Twitter Conversation Networks and Analysis. This package uses the Twitter API v2 endpoints to collect tweets and generate networks for threaded conversations identified using the new tweet conversation identifier.
An introduction to the Twitter API v2 can be found here, and the Twitter Developer Application process here.
Note
Please note that due to significant changes to the Twitter/X API project plans in 2023 that this package is not currently actively maintained. However, as it uses the Twitter v2 API endpoints it should remain fully functional for users with API access (pending any future breaking changes to the Twitter v2 REST API).
Install the most recent CRAN release:
install.packages("voson.tcn")Install the most recent release tag via GitHub:
install.packages(
"https://github.com/vosonlab/voson.tcn/releases/download/v0.5.0/voson.tcn-0.5.0.tar.gz",
repo = NULL, type = "source")Install the latest development version:
# library(remotes)
remotes::install_github("vosonlab/voson.tcn")This package currently uses app based authentication approach with an
OAuth2 bearer token rather than a user based one that uses an
OAuth1a token. Bearer tokens have read-only API access and higher
rate-limits, whereas user tokens have lower rate-limits and broader
permissions that are not required for searching and collecting tweets.
To retrieve a bearer token, both the consumer key and
consumer secret for a Developer Standard Project or
Academic Research Project app (that has been approved to use the
Twitter API v2 endpoints) are required. These can be found or created on
the Twitter Developer Portals Projects &
Apps page.
If you already have your bearer token you can also assign it directly to
a voson.tcn token object using the bearer string parameter.
By default the recent search endpoint is used that makes available for
collection only tweets that were made within the last ~7 days. If the
user has an Academic Research Project they can also use the
tcn_threads parameter endpoint = "all" to collect on full-archive
conversation tweets.
If collecting on historical tweets a
start_time = "2021-03-18T00:00:00Z" datetime parameter will need to be
specified if the conversation is older than 30 days old (the default API
search start time). The datetime is in UTC and ISO 8601 format passed as
a string.
The API recent search endpoint where the conversation tweets are
retrieved from has a rate-limit of 450 requests per 15 min (per app). A
single request can retrieve 100 tweets, translating to an upper limit of
45,000 tweets per 15 mins.
The full-archive search allows 300 requests of 500 tweets, translating
to 150,000 tweets per 15 mins. There is also a limit of only 1 request
per second for the full-archive search endpoint.
The tweet lookup endpoint used by tcn_tweets has a rate-limit of 300
requests of 100 tweets (30,000) per 15 minutes.
The tcn_threads function has a parameter retry_on_limit that when
set to TRUE will wait until the API reset time before continuing when
a rate-limit has been reached.
There is currently a cap of 500 thousand tweets that be collected per
month per project under the Twitter API v2 Standard product track, and
10 million for the Academic Research track. These caps only apply to
certain API endpoints, such as recent and full-archive search. The
voson.tcn tcn_threads function uses the search endpoints and
therefore contributes towards this cap, however the tcn_tweets and
tcn_counts functions do not.
Project caps are only able to be checked from the Twitter Developer Console Dashboard.
- Does not yet support OAuth1a authentication as there is no current use case.
- Does not currently collect additional user metadata for authors of
tweets that were quoted and are external to the conversation. This
can result in incomplete actor node metadata for some quoted tweets:
user_A --replies--> user_B --quotes--> (external user_NA) - Handles but does not report on broken reply chains caused by deleted tweets or suspended users. These can result in a disconnected graph with additional components.
Retrieve and save an app bearer token using its consumer keys.
library(voson.tcn)
token <- tcn_token(consumer_key = "xxxxxxxx",
consumer_secret = "xxxxxxxx")
# alternatively a bearer token string can be assigned directly
token <- tcn_token(bearer = "xxxxxxxx")
# if you save the token to file this step only needs to be done once
saveRDS(token, "~/.tcn_token")Using tweet urls collect conversation tweets and metadata to generate networks.
# read token from file
token <- readRDS("~/.tcn_token")
# choose a twitter conversation thread or multiple threads to collect
# e.g https://twitter.com/Warcraft/status/1372615159311699970, and
# https://twitter.com/Warcraft/status/1372487989385965569
# can use any tweet or tweet id that is part of the conversation thread
# input is a list of tweet ids, tweet urls or combination of both
tweet_ids <- c("https://twitter.com/Warcraft/status/1372615159311699970",
"1372487989385965569")
# collect the conversation thread tweets for supplied ids
thread_tweets <- tcn_threads(tweet_ids, token)
# academic track historical endpoint - specify start_time and optionally end_time
thread_tweets <- tcn_threads(tweet_ids, token = token,
endpoint = "all",
start_time = "2021-03-17T00:00:00Z")The tcn_threads function produces a named list comprising a dataframe
with tweets and metadata and a dataframe of users metadata.
Note: If using the standard product track only recent search API requests can be performed. No tweets older than ~7 days will be collected in the conversation search. The tweets and any directly referenced tweets for the tweet id’s provided will still be collected however.
