forked from hehonghui/android-tech-frontier
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Merge remote-tracking branch 'upstream/master'
- Loading branch information
Showing
15 changed files
with
1,382 additions
and
97 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
Submodule _book
added at
3fa255
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,230 @@ | ||
| Android Espresso 测试框架介绍 | ||
| --- | ||
|
|
||
| > * 原文链接 : [Introduction to Android Espresso](https://androidresearch.wordpress.com/2015/04/04/an-introduction-to-espresso/) | ||
| * 原文作者 : [Veaceslav Grec](https://androidresearch.wordpress.com/author/androidresearch/) | ||
| * [译文出自 : 开发技术前线 www.devtf.cn](http://www.devtf.cn) | ||
| * 译者 : [zhengxiaopeng](https://github.com/zhengxiaopeng) | ||
| * 校对者: [chaossss](https://github.com/chaossss) | ||
| * 状态 : 完成 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Espresso 是一个提供了简单 API 的用于 android app UI 测试的测试框架。最新的 2.0 版本发布后已经可以在 Android Support Repository 中下载了,那么在项目中集成它就方便多了。 | ||
|
|
||
| 但在我们看 Espresso 的 API 之前,让我们来细看下它与其它测试框架的不同: | ||
|
|
||
| - 你首先会注意到的是,他写出来的代码很像英文,可想而知它是很容易学习的 | ||
| - API 相当的小,当然也会对扩展开放的 | ||
| - Espresso 的测试跑起来那是相当的快(没有等待、睡眠) | ||
| - Gradle 和 Android Studio 的支持 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## 在你的项目中添加 Espresso | ||
|
|
||
| 1、首先保证你的 Android Support Repository 已经成功安装 | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 2、在你程序的 build.gradle 文件中添加依赖 | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Gradle | ||
| dependencies { | ||
| androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test:testing-support-lib:0.1' | ||
| androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.0' | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 3、最后,在默认配置中指定 test instrumentation runner | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Gradle | ||
| android { | ||
| defaultConfig { | ||
| // .... | ||
| testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner" | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 这些基本上就是在你的项目中集成 Espresso 测试框架了(给你的项目一杯浓咖啡提提神~)! | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Espresso 的主要组件 | ||
|
|
||
| Espresso 由 3 个主要的组件构成。 | ||
|
|
||
| 这些组件是: | ||
|
|
||
| - ViewMatchers - 在当前的 view 层级中定位一个 view | ||
| - ViewActions - 跟你的 view 交互 | ||
| - ViewAssertions - 给你的 view 设置断言 | ||
|
|
||
| 更简单的可以用下面的短语来表述它们: | ||
|
|
||
| - ViewMatchers – “ `找` 某些东西“ | ||
| - ViewActions – “ `做` 某些事情“ | ||
| - ViewAssertions – “ `检查` 某些东西“ | ||
|
|
||
| 举个例子,当你需要 `检查` 某些东西(像在屏幕中显示一些文字),你就会知道你需要一个 ViewAssertions 来做这些工作。 | ||
|
|
||
| Below is an example of a test in Espresso, and where the main components find their place. | ||
|
|
||
| 下面是使用 Espresso 的例子,你会看到那些主要的组件将会在哪里出现使用。 | ||
|
|
||
| 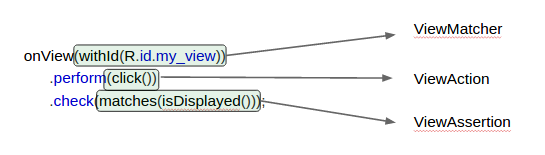 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## 一个使用 onView() 的简单测试 | ||
|
|
||
| 假设我们有一个 app,需要用户输入它的名字。 | ||
|
|
||
| 输入名字之后,用户按下了“下一步”按钮然后就会跳转到另一个显示问候信息的 activity。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 如果我们按这个方案来写一个测试的话,它看上去将会这样: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Java | ||
