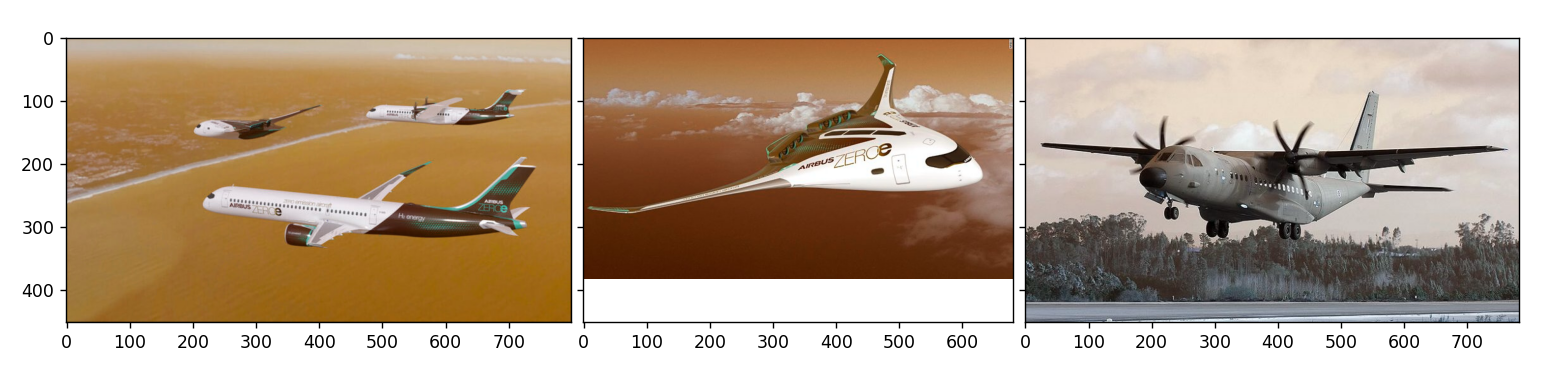
The goal of this project is to use a CNN that can identify airplanes and create a rectangle around their position.
In this project I use a dataset of 18 images containning one or more airplanes. The goal is to use a CNN that can identify these airplanes and create a rectangle around their position. This is a problem of object detection, these CNN's are hard to train, that's why in this example I will used a pre-trained CNN for object detection, in this case MobileNet, know for being a light-weighted neuronal network.
The first step of this script is to gather the 18 images, that were extracted from the internet. After the image collection phase, some of the collected images are shown bellow. It is possible to see that the images contain different number and types of airplanes.
In this second phase, imageLabel is used to draw rectangles around the objects to detect, and save their "coordinates" into a XML file.
This process is called the definition of the ground truth, if this was a classification or regression problem, the ground truth would be the target variable.
Since the target variable is not available, we need to create it.
This phase is important to evaluate the performance of the model, given that it will allow the comparison of the identification of objects between humans and the CNN.
These annotated images are saved into the images/gt directory located in the main branch.
To detect the airplanes, pre-trained MobileNet CNN is used. Firstly, the import of the model and some extra need information is done, such as the configuration file of the model, and the classes that this model is trained to detect.
These informations are saved in MobileNet directory located in the main branch.
-
First, import model with CV2 and TensorFlow
-
Define confidence level, but what is this value?
The algorithm will detect objects of several classes, and for each detection there will be a probability level. For example, the algorithm may detect a car with 0.99 trust or detect a sheep with 0.1 trust.
So the CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD variable will be used to select the detections that present a trust level above 0.50.
# Define threshold
CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD = 0.50
# Load model
model = cv2.dnn.readNet(model=MODEL_FILE, config=CONFIG_FILE, framework="TensorFlow")
The following code itters through all the images. For each image, the MobileNet is used to detect objects of 91 diferent classes.
From all of these detections, only consider the ones that are airplanes with a trust level higher than 0.5, these are saved into a dataframe (predicted_boxes).
After the execution of this code, images with rectangles, corresponding to the identified airplanes, are saved into the directory images/predicted.
