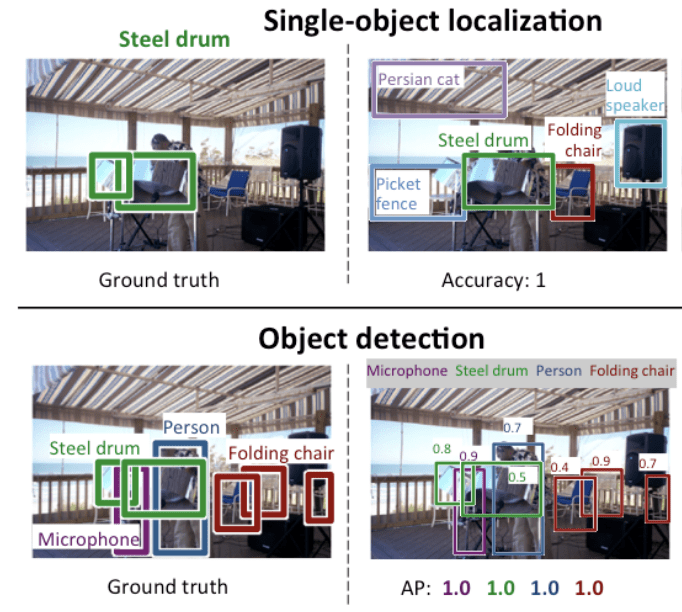
Deep learning has been widely employed in artificial intelligence object identification, which is the process of identifying and finding objects in digital photos or videos. Deep learning neural networks for object detection are trained on huge datasets of labeled photos, where the algorithms learn to recognize things by extracting features such as edges, corners, textures, and colors from the images. These traits are then utilized to forecast the existence and placement of items in previously unseen images.
Furthermore, detecting items that take up between 2% and 60% of an image's area is an area where object detection excels. It is also very efficient at detecting items with distinct borders Additionally, it detects groups of objects as a single item and performs object localization at high speed (>15fps).
Moreover, object detection is expanding into a variety of sectors, with applications ranging from business productivity to personal security. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), for example, have demonstrated exceptional success in obtaining high accuracy and real-time performance in a variety of applications, including autonomous vehicles, surveillance systems, and facial recognition systems. These algorithms are very successful at recognizing objects in complex and dynamic environments because they can automatically learn and adapt to varied object classes, orientations, sizes, and lighting conditions.
- A Gentle Introduction to Object Recognition With Deep Learning
- Application of Deep Learning for Object Detection
- How Deep Learning Works
- Deep Learning: Fundamentals, Theory and Applications
Image description (Karpathy and Fei-Fei 2017; Vinyals et al. 2017; Xu et al. 2015) is a difficult and dynamic research issue that necessitates both computer vision and natural language processing approaches. Its purpose is to generate natural language descriptions of photographs on the corresponding regions automatically. Different models have been presented by researchers to learn about the correspondences between linguistic and visual data. Karpathy and Fei-Fei (2017), for example, offer a multimodal RNN architecture to align a modality learnt by CNNs over picture regions with a modality trained by bidirectional RNNs over phrases. CNNs are used to learn the representation of images in Vinyals et al. (2017), while LSTMs are used to output phrases. A direct model is constructed to optimize the probability of the text given the image. In Xu et al. (2015), CNNs are used to construct image representations, and LSTMs are used to generate captions, similar to Vinyals et al. (2017). The essential improvement is to incorporate attention-based strategies to boost model performance even further. As new algorithms are proposed, the performance of image captioning improves. Bernardi et al. (2016) provide additional information.
Karpathy A, Fei-Fei L (2017) Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(4):664–676
Vinyals O, Toshev A, Bengio S, Erhan D (2017) Show and tell: lessons learned from the 2015 MSCOCO image captioning challenge. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(4):652–663
Xu K, Ba J, Kiros R, Cho K, Courville CA, Salakhutdinov R, Zemel SR, Bengio Y (2015) Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In: ICML, Lille, pp 2048–2057
Anaconda is a conditional free and open-source distribution of the Python and R programming languages for scientific computing, that aims to simplify package management and deployment.
After successfully installing anaconda, just go to the anaconda prompt and use this command to install OpenCV:
conda install -c conda-forge opencv After this command is successfully executed, OpenCV will be available on your computer.
Now for OpenCV to work on any image, it must be able to read it
cv2.imread(path, flag)The path parameter takes a string representing the path of the image to be read.The file should be in the working directory or we must give the full path to the image.The other parameter is the flag which is used to specify how our image should be read. Here are possible values that it takes and their working:
cv2.IMREAD_COLORIt specifies to convert the image to the 3 channel BGR colour image. Any transparency of image will be neglected. It is the default flag. Alternatively, we can passinteger value 1 for this flag.
cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALEIt specifies to convert an image to thesingle channel grayscale image. Alternatively, we can pass integer value 0 for this flag.
OpenCV can also be used for video processing. With OpenCV, we can capture a video from the camera and it also lets us create a video capture object which is helpful to capture videos through webcam and then you may perform desired operations on that video.
capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)In OpenCV we need to create a VideoCapture object to capture a video. We pass either the device index or the name of a video file as its arguments. Device index is just the number to specify the camera in case we have multiple webcams available.
Install my-project with npm
npm install my-project
cd my-projectTo deploy this project run
npm run deployThe bounding boxes used during object detection are rectangular. As a result, if the object has a curved component, establishing the contour of the object may be difficult.
Some metrics, such as an object's area and perimeter, cannot be estimated accurately by object detection.