-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1.8k
Servo
The Servo class constructs objects that represent a single Servo attached to the physical board. This class is designed to work well with both Standard and Continuous rotation servos.
See also:
-
pin A Number or String address for the Servo pin.
-
General options An object of property parameters.
Property Type Value/Description Default Required pin Number, String The address of the pin the servo is attached to yes range Array [ lower, upper ]The range of motion in degrees.[0, 180]no pwmRange Array [ min, max ]The pulse width range in microseconds.[600, 2400]no deviceRange Array [ min, max ]The physical range of the servo in degrees.[0, 180]no type String “standard”,“continuous”. The type of servo being created.“standard”no startAt Number Any number within the deviceRange. Degrees to initialize the servo at. no offset Number A positive or negative value to adjust the servo. falseno invert Boolean trueorfalse. Optionally Invert servo movement.falseno center Boolean trueorfalse. Optionally center the servo on initialization.falseno controller String DEFAULT, PCA9685. Controller interface type. DEFAULT no -
Debug Options Although servos can run on digital pins, this can sometimes cause issues. For this reason servos are forced to use only PWM under debug mode and will emit an error if used on a digital pin.
Property Type Value/Description Default Required debug Boolean trueorfalse. Set servo to debug modefalseno -
Continuous Servo Options
Property Type Value/Description Default Required deadband Array [ lower, upper ]. The deadband/stop point of the servo.*[90, 90]no * Some continuous servos do not have a trim pot for fine tuning the stop point, instead they have a built-in "deadband" range, which should be documented but otherwise requires manual measurement. Examples:
-
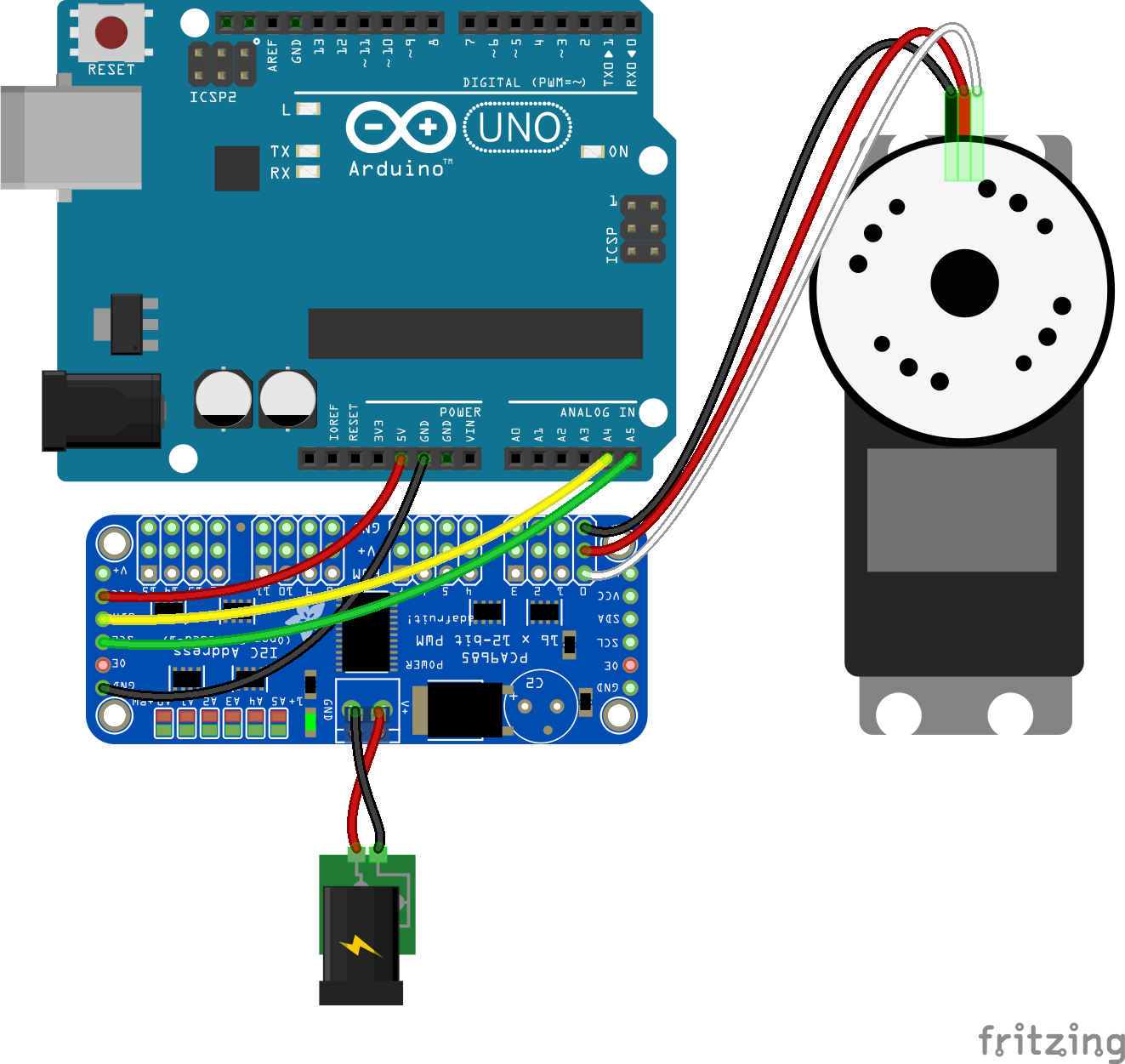
PCA9685 Options (
controller: "PCA9685")Property Type Value/Description Default Required address Number I2C device address. 0x40yes
