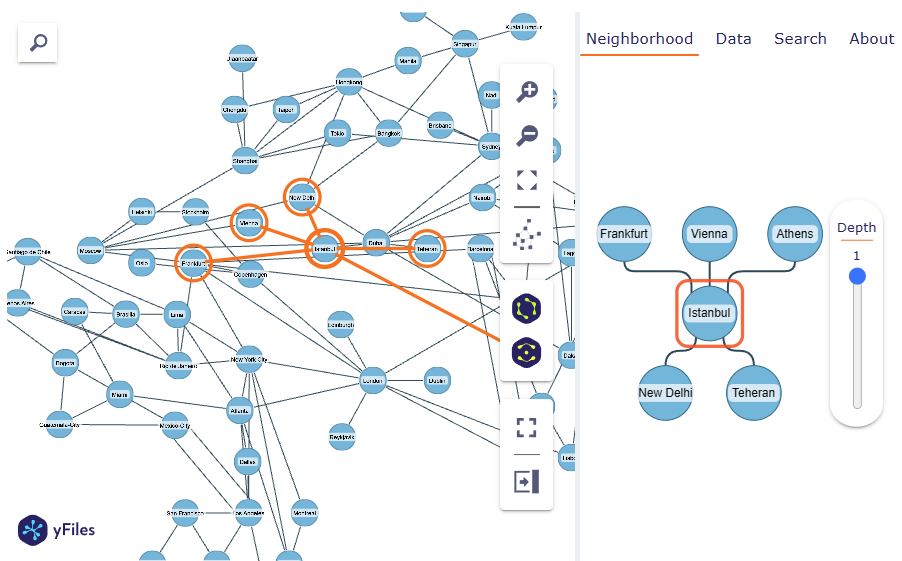
|
Visualize data as heatmap
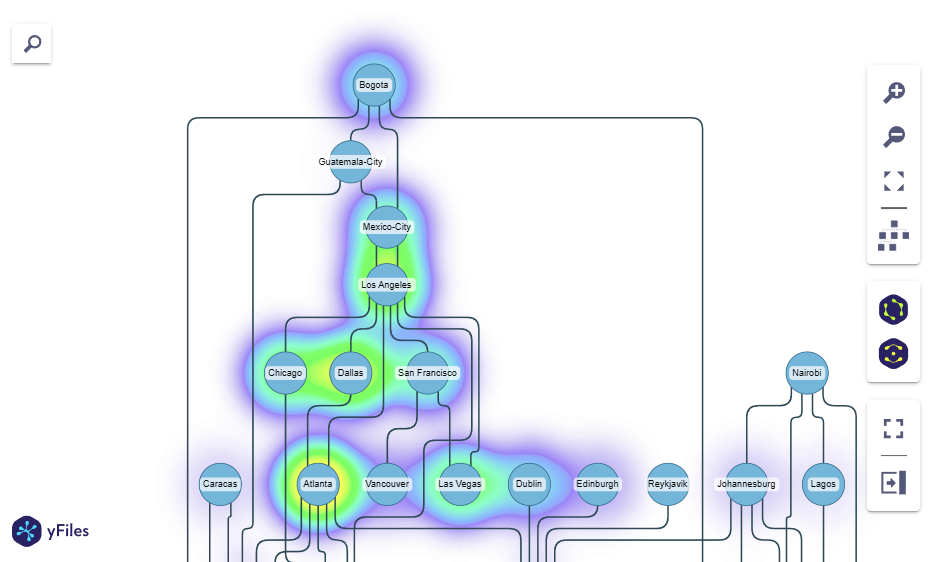
|
Use geospatial data
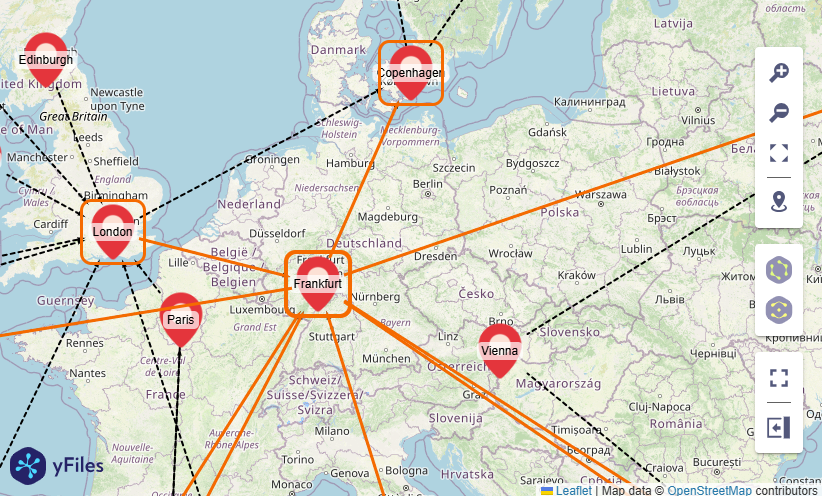
|
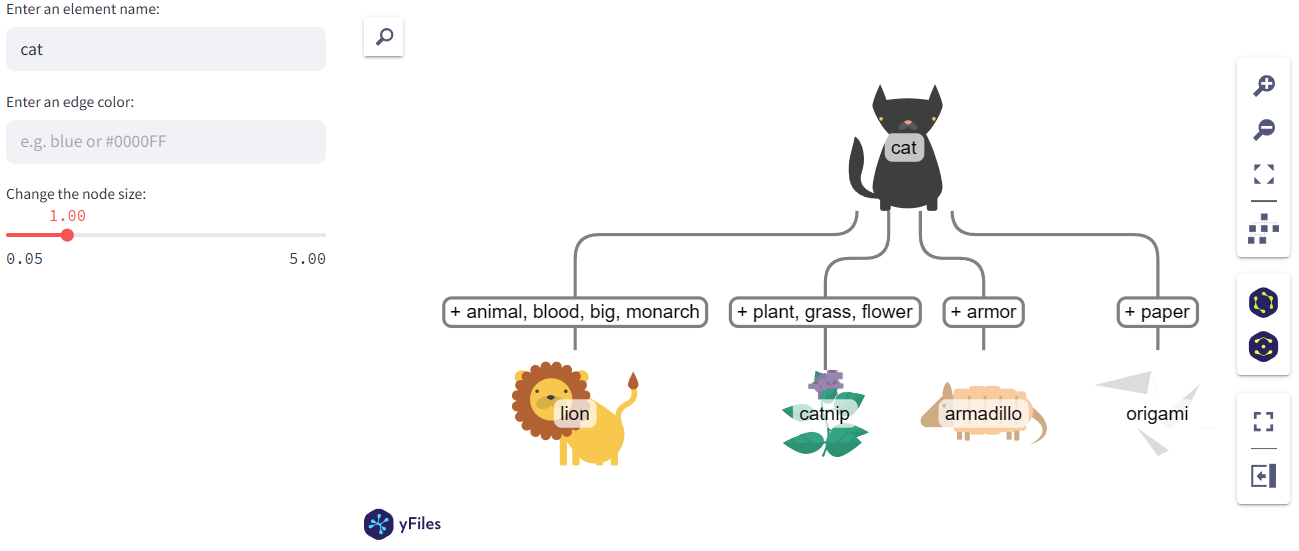
