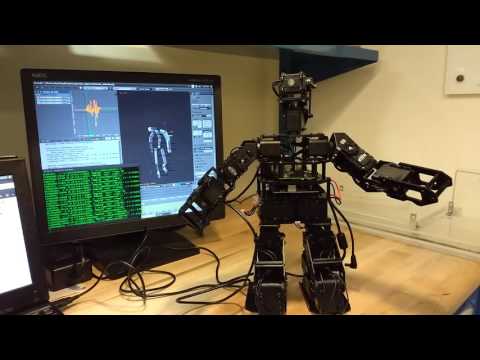
Stream joint angle positions from a Blender skeleton to a ROS node for controlling a robot controller.
- Ubuntu 14.04
- Blender 2.7x
- ROS Indigo
arbotix_rospackage- Robot controller:
- Arbotix-M board
- Dynamixel AX-12A servos (on HR-OS1 Endoskeleton Kit)
- Redis
stream.py-- Python code to run inside Blender.blender_ros_subscriber_node.py-- ROS node.
- When
stream.pyscript is run inside Blender, it will publish a (user-selected) set of joint angles to a Redis topic (e.g. 'test1', 'test2'). - The
blender_ros_subscriber_node.pyscript listens to the Redis topic, do necessary transformations (still in progress), and publish the joint angle values to the ROS topic for the robot controller (arbotix_ros)
Make sure Redis is installed and running
- Install Redis; follow the instructions here - Highly recommended to follow the instructions until the Installing Redis more properly section.
- Run the Redis server
Important notes: Blender uses Python 3.x docs. Therefore, it's recommended to install Redis for Python 3.x.
- (Optional, but recommended) Create a Python virtualenv which uses Python 3.x. I use venv which is a wrapper around Virtualenv.
```
# Install Virtualenv (if not already)
$ sudo pip install virtualenv
# Clone venv (this shows installing in the home directory)
$ cd ~
$ git clone https://github.com/wuub/venv.git
# Source the venv script
$ cd venv
$ source venv.bash
# Create new environment named py3env and tell it to use Python 3.x
$ venv create py3env --python=/usr/bin/python3
# The environment will be created in ~/.venv
# Activate the environment
$ venv use py3env
(py3env)~/venv$ _ # This shows the environment is active
# Install Redis - it will only be installed for this environment
(p3env)~$ pip install redis
```
- If not using a virtual environment, just do:
```
$ [sudo] pip install redis
```
-
Find the directory where Redis Python module is installed. - If with venv/virtualenv:
/home/<username>/.venv/py3env/lib/python3.x/site-packages/redis- If without:/usr/local/lib/python3.x/dist-packages/redisOr something like those ... -
Create a symlink in Blender's Python addons directory.
```
# Go to Blender's Python addon directory
$ cd /usr/share/blender/scripts/addons
$ sudo ln -s /home/<username>/.venv/py3env/lib/python3.x/site-packages/redis redis
```
- Test if the Redis Python module is loadable from Blender:
1. Launch Blender (re-launch if it's already open)
2. Open the Python console (CTRL + right x3)
3. In the Python console, type in
import redisand hit Enter. If it works, no error message will show up.
- Connect the servos to the Arbotix-M board
- Power the Arbotix-M board and connect to the computer via USB (requires an FTDI converter)
Everything here assumes ROS Indigo is installed and configured, including the Catkin workspace. If not, please follow the tutorials here (Also make sure to follow the Indigo tutorials.)
- Clone this ROS package into the Catkin workspace:
```
$ cd catkin_ws/src
$ git clone https://github.com/msunardi/blender_ros.git
```
- (Assuming
arbotix_rosis installed*) Make sure theblender_ros.launchfile points thearbotix_drivernode to thelaunch/arbotix_config_blender.yamlfile. This file defines the robot controller configuration, e.g.: servo IDs, servo names, limits, max/min speeds, etc. * Note: Also make sure the joint names in the.yamlfile match the joint names inblender_ros_subscrbier_node.py. - Run the subscriber node using the launch file
```
$ roslaunch blender_ros blender_ros.launch
```
- Launch Blender
- In the Blender Python console, copy and paste the
stream.py* Make sure the Python Redis package is installed - e.g.$ sudo pip install redis - Click on the 'Run script' button to execute the script.
- Load an animation file/sequence and play it.
* Note: as tested, the animation used was from a .bvh motion capture file and the joint angles used was from a skeleton/rig. Rename the objects in the
stream.pyto match the names of the object/skeleton/rig in the animation file.