| Property Name | Description | Read Only |
|---|---|---|
id |
A user definable id value. Defaults to a generated uid | No |
pin |
The pin address that the Servo is attached to | No |
range |
The range of motion in degrees. Defaults to [0, 180] | No |
invert |
A boolean, indicates whether servo values are inverted | No |
history |
An array containing records of each movement | No |
interval |
A reference to the current interval, if one exists | No |
isMoving |
A boolean flag, true when moving, false when still | No |
last |
The last movement record. | Yes |
position |
The angle the servo is at in the physical world. | Yes |
value |
The angle the servo was last set to. | No |
startAt |
The angle the servo was specified to start at upon initialization | No |
// Create a standard servo...
//
// - attached to pin 10
//
new five.Servo(10);// Create a standard servo...
//
// - attached to pin 10
// - centered
//
new five.Servo({
pin: 10,
center: true
});// Create a standard servo...
//
// - attached to pin 10
// - limited range of 45-135 degrees
//
new five.Servo({
pin: 10,
range: [45, 135]
});// Create a standard servo...
//
// - attached to pin 10
// - starts at 120°
//
new five.Servo({
pin: 10,
startAt: 120
});// Create a standard servo...
//
// - attached to pin 10
// - limited range of 45-135 degrees
// - starts at 120°
//
new five.Servo({
pin: 10,
range: [45, 135],
startAt: 120
});// Direct Constructor
new five.Servo.Continuous(10);
// Options object with type property
new five.Servo({
pin: 10,
type: "continuous"
});// Create a multi-turn servo. 6 rotations = 2160 degrees
// Note that this is not the same as a continuous rotation servo.
//
// - attached to pin 10
//
new five.Servo({
pin: 10,
deviceRange: [0, 2160]
});
// Create a standard servo controlled via PCA9685...
//
// - attached to pin 0 (of the PCA9685)
//
new five.Servo({
controller: "PCA9685",
pin: 0
});// Create a continuous servo controlled via PCA9685...