Data-driven visualization
|
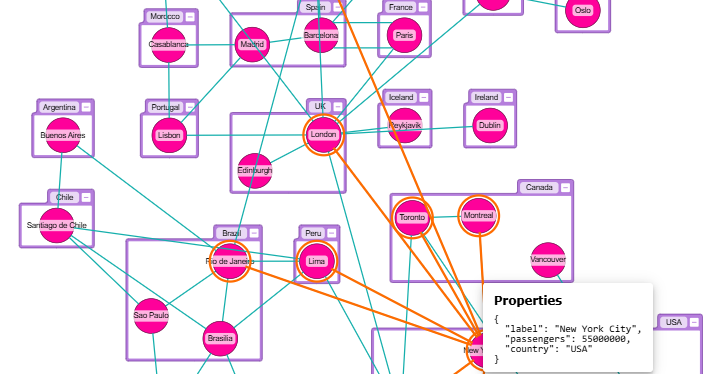
Grouping and Folding
|
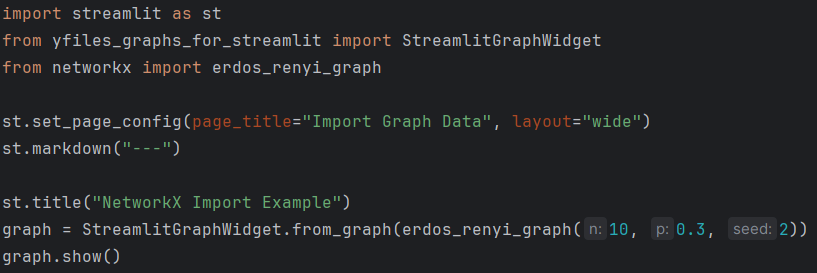
Import graph data
|
You can find example implementations in /examples.
