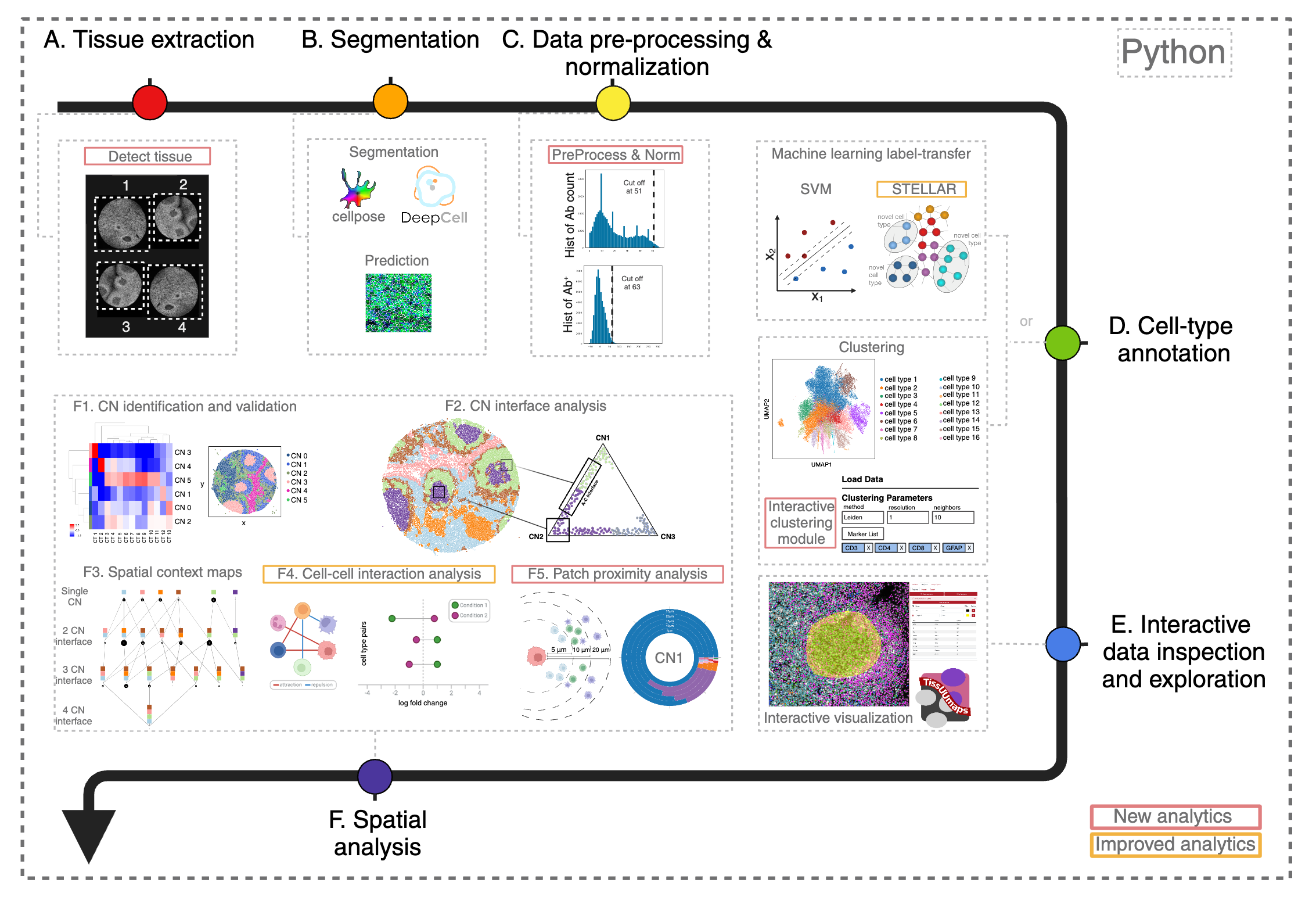
Multiplexed imaging technologies offer valuable insights into intricate tissue structures, yet they pose significant computational hurdles. These include cumbersome data handoffs, inefficiencies in processing large images (often ranging from 8 to 40 gigabytes per image), and limited spatial analysis capabilities. We created SPACEc, an all-in-one, scalable Python platform that advances both analytical capabilities and computational efficiency. Through careful engineering optimization, it streamlines the entire process from image extraction and cell segmentation to data preprocessing, while introducing novel approaches such as Patch Proximity Analysis for mapping cellular microenvironments to fill in the current analytic gaps. The platform significantly improves the performance of existing tools through parallelization and GPU acceleration, including enhanced cell-cell interaction analysis and simplified deep-learning annotation workflows, while its intuitive user-friendly design makes these advanced spatial analyses accessible to a wider scientific audience.
For an in-depth introduction to SPACEc, take a look at this YouTube video.