Note: When specifying start and end times note that the API returns
tweet created dates in 2021-03-17T00:00:00.000Z format, however API
requests require the shorter 2021-03-17T00:00:00Z format.
names(thread_tweets)
# [1] "tweets" "users" "errors" "meta"
nrow(thread_tweets$tweets)
# [1] 147
nrow(thread_tweets$users)
# [1] 118
nrow(tweets$errors)
# [1] 0
nrow(thread_tweets$meta)
# [1] 2This function can be used to retrieve the tweet activity in terms of tweet count for conversation id’s. It will return the volume of tweets for conversations over time, optionally by specified granularity (day, hour or minute). This can be useful for determining how many tweets will be returned before collecting tweets for a conversation or getting an overview of conversation tweet activity.
The default time granularity is tweet counts per hour for the last ~7
days using the recent counts API endpoint. Researchers on the
Academic track can specify an endpoint of all and access
full-archive tweet counts.
Tweet counts do not contribute towards your Twitter projects monthly tweet cap.
# get tweet count for conversation thread over approximately 3 days
# start time set approximately when conversation started
thread_counts <-
tcn_counts(
ids = "1491430617111674882",
token = token,
endpoint = "recent",
start_time = "2022-02-09T15:00:00Z",
end_time = "2022-02-12T10:00:00Z",
granularity = "day"
)
names(thread_counts)
# [1] "data" "errors" "meta" "counts"
print(thread_counts$counts)
# # A tibble: 4 x 6
# end start tweet_count timestamp conversation_id page
# <chr> <chr> <int> <int> <chr> <lgl>
# 1 2022-02-10T00:00:00.000Z 2022-02-~ 3 1.64e9 14914306171116~ NA
# 2 2022-02-11T00:00:00.000Z 2022-02-~ 87 1.64e9 14914306171116~ NA
# 3 2022-02-12T00:00:00.000Z 2022-02-~ 29 1.64e9 14914306171116~ NA
# 4 2022-02-12T10:00:00.000Z 2022-02-~ 0 1.64e9 14914306171116~ NA
# get total tweets per conversation id for specified period
library(dplyr)
thread_counts$counts |> dplyr::count(conversation_id, wt = tweet_count)
# # A tibble: 1 x 2
# conversation_id n
# <chr> <int>
# 1 1491430617111674882 119Using tweet urls or id’s it’s also possible collect specific tweets and their metadata.
# choose tweets to collect
# e.g https://twitter.com/Warcraft/status/1372615159311699970, and
# https://twitter.com/Warcraft/status/1372487989385965569
tweet_ids <- c("https://twitter.com/Warcraft/status/1372615159311699970",
"1372487989385965569")
# collect the tweets for supplied ids
tweets <- tcn_tweets(tweet_ids, token, referenced_tweets = FALSE)
names(tweets)
# [1] "tweets" "users" "errors"
nrow(tweets$tweets)
# [1] 2
nrow(tweets$users)
# [1] 1
nrow(tweets$errors)
# [1] 0Tweets from any time can be collected using any product track access token and do not contribute to your Twitter projects monthly tweet cap.
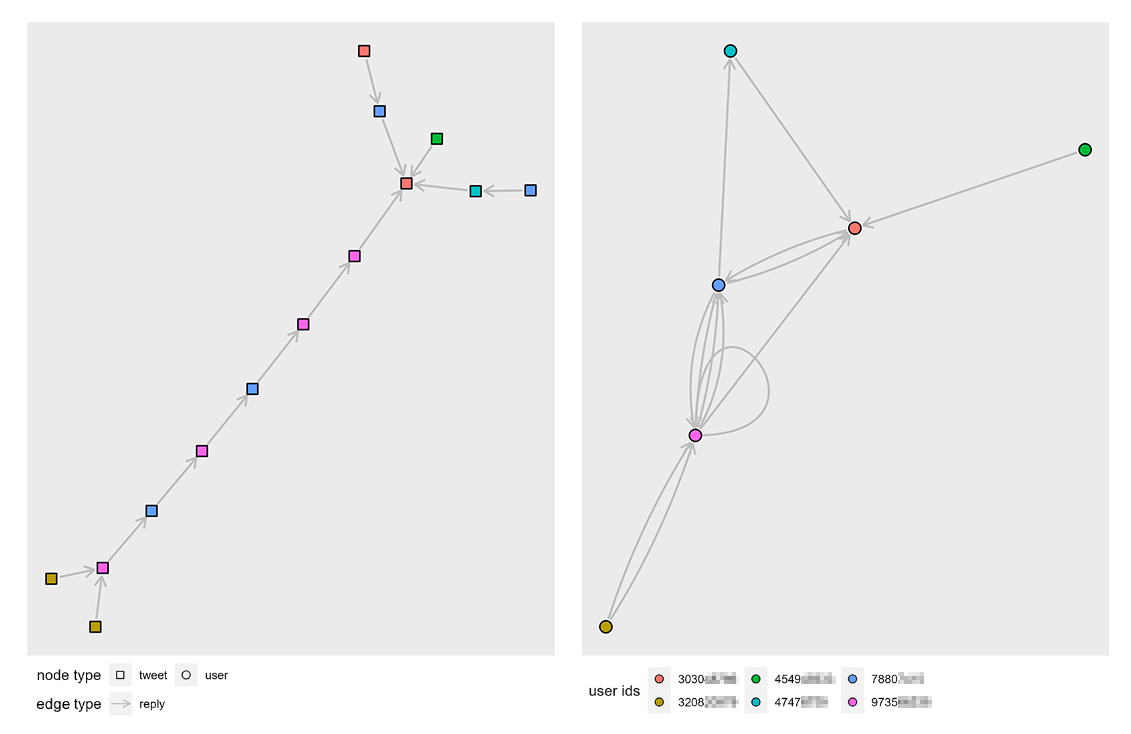
Two types of networks can be generated from the tweets collected. An
activity network in which tweets are the nodes and an actor network
where Twitter users are the nodes. Edges are the relationships between
nodes, in both networks these are either a reply or a quote,
signifying for example that a tweet is a reply-to another tweet or that
a user has replied to another user.