The nodes / edges lists are required to be lists of dicts. There are only few requirements to the structuring of the provided data:
nodes: [Dict]- Each node dict must provide an
idproperty
- Each node dict must provide an
edges: [Dict]- Each edge dict must provide an
id,startandendproperty that resolve to the nodeids to form the graph structure.
- Each edge dict must provide an
Optionally, provide additional properties in a properties property.
For example, see basic-example.py.
To map custom properties to visual features, see Data-driven visualization mappings.
Aside from passing structured data, you can also import from other graph formats:
from_graph(graph)graphsupportsneo4j,graph_tool,networkx,pygraphvizandpandasdataframes. For details on the different graph importers, see Graph Importers.- Each data-mapping property can also be passed as a keyword argument. Due to type hints, keyword arguments are preferred for defining data mappings.
Example usage:
from yfiles_graphs_for_streamlit import StreamlitGraphWidget
from networkx import erdos_renyi_graph
# import other graph packages
graph = StreamlitGraphWidget.from_graph(erdos_renyi_graph(10, 0.3, 2))
# create an interactive graph visualization
graph.show()The default constructor consumes structured node and edge lists, see Providing Data for structural requirements.
Alternatively, use the from_graph constructor to import from other graph formats (Importing from other graph packages).
Each data-mapping property can also be passed as a keyword argument to the constructor or from_graph(). Due to type hints, keyword arguments are preferred for defining data mappings.
Call show() to render the component in a streamlit file. There are optional arguments with which the embedding can be adjusted:
| Argument | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
directed |
bool |
Whether the edges should show a direction indicator. | True |
graph_layout |
Layout |
Can be used to specify a general default automatic layout. See Layout. | Layout.ORGANIC |
sync_selection |
bool |
Whether the component returns the lists of interactively selected nodes and edges. Enabling this may require caching the component to avoid excessive rerendering. | False |
sidebar |
dict |
Sidebar options: {enabled, start_with}. start_with may be one of 'Neighborhood', 'Data', 'Search', 'About' |
{'enabled': False} |
neighborhood |
dict |
{max_distance, selected_nodes} to filter neighbors. |
{'max_distance': 1, 'selected_nodes': []} |
overview |
bool |
Whether the overview is expanded | True |
highlight |
list |
Nodes/edges to highlight. | [] |
key |
str |
Streamlit's optional unique key for multiple component instances. | None |
The return value of show() is a tuple of node and edge lists that are interactively selected. The returned lists are only updated when sync_selection is set to True.
For example, see selection.py.
You can adjust the graph visualization on an item basis by providing the following mapping functions. Each mapping is passed the original data object of your original node / edge data, and you need to return a mapping specific dict or value to that is reflected in the graph visualization.
To return to the default behavior, simply assign None to the mapping.
Specify what data should be put on the items and therefore be considered by the other data mappings
node_property_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], dict]]]edge_property_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], dict]]]
By default, the origin dict for each item is returned.
