-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
- Loading branch information
Showing
1 changed file
with
268 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,268 @@ | ||
| # MP-CodeCheckBin-RedHat | ||
| MP-CodeCheck Binary RedHat Release | ||
| Thank you for visiting Merly's MP-CodeCheck (BETA) GitHub repository! We are happy you are here! If you enjoy using MP-CodeCheck and find it useful, we would greatly appreciate your feedback. | ||
|
|
||
| Please email us with any questions, comments, issues, or anything related to MP-CodeCheck to support@merly.ai or debugging@merly.ai. We would love to hear from you! | ||
|
|
||
| MP-CodeCheck currently works with C, C++, C#, Go, Java, JavaScript, and Python. We plan to continue to add support for other languages in the coming months. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| # What is MP-CodeCheck? | ||
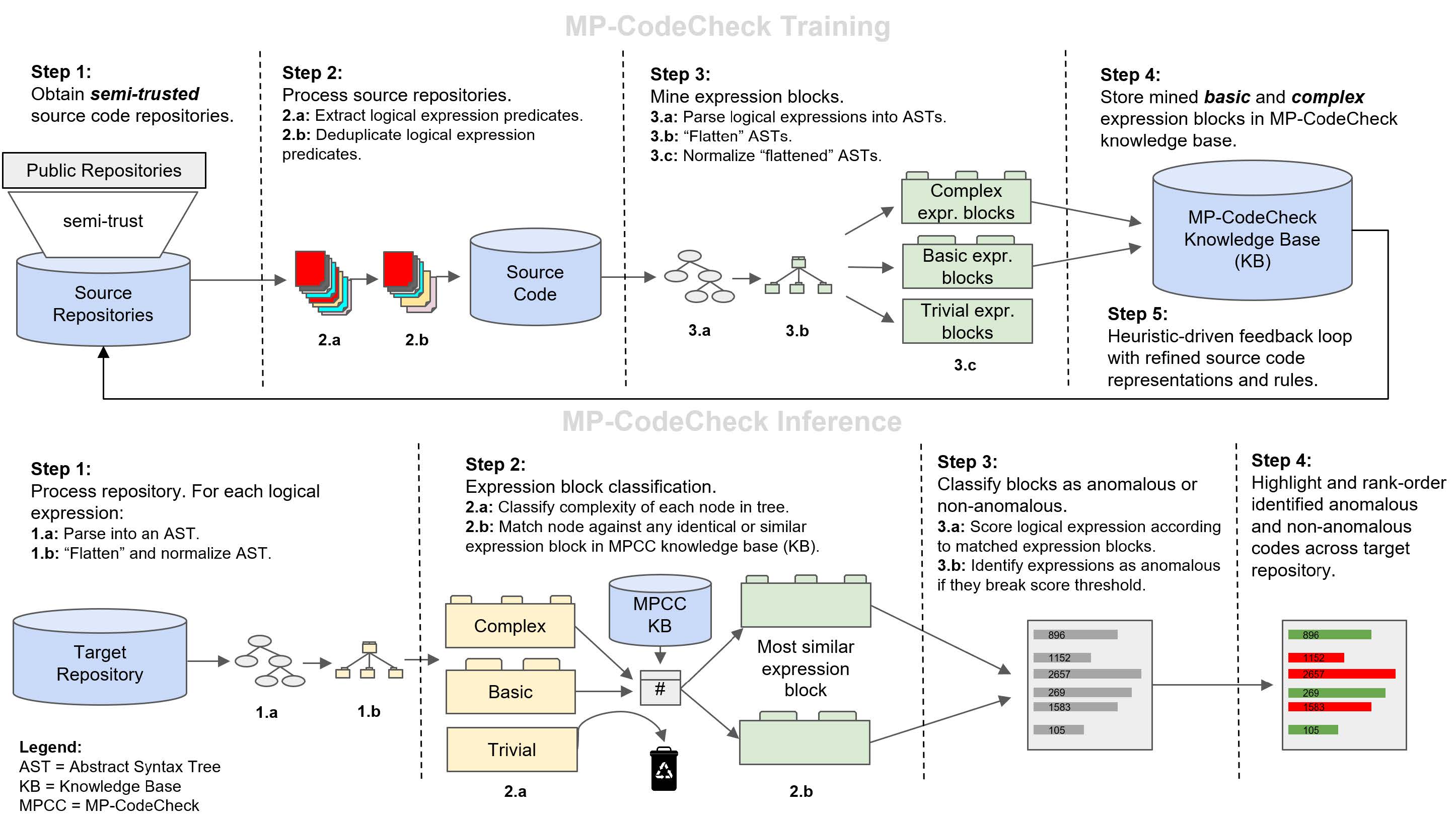
| MPCC is an AI-based code anomaly detection system. More specifically, MPCC uses self-supervision, iterative learning, and programmatic-guided evolution to detect anomalous code patterns. MPCC was designed to learn good and bad code syntax, patterns, and semantics from a large corpora of existing code. Once trained, MPCC’s model can be used for a variety of tasks such as: (i) detecting potential anomalies in existing code, | ||
| (ii) grading the quality of an existing repository, and (iii) guiding programmers through the important aspects of an unfamiliar or updated code | ||
| repository, to name a few. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| At its core, MPCC is a machine programming (MP) system that autonomously identifies anomalous logical expressions directly | ||
| in source code. These anomalous expressions, also known as anomalies, are often latent defects in the existing code that | ||
| programmers have failed to identify or correct. MPCC helps programmers find these anomalies and correct them, thereby | ||
| improving the overall quality of the existing software. For this limited release version of MPCC, we only include MPCC the | ||
| ability to perform inference (i.e., detect good or bad patterns) on code. In subsequent releases of MPCC, we may also include | ||
| the ability to train new models on other code bases, including users’ own proprietary ones. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Pre-Setup Instructions | ||
| For Linux RedHat, go to the Command Line Interface (CLI) and execute the following commands: | ||
|
|
||
| *mkdir MPCC* | ||
|
|
||
| *cd MPCC/* | ||
|
|
||
| *curl -OL https://github.com/merly-ai/MP-CodeCheckBin-RedHat/raw/main/bin/latest/MerlyInstaller* | ||
|
|
||
| *chmod +x MerlyInstaller* | ||
|
|
||
| *./MerlyInstaller install* | ||
|
|
||
| Your’re now ready to launch MP-CodeCheck! | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Setup Instructions | ||
| Prior to running inference and reviewing the results, let’s set up the environment. To run MPCC, you’ll need the following three | ||
| things (at a minimum): | ||
| 1. A model trained on code (provided by Merly). | ||
| 2. The MPCC executable (provided by Merly). | ||
| 3. A code base to run inference against (provided by you, the user). | ||
|
|
||
| Please ensure both the MPCC model and the executable file were placed in the same folder. (This should have been completed | ||
| for you by following the steps in pre-setup.) Then, to simplify inference, we recommend you place the code repository folder in | ||
| the same directory as MPCC. Your setup is now complete! | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Launching MP-CodeCheck | ||
