The goal of megadepth is to provide an R interface to the command line
tool Megadepth for
BigWig and BAM related utilities created by Christopher
Wilks. This R package enables fast
processing of BigWig files on downstream packages such as
dasper and
recount3. The
Megadepth software also
provides utilities for processing BAM files and extracting coverage
information from them.
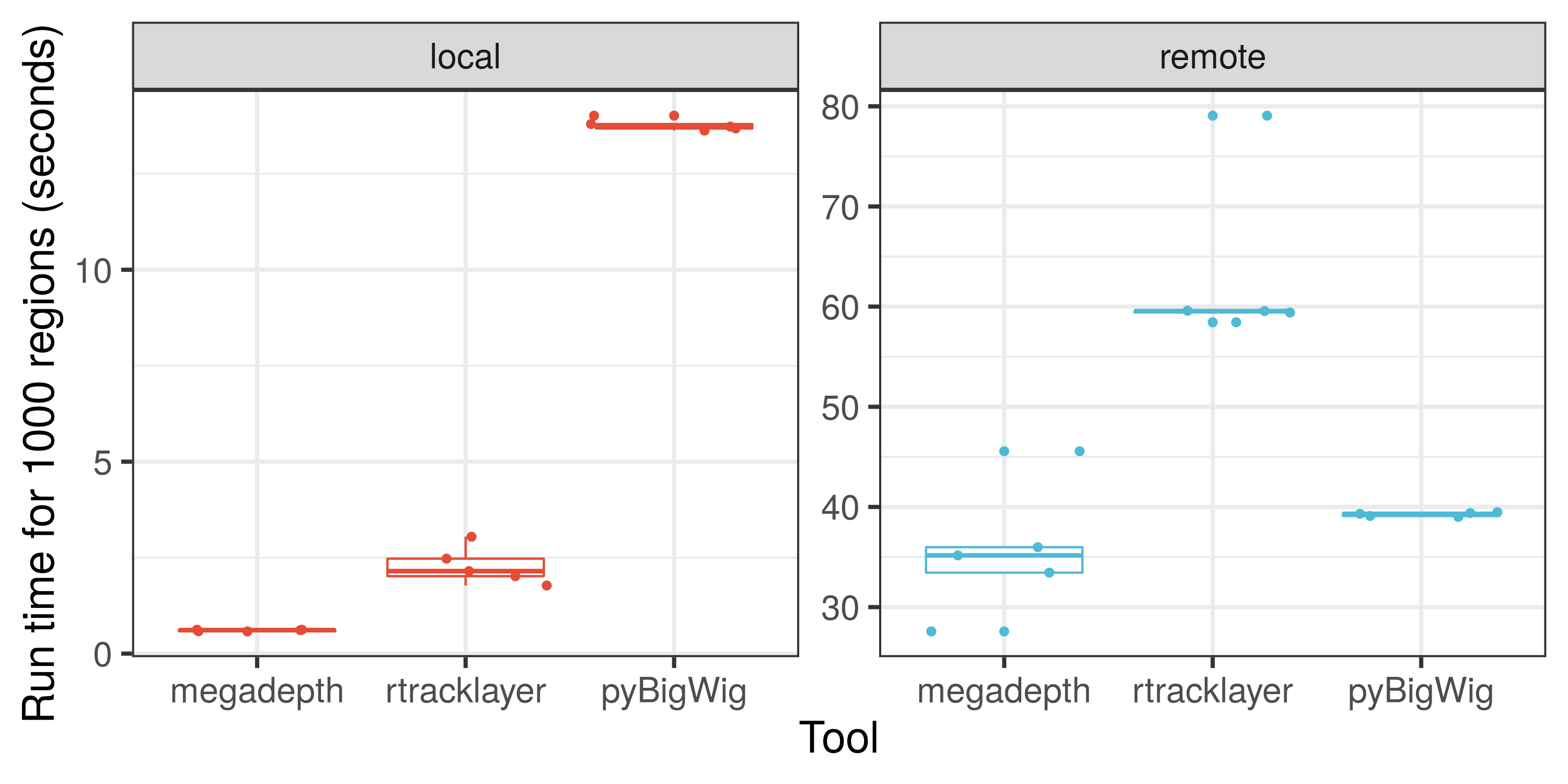
Here is an illustration on how fast megadepth is compared to other
tools for processing local and remote BigWig files.