The activity network has tweet metadata such as tweet metrics and author usernames as node attributes.
activity_net <- tcn_network(thread_tweets, "activity")
# activity nodes dataframe structure
print(activity_net$nodes, n = 3)
# # A tibble: 148 x 11
# tweet_id user_id source created_at text public_metrics.~ public_metrics.~
# <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <int> <int>
# 1 13726476~ 9427940~ Twitt~ 2021-03-1~ @Warcr~ 0 0
# 2 13726461~ 1609030~ Twitt~ 2021-03-1~ @Patri~ 0 0
# 3 13726452~ 1190870~ Twitt~ 2021-03-1~ @Warcr~ 0 0
# # ... with 145 more rows, and 4 more variables:
# # public_metrics.like_count <int>, public_metrics.quote_count <int>,
# # profile.name <chr>, profile.username <chr>
# activity edges dataframe structure
print(activity_net$edges, n = 3)
# # A tibble: 122 x 3
# from to type
# <chr> <chr> <chr>
# 1 1372636834971455494 1372630068162297860 replied_to
# 2 1372635200748937223 1372615159311699970 replied_to
# 3 1372634777275265029 1372615159311699970 replied_to
# # ... with 119 more rowsThe actor network has additional user profile metadata as node attributes.
actor_net <- tcn_network(thread_tweets, "actor")
# actor nodes dataframe structure
print(actor_net$nodes, n = 3)
# # A tibble: 105 x 13
# user_id source profile.name profile.profile~ profile.location profile.username
# <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
# 1 275993~ Twitt~ "\U0001d43f~ https://pbs.twi~ England Stab~
# 2 133101~ Twitt~ "Andr ~ https://pbs.twi~ NA virg~
# 3 240160~ Twitt~ "Sebast ~ https://pbs.twi~ NA Nord~
# # ... with 102 more rows, and 7 more variables: profile.created_at <chr>,
# # profile.description <chr>, profile.verified <lgl>,
# # profile.public_metrics.followers_count <int>,
# # profile.public_metrics.following_count <int>,
# # profile.public_metrics.tweet_count <int>,
# # profile.public_metrics.listed_count <int>
# actor edges dataframe structure
print(actor_net$edges, n = 3)
# # A tibble: 124 x 6
# from to type tweet_id created_at text
# <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
# 1 2759935913 24599~ reply 1372636834~ 2021-03-18T19~ "@Limp ~ @Warcraft @MSF_~
# 2 133101119~ 61033~ reply 1372635200~ 2021-03-18T19~ "@Warcraft @MSF_USA Coming~
# 3 2401609580 61033~ reply 1372634777~ 2021-03-18T19~ "@Warcraft @MSF_USA When d~
# # ... with 121 more rowsNetworks can be converted into different formats and plotted using graph
packages such as igraph and ggraph. Below is an example for plotting
a threads actor network.
library(ggraph)
library(igraph)
# create igraph
g <- graph_from_data_frame(
actor_net$edges,
vertices = actor_net$nodes
)
# dashed lines for quote edges
line_vals <- c(reply = "solid", quote = "dashed")
# plot actor network
ggraph(g, layout = layout.auto(g)) +
geom_edge_loop(color = "gray") +
geom_edge_fan(
aes(linetype = as.factor(type)),
color = "gray",
arrow = arrow(length = unit(2, 'mm')),
start_cap = circle(1.5, 'mm'),
end_cap = circle(1.5, 'mm'),
strength = 1.2
) +
scale_linetype_manual(values = line_vals) +
geom_node_point(
size = 2.5,
aes(color = as.factor(name))
)Plots of an activity network and corresponding actor reply network graph generated from a small Twitter conversation thread.
Please note that the VOSON Lab projects are released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.