//
// - attached to pin 0 (of the PCA9685)
//
new five.Servo.Continuous({
controller: "PCA9685",
pin: 0
});
Standard Servo
var five = require("johnny-five");
var board = new five.Board();
board.on("ready", function() {
var servo = new five.Servo(10);
// Sweep from 0-180 and repeat.
servo.sweep();
});Continuous Servo
var five = require("johnny-five");
var board = new five.Board();
board.on("ready", function() {
var servo = new five.Servo({
pin: 10,
type: "continuous"
});
// Clockwise, top speed.
servo.cw(1);
});I2C Servo (i.e. via Adafruit PWM controller)
var five = require("johnny-five");
var board = new five.Board();
board.on("ready", function() {
var servo = new five.Servo({
pin: 0,
controller: "PCA9685",
address: 0x41 // Defaults to 0x40
});
// Sweep from 0-180.
servo.sweep();
});-
to(degrees 0-180 [, ms [, rate]]) Move a servo horn to specified position in degrees, 0-180 (or whatever the current valid range is). If
msis specified, the servo will take that amount of time to move to the position. Ifrateis specified, the angle change will be split into distance/rate steps for themsoption. If the specified angle is the same as the current angle, no commands are sent.var servo = new five.Servo(10); // Set the horn to 90degrees servo.to(90); // Angle change takes 500ms to complete servo.to(90, 500); // Angle change takes 500ms to complete over 10 steps servo.to(90, 500, 10);
-
min() Set Servo to minimum degrees. Defaults to 0deg, respects explicit range.
var servo = new five.Servo(10); // Set horn to 0degrees servo.min();
Or
var servo = new five.Servo({ pin: 10, range: [ 45, 135 ] }); // Set horn to 45° servo.min();
-
max() Set Servo to maximum degrees. Defaults to 180deg, respects explicit range.
var servo = new five.Servo(10); // Set horn to 135° servo.max();
Or
var servo = new five.Servo({ pin: 10, range: [ 45, 135 ] }); // Set horn to 135° servo.max();
-
center([ ms [, rate ]]) Set Servo to center point. Defaults to 90deg, respects explicit
range. Ifmsis specified, the servo will take that amount of time to move to the position. Ifrateis specified, the angle change will be split into distance/rate steps for themsoption. If the specified angle is the same as the current angle, no commands are sent.var servo = new five.Servo(10); // Set horn to 90degrees servo.center();
Or
var servo = new five.Servo({ pin: 10, range: [ 40, 80 ] }); // Set horn to 60degrees servo.center();
-
home() Set Servo to it's startAt position.
var servo = new five.Servo({ pin: 10, startAt: 20 }); // Set horn to 90 degrees servo.to(90); // Return to startAt value of 20 degrees servo.home();
-
sweep() Sweep the servo between default
minandmax, repeatedly.var servo = new five.Servo(10); servo.sweep();
-
sweep([ low, high ]) Sweep the servo between an explicit range, repeatedly.
var servo = new five.Servo(10); // Repeated full range movement servo.sweep([45, 135]);
-
sweep(options) Sweep the servo between an (optional) explicit range, within an (optional) explicit interval, and (optional) explicit steps (in degrees), repeatedly.
-
options: An object containing:-
range: An array containing[low, high]boundaries to sweep between. -
interval: The interval of a half sweep (eg.low -> high; a full sweep islow -> high -> low) -
step: The size of each step in degrees.
var servo = new five.Servo(10); servo.sweep({ range: [45, 135] }); servo.sweep({ range: [45, 135], interval: 1000, }); servo.sweep({ range: [45, 135], interval: 1000, step: 10 });
-
-
-
stop() Stop a moving servo.
var servo = new five.Servo(10); servo.stop();
-
cw(speed) (Continuous only) Move a continuous servo clockwise at speed, 0-1
var servo = new five.Servo({ pin: 10, type: "continuous" }); // full speed servo.cw(1);
-
ccw(speed) (Continuous only) Move a continuous servo counter clockwise at speed, 0-1
var servo = new five.Servo({ pin: 10, type: "continuous" }); // full speed servo.ccw(1);
It's recommended to use a rotary potentiometer as the mechanism for determining servo movement.
-
move:complete This is emitted when a timed move is completed. The event won't fire unless a time argument has been passed to the
servo.to()method.
