The Deep-Fake-Detector-Model is a cutting-edge deep learning system designed to enhance deepfake detection through multimodal analysis. By leveraging the Vision Transformer (ViT) architecture (google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k) and fine-tuning it on benchmark datasets like Kaggle's deepfake and real images, FaceForensics++ and the DeepFake Detection Challenge (DFDC), the model classifies images as either "Real" or "Fake" with high accuracy. This project explores multimodal approaches, integrating visual and contextual cues to improve robustness against advanced manipulations. Inspired by initiatives such as the Meta Deepfake Detection Challenge, it aims to advance model generalization, interpretability, and scalability, contributing to open-source research in deepfake forensics and AI-driven media verification.
- Architecture: Vision Transformer (ViT) -
google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k. - Input: RGB images resized to 224x224 pixels.
- Output: Binary classification ("Real" or "Fake").
- Training Dataset: A curated dataset of real and deepfake images (
Hemg/deepfake-and-real-images, CelebDF v2). - Fine-Tuning: The model is fine-tuned using Hugging Face's
TrainerAPI with advanced data augmentation techniques. - Performance: Achieves high accuracy and F1 score on validation and test datasets.
Hugging Face Model Finetuned on Celeb DF v2 : https://huggingface.co/ashwin-raikar/vit-deepfake-detector-celebdfv2
Hugging Face Model Finetuned on Hemg/deepfake-and-real-images : https://huggingface.co/prithivMLmods/Deep-Fake-Detector-Model
The Vision Transformer (ViT) is a transformer encoder model (BERT-like) pretrained on a large collection of images in a supervised fashion, namely ImageNet-21k, at a resolution of 224x224 pixels.
Images are presented to the model as a sequence of fixed-size patches (resolution 16x16), which are linearly embedded. One also adds a [CLS] token to the beginning of a sequence to use it for classification tasks. One also adds absolute position embeddings before feeding the sequence to the layers of the Transformer encoder.
Note that this model does not provide any fine-tuned heads, as these were zero'd by Google researchers. However, the model does include the pre-trained pooler, which can be used for downstream tasks (such as image classification).
By pre-training the model, it learns an inner representation of images that can then be used to extract features useful for downstream tasks: if you have a dataset of labeled images for instance, you can train a standard classifier by placing a linear layer on top of the pre-trained encoder. One typically places a linear layer on top of the [CLS] token, as the last hidden state of this token can be seen as a representation of an entire image.
Key components include:
- Patch Embedding: Divides the input image into fixed-size patches (16x16 pixels).
- Transformer Encoder: Processes patch embeddings using multi-head self-attention mechanisms.
- Classification Head: A fully connected layer for binary classification.
- Optimizer: AdamW with a learning rate of
1e-6. - Batch Size: 32 for training, 32 for evaluation.
- Epochs: 100.
- Dataset: Celeb DF v2.
- Data Augmentation:
- Random rotation (±90 degrees).
- Random sharpness adjustment.
- Random resizing and cropping.
- Loss Function: Cross-Entropy Loss.
- Evaluation Metrics: Accuracy, F1 Score, and Confusion Matrix.
from transformers import pipeline
# Load the model
pipe = pipeline('image-classification', model="ashwin-raikar/vit-deepfake-detector-celebdfv2", device=0)
# Predict on an image
result = pipe("path_to_image.jpg")
print(result)from transformers import ViTForImageClassification, ViTImageProcessor
from PIL import Image
import torch
# Load the model and processor
model = ViTForImageClassification.from_pretrained("ashwin-raikar/vit-deepfake-detector-celebdfv2")
processor = ViTImageProcessor.from_pretrained("ashwin-raikar/vit-deepfake-detector-celebdfv2")
# Load and preprocess the image
image = Image.open("path_to_image.jpg").convert("RGB")
inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
# Perform inference
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**inputs)
logits = outputs.logits
predicted_class = torch.argmax(logits, dim=1).item()
# Map class index to label
label = model.config.id2label[predicted_class]
print(f"Predicted Label: {label}")-
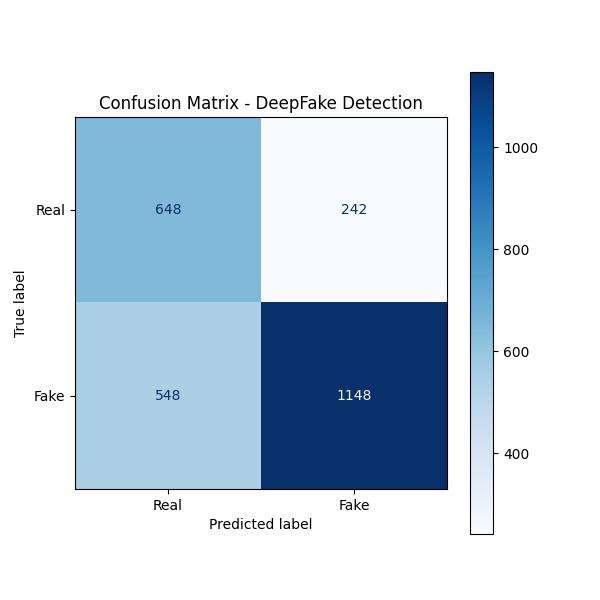
Confusion Matrix:
[[True Positives, False Negatives], [False Positives, True Negatives]]Classification report: precision recall f1-score support Real 0.54 0.73 0.62 890 Fake 0.83 0.68 0.74 1696 accuracy 0.69 2586 macro avg 0.68 0.70 0.68 2586 weighted avg 0.73 0.69 0.70 2586
The model is fine-tuned on the CelebDF v2 dataset, which contains:
- Real Images: Authentic images of human faces.
- Fake Images: Deepfake images generated using face swapping. The source for this dataset was CelebDF v2, where we extracted images from 200 videos, with a maximum of 5 frames per video. Each image is a 256 X 256 jpg image of human face either real or fake.
- Confusion Matrix:
[[True Positives, False Negatives], [False Positives, True Negatives]]
Classification report:
precision recall f1-score support
Real 0.6276 0.9823 0.7659 38054
Fake 0.9594 0.4176 0.5819 38080
accuracy 0.6999 76134
macro avg 0.7935 0.7000 0.6739 76134
weighted avg 0.7936 0.6999 0.6739 76134
The model is fine-tuned on the Kaggle Hemg/deepfake-and-real-images dataset, which contains:
- Real Images: Authentic images of human faces.
- Fake Images: Deepfake images generated using advanced AI techniques. The source for this dataset was https://zenodo.org/record/5528418#.YpdlS2hBzDd this dataset was processed as our will to get maximum outcome out of these images. Each image is a 256 X 256 jpg image of human face either real or fake.
The model is trained on a specific dataset and may not generalize well to other deepfake datasets or domains.
- Performance may degrade on low-resolution or heavily compressed images.
- The model is designed for image classification and does not detect deepfake videos directly.
Misuse: This model should not be used for malicious purposes, such as creating or spreading deepfakes. Bias: The model may inherit biases from the training dataset. Care should be taken to ensure fairness and inclusivity. Transparency: Users should be informed when deepfake detection tools are used to analyze their content.
- Extend the model to detect deepfake videos.
- Improve generalization by training on larger and more diverse datasets like FaceForensics++ and the DeepFake Detection Challenge (DFDC).
- Incorporate explainability techniques to provide insights into model predictions.
@misc{Deep-Fake-Detector-Model,
author = {prithivMLmods},
title = {Deep-Fake-Detector-Model},
initial = {2024},
last_updated = {31 Jan 2025}
}