A comprehensive tool for solving linear programming problems, offering multiple interfaces including a command-line solver, a Domain Specific Language (DSL), and a graphical user interface (GUI).
The core solver is implemented using scipy.optimize.linprog and provides the fundamental capabilities for solving linear programming problems. It handles maximization and minimization, various inequality types (<=, >=, <, >), and equality constraints (=).
Define your linear programming problems using a human-readable string format. This DSL supports both direct string input and loading from standard .lp files. It automatically handles variable types, including "free" variables by converting them into a pair of non-negative variables.
Example Usage (String Input):
from dsl import DSL
problem = DSL("""
MINIMIZE z = 3*x1 + 5*x2
SUBJECT TO
2*x1 + x2 >= 8
x1 + 3*x2 >= 9
x1 <= 5
x2 >= 1
BOUNDS
x1 >= 0
x2 free
""")
simplex = problem.to_simplex()
simplex.solve_problem()
simplex.show_results()Example Usage (LP File Input):
from dsl import DSL
# Assuming 'my_problem.lp' contains the problem definition
problem = DSL("my_problem.lp")
simplex = problem.to_simplex()
simplex.solve_problem()
simplex.show_results()For a more integrated and programmatic approach, use the Pythonic DSL inspired by sympy. Define variables and construct your objective function and constraints directly using Python objects and operators.
Example Usage:
from pythonic_dsl import Model, Var, maximize
m = Model("example_lp")
x1 = Var("x1", low=0)
x2 = Var("x2", low=0)
m += maximize(5 * x1 + 4 * x2)
m += (6 * x1 + 4 * x2 <= 24)
m += (x1 + 2 * x2 <= 6)
m += (-x1 + x2 <= 1)
m += (x2 <= 2)
result = m.solve()
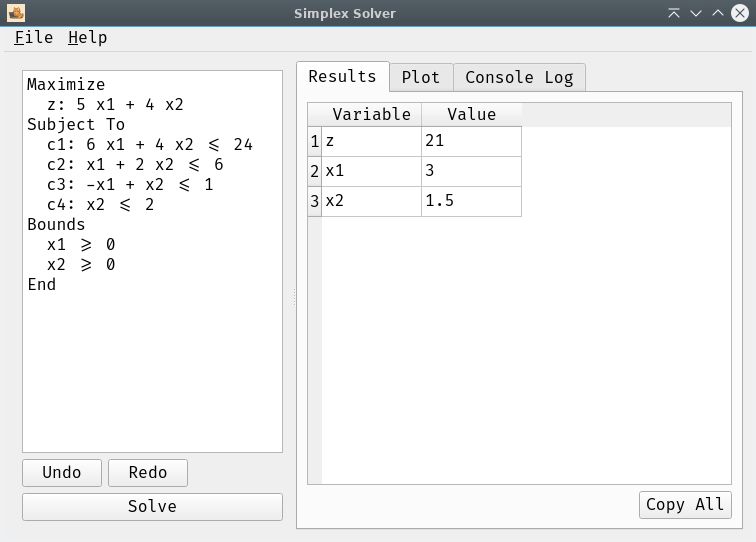
result.show_results()A user-friendly desktop application built with PySide6 (Qt for Python) provides an interactive environment for defining, solving, and visualizing linear programming problems.
- Input Widget: A text editor where you can type or load your problem definition.
- Results Table: Displays the optimal values for variables and the objective function.
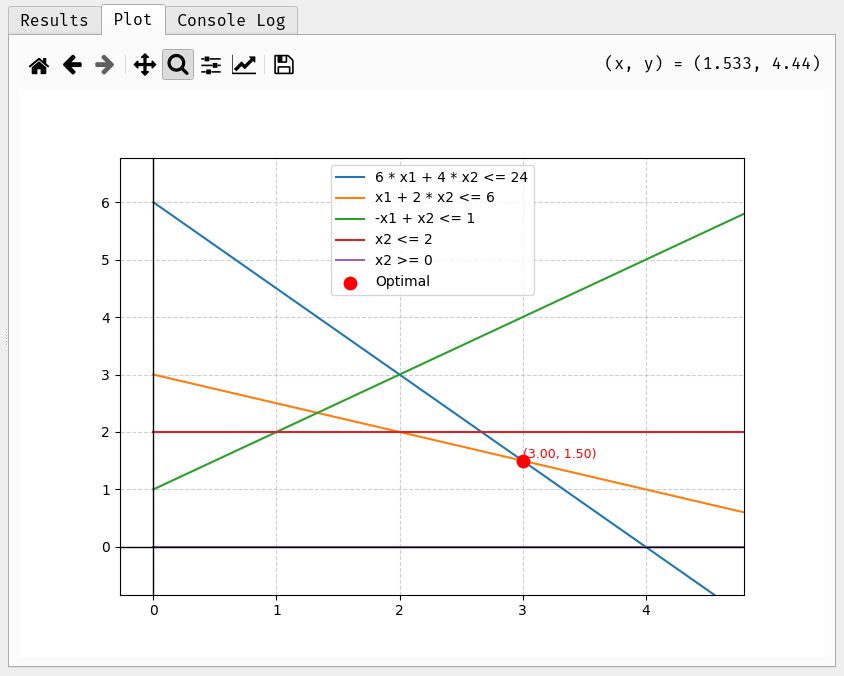
- Plotting: For problems with two variables, a dedicated tab visualizes the constraints and the optimal solution point.
- Console Log: Redirects and displays all terminal output (e.g.,
printstatements, error messages) within a dedicated tab in the GUI, ensuring readability by stripping ANSI escape codes. Includes a "Clear Console" button. - Menu Bar:
- File:
Open: Load problem definitions from.lpor.txtfiles.Save: Save the current problem definition from the editor to an.lpfile.Quit: Exit the application.
- Help:
About: Displays a custom dialog with application information, author, license, and links to GitHub and donation pages.
- File:
- User Experience:
- Responsive UI: The solver runs in a separate thread to prevent the application from freezing during calculations.
- Custom application icon (
pixel-cat.png). - Uses the FiraCode font for enhanced readability and a modern aesthetic.
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/xeland314/simplex.git cd simplex - Create a virtual environment (recommended):
python -m venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate # On Windows: .venv\Scripts\activate
- Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Run the basic interactive solver:
python simplex.pyIntegrate the DSLs into your Python scripts as shown in the "Domain Specific Languages (DSLs)" section above.
Launch the graphical interface:
python app.pyCheck the examples/ directory for sample .lp and .txt files that can be loaded into the GUI or used with the DSLs.
- Testing: Run all unit tests with:
uv run python -m unittest discover
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.