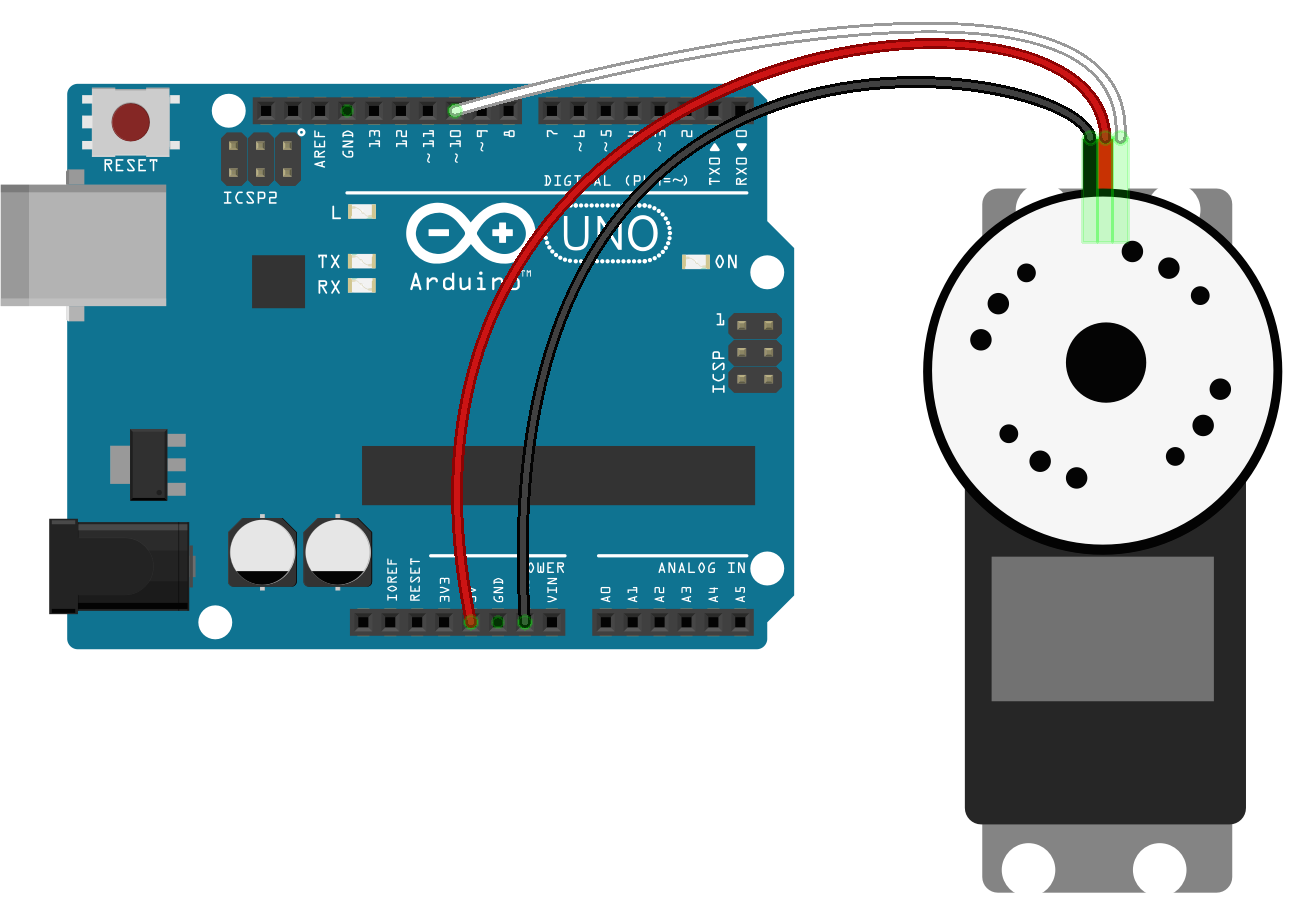
If you are experiencing memory leak crashes when using your servo, make sure that you are not powering the servo directly from your board. Excessive power draw on the USB port causes such crashes. The following diagram shows an example of how to provide external power for servos:

If your continuous servo moves when it should be stopped, it likely needs to be calibrated. Find instructions here.