| Now that setup is complete, let’s launch MPCC to perform inference analysis. From the command line interface (CLI), type the | ||
| following (where ”[code base folder]” is a directory that contains the code you want to analyze): | ||
|
|
||
| *./MPCC infer -D [code base folder]* | ||
|
|
||
| When run successfully, MPCC will display information that looks similar to the following screen. This shows the progress of MPCC extracting the code DNA from the training data. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="769" alt="launch1" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/169102884-2df8f152-5b54-4546-a194-d3ceb32c12c3.png"> | ||
|
|
||
| When MPCC has loaded its trained model and processed the code DNA, it begins inference analysis on all source code that | ||
| it finds in the files of the directory (or subdirectories) you have supplied when launching it. The image below shows an example of | ||
| MPCC’s inference progress in analyzing a code repository, how much work it has completed, and how much work is remaining. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="769" alt="launch2" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/169102952-dffaab20-4a7c-4c2d-a09b-f4fde0373321.png"> | ||
|
|
||
| When inference analysis has completed, the Code View screen will appear (see image below), which will allow a user to | ||
| analyze the inference results as discussed in the next section. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="769" alt="CodeView" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/169102988-d6b250f8-d681-4167-8f1e-63919cc7c031.png"> | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## Exploring MPCC's Inference Results | ||
|
|
||
| After inference analysis is performed, MPCC will show a user interface that includes source code, with an expression highlighted. | ||
| We call this screen the *Code View*, which will be described in more detail in Views section of this manual. The image below provides an | ||
| example of an anomalous code example found by MPCC. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="1395" alt="anomaly" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/169103117-e039e3f9-61a7-4c82-a883-ab99abd8eb96.png"> | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Here's a description of what you'll see on this screen: | ||
|
|
||
| **Sort Criteria:** This refers to how MPCC is sorting the list of expressions it has found. This can be via score (a numeric value | ||
| assigned by anomaly identification and complexity), or location (sequential code order). | ||
|
|
||
| **Class Filter:** This refers to which class of complexity is being filtered in the current view. This can be set from a minimum | ||
| value of trivial to a high value of Max complexity. | ||
|
|
||
| **Cost Filter:** This refers to a “mental cost” of an expression. This filter can be set from a minimum value of 0 to a maximum | ||
| value of 2,000. | ||
|
|
||
| **Displayed Items:** This refers to which items MPCC is displaying. It can be set to all expressions, or only anomalous | ||
| expressions. | ||
|
|
||
| **Hide/Show Known Good:** This refers to whether or not MPCC displays expressions that have been marked by the user as | ||
| Known Good. | ||
|
|
||
| **Anomaly Identification:** This displays whether or not MPCC has identified the current expression as an anomaly. Non- | ||
| anomalous expressions will be classified as “known pattern detected” and highlighted in green. Anomalous expressions will be | ||