Throughout the documentation we use a capital M to refer to the
software by Christopher Wilks and a lower case m to refer to this
R/Bioconductor package.
Get the latest stable R release from
CRAN. Then install megadepth from
Bioconductor using the following code:
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("BiocManager")
}
BiocManager::install("megadepth")And the development version from GitHub with:
BiocManager::install("LieberInstitute/megadepth")In the following example, we install
Megadepth with
install_megadepth(), which downloads a binary for your OS (Linux,
Windows or macOS). We can then use with an example BigWig file to
compute the coverage at a set of regions.
## Load the R package
library("megadepth")
## Install Megadepth's pre-compiled binary on your system
install_megadepth()
#> The latest megadepth version is 1.1.0c
#> This is not an interactive session, therefore megadepth has been installed temporarily to
#> /var/folders/kb/g5h79h8d5zv_0wpyg6pb2sph0000gn/T//RtmpuyvsB8/megadepth
## Next, we locate the example BigWig and annotation files
example_bw <- system.file("tests", "test.bam.all.bw",
package = "megadepth", mustWork = TRUE
)
annotation_file <- system.file("tests", "testbw2.bed",
package = "megadepth", mustWork = TRUE
)
## We can then use megadepth to compute the coverage
bw_cov <- get_coverage(example_bw, op = "mean", annotation = annotation_file)
bw_cov
#> GRanges object with 4 ranges and 1 metadata column:
#> seqnames ranges strand | score
#> <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <numeric>
#> [1] chr10 0-10 * | 0.00
#> [2] chr10 8756697-8756762 * | 15.85
#> [3] chr10 4359156-4359188 * | 3.00
#> [4] GL000219.1 168500-168620 * | 1.26
#> -------
#> seqinfo: 2 sequences from an unspecified genome; no seqlengthsMegadepth is very
powerful and can do a lot of different things. The R/Bioconductor
package provides two functions for interfacing with
Megadepth,
megadepth_cmd() and megadepth_shell(). For the first one,
megadepth_cmd(), you need to know the actual command syntax you want
to use and format it accordingly. If you are more comfortable with R
functions, megadepth_shell() uses
cmdfun to power this
interface and capture the standard output stream into R.
To make it easier to use, megadepth includes functions that simplify
the number of arguments, read in the output files, and converts them
into R/Bioconductor friendly objects, such as get_coverage()
illustrated above.
We hope that you’ll find megadepth and
Megadepth useful for
your work. If you are interested in checking how fast megadepth
is, check out the speed
analysis
comparison against other tools. Note that the size of the files used and
the number of genomic regions queried will affect the speed comparisons.
## R-like interface
## that captures the standard output into R
head(megadepth_shell(help = TRUE))
#> [1] "megadepth 1.1.0c" ""
#> [3] "BAM and BigWig utility." ""
#> [5] "Usage:" " megadepth <bam|bw|-> [options]"
## Command-like interface
megadepth_cmd("--help")#> megadepth 1.1.0c
#>
#> BAM and BigWig utility.
#>
#> Usage:
#> megadepth <bam|bw|-> [options]
#>
#> Options:
#> -h --help Show this screen.
#> --version Show version.
#> --threads # of threads to do: BAM decompression OR compute sums over multiple BigWigs in parallel
#> if the 2nd is intended then a TXT file listing the paths to the BigWigs to process in parallel
#> should be passed in as the main input file instead of a single BigWig file (EXPERIMENTAL).
#> --prefix String to use to prefix all output files.
#> --no-auc-stdout Force all AUC(s) to be written to <prefix>.auc.tsv rather than STDOUT
#> --no-annotation-stdout Force summarized annotation regions to be written to <prefix>.annotation.tsv rather than STDOUT
#> --no-coverage-stdout Force covered regions to be written to <prefix>.coverage.tsv rather than STDOUT
#> --keep-order Output annotation coverage in the order chromosomes appear in the BAM/BigWig file
#> The default is to output annotation coverage in the order chromosomes appear in the annotation BED file.