This will allow the visualization of the original images with the detected objects.
predicted_boxes = pd.DataFrame({})
TP = 0
FP = 0
# Get location of Detected Objects
for image_path in os.listdir("images/normal"):
# Read image and get shape
img = cv2.imread(f"images/normal/{image_path}")
img_height, img_width, img_channels = img.shape
img_height, img_width, channels = img.shape
# Normalize data dimensions
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(image=img, size=(300, 300), swapRB=True)
model.setInput(blob)
output = model.forward()
for detection in output[0, 0, :, :]: #[0, class_id, trust, box_x, box_y, box_w, box_h]
# Trust
confidence = detection[2]
if detection[1] == 5:
if confidence > CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD:
class_id = detection[1] # Class id
class_name = class_names[int(class_id) - 1]
# obter as coordenadas e dimensoes das bounding boxes, normalizadas para coordenadas da imagem
bbox_x = detection[3] * img_width
bbox_y = detection[4] * img_height
bbox_width = detection[5] * img_width
bbox_height = detection[6] * img_height
predicted_boxes = predicted_boxes.append({"name": image_path,
"x": bbox_x,
"y": bbox_y,
"x_size": bbox_width,
"y_size": bbox_height}, ignore_index=True)
# colocar retangulos e texto a marcar os objetos identificados
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(bbox_x), int(bbox_y)), (int(bbox_width), int(bbox_height)), 1, thickness=2)
cv2.putText(img, class_name, (int(bbox_x), int(bbox_y - 5)), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, 1, 2)
TP += 1
else:
FP += 1
cv2.imwrite("images/predicted/"+image_path, img)
To evaluate the performance of the model the locations of the ground truth and the detected airplanes are needed.
The locations of the detected objects were already calculated on the last code chunk, and saved into the predicted_boxes dataframe.
Now it's necessary to store the same information for the ground truth, the following code will save the locations inside the actual_boxes dataframe.
actual_boxes = pd.DataFrame({})
for image_path in os.listdir("images/gt"):
tree = ET.parse(f'images/gt/{image_path}')
root = tree.getroot()
sample_annotations = []
for neighbor in root.iter('bndbox'):
xmin = int(neighbor.find('xmin').text)
ymin = int(neighbor.find('ymin').text)
xmax = int(neighbor.find('xmax').text)
ymax = int(neighbor.find('ymax').text)
actual_boxes = actual_boxes.append({"name": image_path,
"x": xmin,
"y": ymin,
"x_size": xmax,
"y_size": ymax}, ignore_index=True)
Now it is possible to calculate the intersection over union metric.
This metric is used to evaluate the performance of the model in corretly identifying the locations of the objects. To do that, a ratio between the intersection of both rectangles and the union of both rectangles is calculated. This way, if the two rectangles completely overlap, the areas of the intersection rectangle and union rectangle are coincident, giving origin to a IoU of 1. On the other hand, if the two rectangles don't share any area in common, the area of the intersection rectangle is 0, giving origin to a IoU of 0.
- The function bellow compute the IoU:
def IoU(boxA, boxB):
# determine the (x, y) - coordinates of the intersection rectangle
xA = max(boxA[1], boxB[1])
yA = max(boxA[3], boxB[3])
xB = min(boxA[2], boxB[2])
yB = min(boxA[4], boxB[4])
# compute the area of intersection rectangle
interArea = max(0, xB - xA + 1) * max(0, yB - yA + 1)
# Area of both boxes
boxAArea = (boxA[2] - boxA[1] + 1) * (boxA[4] - boxA[3] + 1)
boxBArea = (boxB[2] - boxB[1] + 1) * (boxB[4] - boxB[3] + 1)
return interArea / float(boxAArea + boxBArea - interArea)
-
If
IoU > 0.5-> classify the object detection as True Positive (TP) -
If
Iou < 0.5-> wrong detection and classify as False Positive (FP) -
If ground truth is present in the image and model fail to detect the object -> classify as False Negative (FN)
The precision represents the percentage of identified objects that are actual airplanes, from all the identified objects.
The recall shows how accurate the detections are. In this case the value is 1, this means that all the identifyed objects are actual airplanes.
The precision level is low because the model identifies 315 planes with a trust level under 0.5, and only 25 planes with a trust higher than 0.5.
Despite that the percentage of correctly identified airplanes is 100%, given that no planes were wrongly identified.
If you liked this project please leave a star 🌟 and contributions are welcome! ❤️
Thanks! ❤️