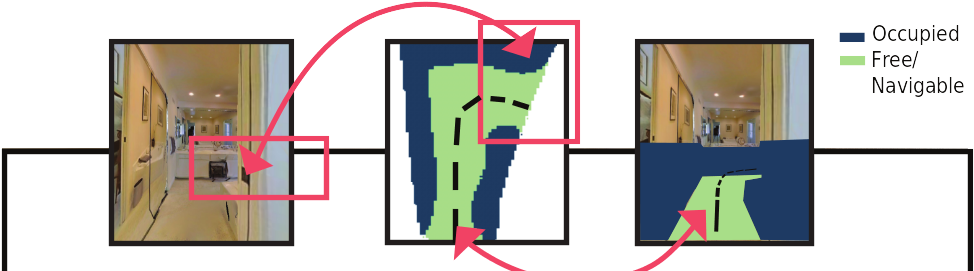
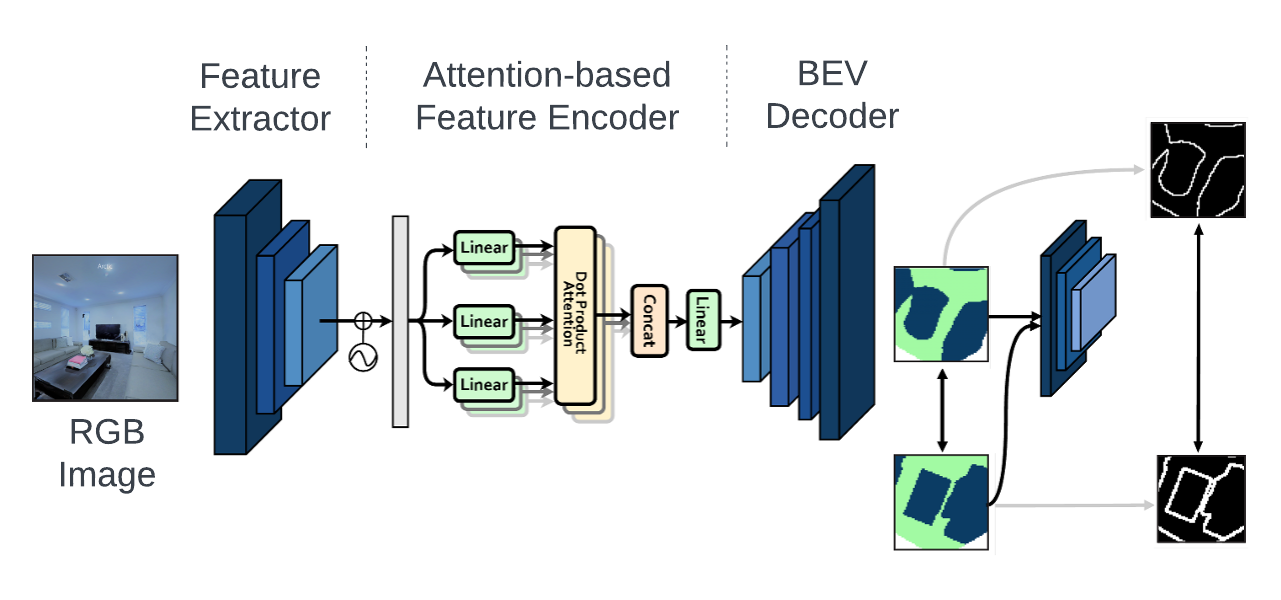
IndoLayout is a lightweight and real-time deep learning model that estimates amodal indoor layouts from a single monocular RGB image. Unlike traditional methods that only detect visible occupancy, IndoLayout leverages self-attention and adversarial learning to predict the hallucinated occupancy of occluded spaces, enabling better mapping and planning for indoor robots.
This repository contains the official implementation of IndoLayout, a method for extended indoor layout estimation from a single RGB image. IndoLayout leverages attention mechanisms to improve the accuracy and robustness of layout predictions in complex indoor scenes.
- Installation
- Dataset Preparation
- Baselines
- Indolayout
- Supplementary
- Results
- Citation
- License
- Acknowledgements
Clone the repository and install the required dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/indoor-layout-estimation.git
cd indoor-layout-estimation
pip install -r requirements.txtIndoLayout uses a combination of:
- ResNet-18 encoder (pretrained on ImageNet)
- Transformer-style self-attention module
- Convolutional decoder
- Patch-based discriminator (GAN)
The model outputs a 3-channel top-down occupancy map with probabilities for:
- Free/Navigable space
- Occupied space
- Unknown/Unexplored area
We train and evaluate on the following photorealistic indoor datasets using the Habitat simulator:
- Gibson 4+ (train/val)
- Gibson Tiny (train/val)
- Matterport3D (val only)
- HM3D (val only)
The generate_habitat_data.py script in the repository is for getting a quick overview.