#> This is only applicable if --annotation is used for either BAM or BigWig input.
#>
#> BigWig Input:
#> Extract regions and their counts from a BigWig outputting BED format if a BigWig file is detected as input (exclusive of the other BAM modes):
#> Extracts all reads from the passed in BigWig and output as BED format.
#> This will also report the AUC over the annotated regions to STDOUT.
#> If only the name of the BigWig file is passed in with no other args, it will *only* report total AUC to STDOUT.
#> --annotation <bed> Only output the regions in this BED applying the argument to --op to them.
#> --op <sum[default], mean, min, max> Statistic to run on the intervals provided by --annotation
#> --sums-only Discard coordinates from output of summarized regions
#> --bwbuffer <1GB[default]> Size of buffer for reading BigWig files, critical to use a large value (~1GB) for remote BigWigs.
#> Default setting should be fine for most uses, but raise if very slow on a remote BigWig.
#>
#>
#> BAM Input:
#> Extract basic junction information from the BAM, including co-occurrence
#> If only the name of the BAM file is passed in with no other args, it will *only* report total AUC to STDOUT.
#> --fasta Path to the reference FASTA file if a CRAM file is passed as the input file (ignored otherwise)
#> If not passed, references will be downloaded using the CRAM header.
#> --junctions Extract co-occurring jx coordinates, strand, and anchor length, per read
#> writes to a TSV file <prefix>.jxs.tsv
#> --all-junctions Extract all jx coordinates, strand, and anchor length, per read for any jx
#> writes to a TSV file <prefix>.all_jxs.tsv
#> --longreads Modifies certain buffer sizes to accommodate longer reads such as PB/Oxford.
#> --filter-in Integer bitmask, any bits of which alignments need to have to be kept (similar to samtools view -f).
#> --filter-out Integer bitmask, any bits of which alignments need to have to be skipped (similar to samtools view -F).
#> --add-chr-prefix Adds "chr" prefix to relevant chromosomes for BAMs w/o it, pass "human" or "mouse".
#> Only works for human/mouse references (default: off).
#>
#> Non-reference summaries:
#> --alts Print differing from ref per-base coverages
#> Writes to a CSV file <prefix>.alts.tsv
#> --include-softclip Print a record to the alts CSV for soft-clipped bases
#> Writes total counts to a separate TSV file <prefix>.softclip.tsv
#> --only-polya If --include-softclip, only print softclips which are mostly A's or T's
#> --include-n Print mismatch records when mismatched read base is N
#> --print-qual Print quality values for mismatched bases
#> --delta Print POS field as +/- delta from previous
#> --require-mdz Quit with error unless MD:Z field exists everywhere it's
#> expected
#> --head Print sequence names and lengths in SAM/BAM header
#>
#> Coverage and quantification:
#> --coverage Print per-base coverage (slow but totally worth it)
#> --auc Print per-base area-under-coverage, will generate it for the genome
#> and for the annotation if --annotation is also passed in
#> Defaults to STDOUT, unless other params are passed in as well, then
#> if writes to a TSV file <prefix>.auc.tsv
#> --bigwig Output coverage as BigWig file(s). Writes to <prefix>.bw
#> (also <prefix>.unique.bw when --min-unique-qual is specified).
#> Requires libBigWig.
#> --annotation <BED|window_size> Path to BED file containing list of regions to sum coverage over
#> (tab-delimited: chrm,start,end). Or this can specify a contiguous region size in bp.
#> --op <sum[default], mean> Statistic to run on the intervals provided by --annotation
#> --no-index If using --annotation, skip the use of the BAM index (BAI) for pulling out regions.
#> Setting this can be faster if doing windows across the whole genome.
#> This will be turned on automatically if a window size is passed to --annotation.
#> --min-unique-qual <int>
#> Output second bigWig consisting built only from alignments
#> with at least this mapping quality. --bigwig must be specified.