| // locate the view with id "user_name" and type the text "John" | ||
| onView(withId(R.id.user_name)).perform(typeText("John")); | ||
|
|
||
| // locate the view with id "next" and click on it | ||
| onView(withId(R.id.next)).perform(click()); | ||
|
|
||
| // locate the view with id "greeting_message" and check its text is equal with "Hello John!" | ||
| onView(withId(R.id.greeting_message)).check(matches(withText("Hello John!"))); | ||
|
|
||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 注意到我们并没有特别指定与其交互的 view 的信息(eg: EditText、Button),我们只是简单的说明了我们要找一个指定 id 的 view。 | ||
|
|
||
| 同样,当点击“下一步”按钮时然后检测文本时,我们也没有写代码来告诉 Espresso 我们有跳转到其它的 activity。 | ||
|
|
||
| 现在,如果要跑起这个测试用例,我们需要把这写代码写到一个类中,然后对于在 Gradle 中这个类应该保存的位置:yourApp`/src/androidTest/java`。 | ||
|
|
||
| 这个就是测试类的样子和它的主要特征: | ||
|
|
||
| 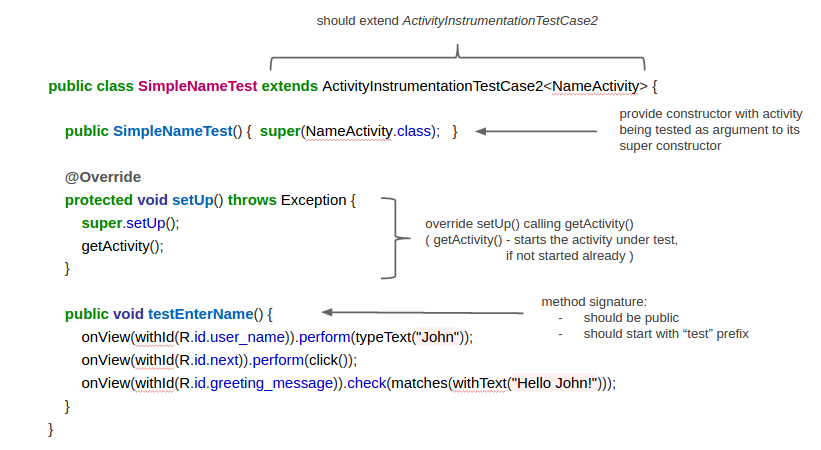 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 一个使用 onData 的简单测试 | ||
|
|
||
| 每当你有一个 ListView、GridView、Spinner 或者其它基于 Adapter 的view时,你都必须使用 `onData()` 来把 item 和 list 的数据联系起来。 | ||
|
|
||
| **onData()** 是给你的 adapter 提供数据的。这是什么意思呢,接下来你就会知道了。 | ||
|
|
||
| 在一个假想的程序中我们需要在一个 **Spinner** 中选择一个国家,一旦选定,这个国家的名字就会在 Spinner 的旁边显示出来。 | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 下面的测试就是检查显示出的国家是否与我们选择的相符合,代码长这样: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Java | ||
| // locate the view with id "country_spinner" and click on it | ||
| onView(withId(R.id.country_spinner)).perform(click()); | ||
|
|
||
| // match an item that is a String and is equal with whatever value the COUNTRY constant is initialized, then click on it. | ||
| onData(allOf(is(instanceOf(String.class)), is(COUNTRY))).perform(click()); | ||
|
|
||
| // locate the view with id "selected_country" and check its text is equal with COUNTRY | ||
| onView(withId(R.id.selected_country)).check(matches(withText("selected: " + COUNTRY))); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 上文中你看到的这个 Spinner 的适配数据是一个字符串的简单数组,所以对于我们要找的 item 来说我们也要指定 String 的数据类型。如果不是一个 String 而是一些自定义的对象呢,我们应该指定这些自定义的对象。 | ||
|
|
||
| 思考下下面这个显示一个 books 的 list 集合数据的例子: | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 把 item 的数据改为 Book 后,来看看查询: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Java | ||
| onData(allOf(is(instanceOf(Book.class)), withBookTitle(BOOK_TITLE))).perform(click()); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## 数据交互 | ||
|
|
||
| Espresso 有一些很有用的方法可以用来处理数据间的交互。 | ||
|
|
||
| **atPosition()** - 在下述的这些情况中会很有用,与相应元素交互的对象是不相关的,或 items 的顺序是特定的所以你知道每个 item 在哪个位置。 | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Java | ||
| onData(...).atPosition(2).perform(click()); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| **inRoot()** - 在没有默认窗口的情况下使用 inRoot()。这个场景可以应用在测试需自动完成时。这个 list 出现在自动输入填写完成的 view 是属于应用窗口之上的窗口视图。 | ||
|
|
||
| 这种情况下你必须指定你要查找的数据,而这数据并不在主程序窗口中。 | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Java | ||
| onView(withText("AutoCompleteText")) | ||
| .inRoot(withDecorView(not(is(getActivity().getWindow().getDecorView())))) | ||