Specify the visualized text on each item.
node_label_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], Union[str, LabelStyle]]]]edge_label_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], Union[str, LabelStyle]]]]
Returning a string will first be resolved against the properties of the item's dict and if there is no such property key the value is used as-is. Alternatively, return a LabelStyle object with the following properties to have full control over the item's text.
font: Font: The font used for the label.text: string: The text that is added to the item.font_size: int: The text size.font_weight: FontWeight: The font weight. See FontWeight.color: string: The text color.background_color: string: A color string that is used as the label's background.position: LabelPosition: Where the label is placed relatively to the node. See LabelPosition.maximum_width: int: The maximum width of the label. By default, the label is clipped at the given size, or wrapped whenwrappingis set.maximum_height: int: The maximum height of the label. Clips the label at the given height. May be combined withwrapping.wrapping: TextWrapping: Text wrapping for the label. Must be set in combination withmaximum_width. See TextWrapping.text_alignment: TextAlignment: The horizontal text alignment whenwrappingis enabled. See TextAlignment.
For example, see data-mapping.py.
Specify the color of each item.
node_color_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], str]]]edge_color_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], str]]]
Return any CSS color value (e.g., a color constant, a hex value, a rgb string, etc.).
For example, see data-mapping.py.
Specify the visualization properties of nodes and edges.
node_styles_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], NodeStyle]]]- Available node properties on
NodeStyle:color: CSS color valueimage: URL or data URL of the imageshape:NodeShapeenum, see NodeShape
- Available node properties on
edge_styles_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], EdgeStyle]]]- Available edge properties on
EdgeStyle:color:str(a CSS color value)directed:boolthickness:floatdash_style:DashStyle(see DashStyle) or a dashing string like'5 10'or'5, 10'
- Available edge properties on
edge_thickness_factor_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], float]]]- Controls the thickness of the edges with a factor that is multiplied to its base size.
directed_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], bool]]]- Allows specifying which edge should be visualized with direction (indicated by an arrow).
For example, see data-mapping.py.
Specify the location and/or size of nodes. Note that the location of an item is overwritten from an automatic layout,
unless the no_layout option is used.
node_scale_factor_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], float]]]- Controls the node size with a factor that is multiplied to its base size.
node_size_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[int, dict], float]]]- Controls the node size by width and height by returning a tuple
(width, height).
- Controls the node size by width and height by returning a tuple
node_position_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], Tuple[float, float]]]]- Controls the position of the node by returning a tuple:
(x, y).
- Controls the position of the node by returning a tuple:
node_layout_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], Tuple[float, float, float, float]]]]- Controls the bounding box of the nodes (position and size) by returning a 4-tuple:
(x, y, width, height).
- Controls the bounding box of the nodes (position and size) by returning a 4-tuple:
For example, see data-mapping.py.
Specify a geo-coordinate for the nodes that is used by the geospatial layout option.
node_coordinate_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], Tuple[float, float]]]]- The mapping is supposed to return a tuple of
(latitude, longitude).
- The mapping is supposed to return a tuple of
For example, see geodata.py.
Specify which nodes should be grouped together.
node_parent_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], Union[str, int, float]]]]- This mapping does not create new group nodes and just resolves the mapped id against the given dataset. It should be used when the group nodes are already part of the given dataset.
node_parent_group_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], Union[str, dict]]]]- This mapping always creates new dicts based on the given mapping. It should be used when the group nodes are not part of the given dataset.
For example, see grouping.py.
Some mappings affect specific automatic layouts
node_type_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], str]]]- Assign a specific "type" string to each item. This affects most of the automatic layouts such that same types are placed adjacent to each other, if possible.
node_cell_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], Tuple[int, int]]]]- Assign a cell tuple
(row, column)to each node. This information is considered by the hierarchical layout and helps to fine-tune the result, for example, to highlight specific structures of the graph or to convey critical information.
- Assign a cell tuple
Numeric values on nodes and edges may be visualized as a heatmap overlay on the graph visualization.
heat_mapping: Optional[Union[str, Callable[[dict], float]]]- The returned heat needs to be normalized in-between
0and1.
- The returned heat needs to be normalized in-between
For example, see geodata.py.