#> Also produces second set of annotation sums based on this coverage
#> if --annotation is enabled
#> --double-count Allow overlapping ends of PE read to count twice toward
#> coverage
#> --num-bases Report total sum of bases in alignments processed (that pass filters)
#> --gzip Turns on gzipping of coverage output (no effect if --bigwig is passsed),
#> this will also enable --no-coverage-stdout.
#>
#> Other outputs:
#> --read-ends Print counts of read starts/ends, if --min-unique-qual is set
#> then only the alignments that pass that filter will be counted here
#> Writes to 2 TSV files: <prefix>.starts.tsv, <prefix>.ends.tsv
#> --frag-dist Print fragment length distribution across the genome
#> Writes to a TSV file <prefix>.frags.tsv
#> --echo-sam Print a SAM record for each aligned read
#> --ends Report end coordinate for each read (useful for debugging)
#> --test-polya Lower Poly-A filter minimums for testing (only useful for debugging/testing)
#>
#>
Below is the citation output from using citation('megadepth') in R.
Please run this yourself to check for any updates on how to cite
megadepth.
print(citation("megadepth"), bibtex = TRUE)
#>
#> Zhang D, Collado-Torres L (2021). _megadepth: BigWig and BAM related
#> utilities_. doi: 10.18129/B9.bioc.megadepth (URL:
#> https://doi.org/10.18129/B9.bioc.megadepth),
#> https://github.com/LieberInstitute/megadepth - R package version 1.3.3,
#> <URL: http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/megadepth>.
#>
#> A BibTeX entry for LaTeX users is
#>
#> @Manual{,
#> title = {megadepth: BigWig and BAM related utilities},
#> author = {David Zhang and Leonardo Collado-Torres},
#> year = {2021},
#> url = {http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/megadepth},
#> note = {https://github.com/LieberInstitute/megadepth - R package version 1.3.3},
#> doi = {10.18129/B9.bioc.megadepth},
#> }
#>
#> Wilks C, Ahmed O, Baker DN, Zhang D, Collado-Torres L, Langmead B
#> (2020). "Megadepth: efficient coverage quantification for BigWigs and
#> BAMs." _bioRxiv_. doi: 10.1101/2020.12.17.423317 (URL:
#> https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.17.423317), <URL:
#> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.17.423317v1>.
#>
#> A BibTeX entry for LaTeX users is
#>
#> @Article{,
#> title = {Megadepth: efficient coverage quantification for BigWigs and BAMs},
#> author = {Christopher Wilks and Omar Ahmed and Daniel N. Baker and David Zhang and Leonardo Collado-Torres and Ben Langmead},
#> year = {2020},
#> journal = {bioRxiv},
#> doi = {https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.17.423317},
#> url = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.17.423317v1},
#> }Please note that the megadepth was only made possible thanks to many
other R and bioinformatics software authors, which are cited either in
the vignettes and/or the paper(s) describing this package.
Please note that the megadepth project is released with a Contributor
Code of
Conduct.
By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
- Continuous code testing is possible thanks to GitHub actions through usethis, remotes, sysreqs and rcmdcheck customized to use Bioconductor’s docker containers and BiocCheck.
- Code coverage assessment is possible thanks to codecov and covr.
- The documentation website is automatically updated thanks to pkgdown.
- The code is styled automatically thanks to styler.
- The documentation is formatted thanks to devtools and roxygen2.
For more details, check the dev directory.
This package was developed using biocthis.
The main documentation website for all the recount3-related
projects is available at
recount.bio.
Please check that website for more information about how this
R/Bioconductor package and other tools are related to each other.
megadepth was made possible to David Zhang, the author of dasper, and a member of the Mina Ryten’s lab at UCL.
The ReCount family involves the following teams:
- Ben Langmead’s lab at JHU Computer Science
- Kasper Daniel Hansen’s lab at JHBSPH Biostatistics Department
- Leonardo Collado-Torres and Andrew E. Jaffe from LIBD
- Abhinav Nellore’s lab at OHSU
- Jeff Leek’s lab at JHBSPH Biostatistics Deparment
- Data hosted by SciServer from IDIES at JHU
 |
 |
 |
 |