Note: We currently support Python==3.9 and 3.10.
Linux
SPACEc CPU
# Create conda environment
conda create -n spacec python==3.10 graphviz libvips openslide
conda activate spacec
# Install spacec
pip install spacecSPACEc GPU
# Install CUDA
conda install conda-forge::cudatoolkit=11.2.2 cudnn=8.1.0.77 -y
# Set environment variables for Tensorflow to find CUDA libraries
mkdir -p $CONDA_PREFIX/etc/conda/activate.d && \
echo 'export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$CONDA_PREFIX/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH' \
> $CONDA_PREFIX/etc/conda/activate.d/env_vars.sh- OPTIONAL: For GPU-accelerated clustering via RAPIDS run the following. Note that only RTX20XX or better GPUs are supported. More information on rapids-singlecell are available here: https://rapids-singlecell.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Installation.html
pip install spacec[rapids] --extra-index-url=https://pypi.nvidia.com- OPTIONAL: To use STELLAR run the following:
pip install spacec[stellar] \
--extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113 \
-f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-1.12.0+cu113.html- Test if SPACEc loads and if your GPU is visible:
python -c "import spacec as sp; sp.hf.check_for_gpu()"
Apple M1/M2/M3/M4
SPACEc CPU:
# Create conda environment
conda create -y -n spacec python==3.10 graphviz libvips openslide
conda activate spacec
# Install spacec
pip install spacec
# Install remaining requirements for deepcell
# NOTE: Ignore the error about pip's dependency resolver
pip install -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nolanlab/SPACEc/master/requirements/requirements-deepcell-mac-arm64_tf210-metal.txt
pip install deepcell --no-depsSPACEc GPU: Mac GPU support is currently only supported for Tensorflow based methods but not PyTorch (in some cases we try to use the MPS backend if possible but that can be tricky). We recommend to use a Linux system for full GPU acceleration.
Windows
Although SPACEc can run directly on Windows systems, we highly recommend running it in WSL. If you are unfamiliar with WSL, you can find more information on how to use and install it here: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install If you decide to use WSL, follow the Linux instructions.
If you plan to continue with the native Windows environment
- One of the segmentation tools within SPACEc neeeds a C++ compiler. If your environment doesn't have it already, the easiest way is to:
-
Download the community version of Visual Studio from the official Microsoft website: https://visualstudio.microsoft.com. After installing the software on your system, select the following options to install the components needed for C++ development (see screenshots)
-
In the meantime, you can already install libvips (https://www.libvips.org/) by downloading the pre-compiled Windows binaries from this repository: https://github.com/libvips/build-win64-mxe/releases/tag/v8.16.0 and adding them to your PATH. If you are unsure about which version to choose, vips-dev-w64-all-8.16.0.zip should work for you.
-
Unpack the zip file and add the directory to your PATH environment. If you don’t know how to do that, consider watching this tutorial video that explains the process: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O5iBsdAd1_w
-
SPACEc CPU:
# Create conda environment
conda create -n spacec python==3.10
conda activate spacec
# Install dependencies via conda.
conda install -c conda-forge graphviz
# Install spacec
pip install spacecSPACEc GPU:
conda install conda-forge::cudatoolkit=11.2.2 cudnn=8.1.0.77 -y
mkdir %CONDA_PREFIX%\etc\conda\activate.d && (
echo @echo off > %CONDA_PREFIX%\etc\conda\activate.d\env_vars.bat
echo set PATH=%CONDA_PREFIX%\bin;%PATH% >> %CONDA_PREFIX%\etc\conda\activate.d\env_vars.bat
echo set LD_LIBRARY_PATH=%CONDA_PREFIX%\lib;%LD_LIBRARY_PATH% >> %CONDA_PREFIX%\etc\conda\activate.d\env_vars.bat
)
# If Pytorch does not find the GPU try:
# pip install torch==1.12.0+cu113 torchvision==0.13.0+cu113 torchaudio==0.12.0 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113Reinstall SPACEc to be compatible with the GPU setting
# Install spacec
pip install spacecTest if SPACEc loads and if your GPU is visible if you installed the GPU version.
import spacec as sp
sp.hf.check_for_gpu()Docker
If you encounter installation issues or prefer a containerized setup, use the SPACEc Docker image. You can build or modify it using the repository's Dockerfiles.# Run CPU version:
docker build -f ../Docker/spacec_cpu_build.dockerfile -t spacec:cpu .
docker run -p 8888:8888 -p 5100:5100 spacec:cpu
# If running an amd64 image on apple silicon, use the following command:
docker run --platform linux/amd64 -p 8888:8888 -p 5100:5100 spacec:cpu
# Or run GPU version:
docker build -f ../Docker/spacec_gpu_build.dockerfile -t spacec:gpu .
docker run --gpus all -p 8888:8888 -p 5100:5100 spacec:gpu