The enums can be imported from yfiles_graphs_for_streamlit.
| Enum | Description |
|---|---|
Layout.CIRCULAR |
Arranges nodes in singly cycle and bundles edge paths. |
Layout.CIRCULAR_STRAIGHT_LINE |
Arranges nodes in singly cycle and uses straight-line edge paths. |
Layout.HIERARCHIC |
Organizes nodes in hierarchical layers to emphasize directional flow. |
Layout.ORGANIC |
Uses a force-directed algorithm to create a natural, free-form network layout. |
Layout.INTERACTIVE_ORGANIC |
Similar to ORGANIC but dynamically adjusts the layout as the user interacts with it. |
Layout.ORTHOGONAL |
Positions nodes on a grid with right-angled edges for clear, structured diagrams. |
Layout.RADIAL |
Places a central node in the middle and arranges others in rings around it to show hierarchy or influence. |
Layout.TREE |
Displays nodes in a branching tree structure from a defined root node. |
Layout.MAP |
Uses user-defined geo-coordinates to place the nodes on a world map |
Layout.ORTHOGONAL_EDGE_ROUTER |
Reroutes edges at right angles to minimize overlap and improve readability. |
Layout.ORGANIC_EDGE_ROUTER |
Smoothly routes edges around obstacles in a natural, curved manner. |
Layout.NO_LAYOUT |
Leaves node positions unchanged without applying any automatic layout. |
| Enum | Description |
|---|---|
NodeShape.ELLIPSE |
An elliptical shape. |
NodeShape.HEXAGON |
A 6-sided polygon where the top and bottom edges are aligned with the top and bottom edges of the bounding box. |
NodeShape.HEXAGON2 |
A 6-sided polygon where the left and right edges are aligned with the left and right edges of the bounding box. |
NodeShape.OCTAGON |
An 8-sided polygon where the edges are aligned with the edges of the bounding box. |
NodeShape.PILL |
A stadium shape with the shorter sides rounded. |
NodeShape.RECTANGLE |
A rectangular shape. |
NodeShape.ROUND_RECTANGLE |
A rectangular shape with rounded corners. |
NodeShape.TRIANGLE |
A triangular shape that points to the top. |
| Enum | Description |
|---|---|
DashStyle.SOLID |
Solid line style. |
DashStyle.DASH |
Dashed line style. |
DashStyle.DOT |
Dotted line style. |
DashStyle.DASH_DOT |
Single dash and dot line style |
DashStyle.DASH_DOT_DOT |
A single dash and two dots line style |
| Enum | Description |
|---|---|
FontWeight.BOLD |
'bold' |
FontWeight.BOLDER |
'bolder' |
FontWeight.NORMAL |
'normal' |
FontWeight.LIGHTER |
'lighter' |
Only affects multiline texts.
| Enum | Description |
|---|---|
TextAlignment.CENTER |
Center aligned multiline text. |
TextAlignment.LEFT |
Left aligned multiline text. |
TextAlignment.RIGHT |
right aligned multiline text. |
Is only in effect when maximum_width is specified on LabelStyle.
| Enum | Description |
|---|---|
TextWrapping.CHARACTER |
Character wrapping at maximum_width . |
TextWrapping.CHARACTER_ELLIPSIS |
Character wrapping at maximum_width with ellipsis at maximum_height. |
TextWrapping.WORD |
Word wrapping at maximum_width. |
TextWrapping.WORD_ELLIPSIS |
Word wrapping at maximum_width with ellipsis at maximum_height. |
TextWrapping.NONE |
The text is not wrapped, nor clipped. |
| Enum | Description |
|---|---|
LabelPosition.CENTER |
Places the label in the center of the node (interior). |
LabelPosition.NORTH |
Places the label above the node (exterior). |
LabelPosition.EAST |
Places the label on the right side of the node (exterior). |
LabelPosition.SOUTH |
Places the label below the node (exterior). |
LabelPosition.WEST |
Places the label on the left side of the node (exterior). |
This project and everyone participating in it is governed by the Code of Conduct. By participating, you are expected to uphold this code. Please report unacceptable behavior to contact@yworks.com.
This component is by no means perfect. If you find something is not working as expected we are glad to receive an issue report from you. Please make sure to search for existing issues first and check if the issue is not an unsupported feature or known issue. If you did not find anything related, report a new issue with necessary information. Please also provide a clear and descriptive title and stick to the issue templates. See issues.
The following dependencies are bundled with the component (see also THIRD-PARTY-NOTICES.json).
Additionally, the following libraries are used at runtime of the component (see also THIRD-PARTY-NOTICES-RUNTIME.json).
See LICENSE file.