For generating datasets, please use the actual Habitat repositories here: Github
Please refer to the bash_scripts folder to see examples on how to train or evaluate the Indolayout model on different datasets.
To run the code, you need to setup environment variables, which can be done by sourcing the 'vars' file in bash_scripts folders.
Pattern:
source bash_scripts/gibson4_exp.vars {Dataset_dir} {Bev_dir} {Log_Dir} {Train_split_path} {Val_split_path}E.g.:
source bash_scripts/gibson4_exp.vars /home/$USER/gibson4_dataset /home$USER/gibson4_dataset/bev_dir /home/$USER/indolayout_logs /home/$USER/indoor-layout-estimation-main/splits/gibson4/filtered_front_train_files.txt /home/$USER/indoor-layout-estimation-main/splits/gibson4/filtered_front_val_files.txtThe main script for training the baseline models (Occupancy Anticipation RGB and RGB-D) is:
python3 train_posenet_bev.py train_occant_gibson4.yaml --script_mode trainPlease note that this runs both training on the train set and evaluation on the validation set.
You can find additional configs to train different baselines in the repository.
To evaluate the same model, simply change the script_mode to 'val' as follows:
python3 train_posenet_bev.py train_occant_gibson4.yaml --script_mode valSimilar to the baselines, to run the code, you need to setup environment variables, which can be done by sourcing the 'vars' file in bash_scripts folders.
Pattern:
source cross-view/gibson4_exp.vars {Dataset_dir} {Bev_dir} {Log_Dir} {Train_split_path} {Val_split_path}E.g.:
source cross-view/gibson4_exp.vars /home/$USER/gibson4_dataset /home/$USER/gibson4_dataset/dilated_partialmaps /home/$USER/indolayout_logs /home/$USER/indoor-layout-estimation-main/splits/gibson4/filtered_front_train_files.txt /home/$USER/indoor-layout-estimation-main/splits/gibson4/filtered_front_val_files.txtThe main script for training the indolayout model is:
python3 train_disc.py --model_name attention_transformer_discr --data_path /home/$USER/gibson4_dataset --split gibson4 --width 512 --height 512 --num_class 3 --type static --static_weight 1 --occ_map_size 128 --log_frequency 1 --log_root /home/$USER/basic_discr --save_path /home/$USER/basic_discr --semantics_dir None --chandrakar_input_dir None --floor_path None --batch_size 8 --num_epochs 100 --lr_steps 50 --lr 1e-4 --lr_transform 1e-3 --load_weights_folder None --bev_dir /home/$USER/gibson4_dataset/dilated_partialmaps --train_workers 15 --val_workers 8To evaluate the same model, simply change the script to 'eval.py' as follows:
python3 eval.py --model_name attention_transformer_discr --data_path /home/$USER/gibson4_dataset --split gibson4 --width 512 --height 512 --num_class 3 --type static --static_weight 1 --occ_map_size 128 --log_frequency 1 --log_root /home/$USER/basic_discr --load_weights_folder /home/$USER/basic_discr/epoch_100 --semantics_dir None --chandrakar_input_dir None --floor_path None --batch_size 8 --num_epochs 1 --bev_dir /home/$USER/gibson4_dataset/dilated_partialmaps --train_workers 0 --val_workers 8Refer to the notebooks folder to understand experiments and their implementations individually, in particular for:
- data_visualization
- generate_visible_occupancy
- photometric_reconstruction
- evaluate_bev
| Method | mIoU (%) | F1 (%) | SSIM | Boundary IoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANS (RGB) [5] | 32.85 | 47.03 | 49.23 | 14.65 |
| OccAnt (RGB) [27] | 57.09 | 71.07 | 66.19 | 36.42 |
| IndoLayout | 63.45 | 73.49 | 69.37 | 39.06 |
| Difficulty | Method | Success Rate ↑ | SPL ↑ | Time ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | IndoLayout | 0.913 | 0.731 | 127.10s |
| Medium | IndoLayout | 0.763 | 0.566 | 233.80s |
| Hard | IndoLayout | 0.431 | 0.337 | 383.33s |
IndoLayout improves navigation success across difficulty levels without any depth input.
If you use IndoLayout in your research, please cite:
@INPROCEEDINGS{9982106,
author={Singh, Shantanu and Shriram, Jaidev and Kulkarni, Shaantanu and Bhowmick, Brojeshwar and Krishna, K. Madhava},
booktitle={2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)},
title={IndoLayout: Leveraging Attention for Extended Indoor Layout Estimation from an RGB Image},
year={2022},
volume={},
number={},
pages={13128-13135},
keywords={Measurement;Layout;Estimation;Real-time systems;Adversarial machine learning;Indoor environment;Task analysis},
doi={10.1109/IROS47612.2022.9982106}}
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
Developed at the Robotics Research Center, IIIT-Hyderabad, in collaboration with TCS Research.
Thanks to these great repositories: Neural-SLAM, Occupancy Anticipation, Cross-View and many other inspiring works in the community.