| .check(matches(isDisplayed())); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| **onChildView()** - 这个数据交互可以进一步地精取出在一个 list 中的指定的(item) view。 | ||
|
|
||
| 你有一个集合列表,每一行的 item 上都有一个删除按钮。你想点击指定 item 上的删除按钮: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Java | ||
| onData(withBookTitle("My Book")) | ||
| .onChildView(withId(R.id.book_delete)).perform(click()); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| **inAdapterView()** - 可以选择指定一个 adapter view 去操作,默认情况下 Espresso 可以操作任何 adapter view。 | ||
|
|
||
| 你可能会发现这个在处理 `ViewPagers` 和 `Fragments` 时很有用,或者,你想要与当前显示的 AdapterView 交互时,你的 activity 中有多个 adapter view 时。 | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Java | ||
| onData(withBookTitle("My Book")) | ||
| .inAdapterView(allOf(isAssignableFrom(AdapterView.class), isDisplayed())) | ||
| .perform(click()); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Espresso 和 RecyclerView | ||
|
|
||
| [RecyclerView](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/v7/widget/RecyclerView.html) 是一个像 ListView、GridVIew 那样呈现数据集合的 UI 组件,实际上它的目的是要替换掉这两个组件。从测试的角度上来看我们感兴趣的有是 RecyclerView 不是一个 AdapterView,这意味着你不能使用 onData() 去跟你的 list items 交互。 | ||
|
|
||
| Fortunately, there is a class called RecyclerViewActions that exposes a small API to operate on a RecyclerView. RecyclerViewActions is part of a separate lib called espresso-contrib, that also should be added to build.gradle: | ||
|
|
||
| 幸运的是,有一个叫 [RecyclerViewActions](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/support/test/espresso/contrib/RecyclerViewActions.html) 的类提供了简单的 API 给我们操作 RecyclerView。RecyclerViewActions 是 **espresso-contrib**库的一部分,这个库的依赖可以在 build.gradle 中添加: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Gradle | ||
| dependencies { | ||
| // ... | ||
| androidTestCompile('com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-contrib:2.0'); | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 因为你的项目已经包括 recyclerview 依赖, 所以不妨也加上支持库的,一些依赖关系可能出现的冲突。在这种情况下可以在 espresso-contrib 中 exclude 他们: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Java | ||
| dependencies { | ||
| // ... | ||
|
|
||
| androidTestCompile('com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-contrib:2.0') { | ||
| exclude group: 'com.android.support', module: 'appcompat' | ||
| exclude group: 'com.android.support', module: 'support-v4' | ||
| exclude module: 'recyclerview-v7' | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 下面就是示例怎么(在RecyclerView)点击指定位置的 item: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Java | ||
| onView(withId(R.id.recyclerView)) | ||
| .perform(RecyclerViewActions.actionOnItemAtPosition(0, click())); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 或者怎么点击指定 item 上的 view: | ||
|
|
||
| ``` Java | ||
| onView(withId(R.id.recyclerView)) | ||
| .perform(RecyclerViewActions.actionOnItem( | ||
| hasDescendant(withText(BOOK_TITLE)), click())); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| 更多 Espresso 的例子请戳:[https://github.com/vgrec/EspressoExamples](https://github.com/vgrec/EspressoExamples) |
Oops, something went wrong.