| classified as “unfamiliar pattern(s) detected” and will be highlighted in green. | ||
|
|
||
| **Cost:** This displays the “mental cost” of the current expression. | ||
|
|
||
| **Complexity:** This displays the class of complexity of the current expression. | ||
|
|
||
| **Source Code Location:** This displays the file location of the source code under review. | ||
|
|
||
| **Anomaly/Expression Count:** This displays the count of the highlighted expression, as well as the total expressions found in | ||
| this file. If the user toggles the filter to show only anomalies, this will display the count of highlighted anomaly, and the total | ||
| anomalies found in the current file. | ||
|
|
||
| **Walking Through Code:** You can move forwards and backwards through the expressions by using the left and right arrow | ||
| keys, and can page up and page down through the code (by location) using the Page Up and Page Down keys. You can also | ||
| scroll up and down through the code by hold the Control key while pressing the up or the down arrow, respectively. | ||
|
|
||
| ## Basic Commands and Views | ||
|
|
||
| In MPCC, there are a number of supported keyboard and mouse commands. In this section we describe those keystrokes and | ||
| explain mouse behavior. Perhaps the most important initial command to remember is the *help* command which can be launched | ||
| by pressing the character ’h’ on your keyboard. The help command lists all of the keyboard commands, so if you ever find | ||
| yourself not remembering a keyboard command, just press ’h’ and MPCC will launch the keyboard shortcut commands. A | ||
| screenshot of the help dialogue box is shown below. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="666" alt="Help" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/163893676-f5845122-d222-45db-a756-7d8eca1c63a7.png"> | ||
|
|
||
| In addition to commands, there are several screens users can utilize to help them gain deeper insights into specific anomalies, | ||
| general anomaly information, anomalies by file, anomalies per file, and so forth. | ||
|
|
||
| **Code View:** This is the view of all of the code, with the expressions found highlighted. This view is the default view when | ||
| MPCC is initially run. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="769" alt="CodeView" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/169103253-67336b12-1317-4722-bf2e-988bf9ac6f6f.png"> | ||
|
|
||
| **Anomalies View:** Press ‘a’ to switch to the Anomalies view. This view shows all of the expressions in the code (across all | ||
| files) that MPCC has determined to be an anomaly, sorted by score. You can move up and down the list using the up and down | ||
| arrows, or the Page Up and Page Down keys. Press Enter with an anomaly highlighted to switch back to the Code View of that | ||
| specific anomaly. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="769" alt="AnomaliesView" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/169103292-b02129d8-0887-4bc8-a2e2-f072dd90307b.png"> | ||
|
|
||
| **Files View:** Press ‘f’ to switch to the Files view. This view shows all of the source code files, with the total number of | ||
| expressions MPCC found in each file. You can move up and down the list using the up and down arrows, or the Page Up and | ||
| Page Down keys. Press Enter with a file highlighted to switch back to the Code View of the expressions within that specific file. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="769" alt="FilesView" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/169103330-b25af179-4665-47fe-9c90-dbcf5c983b49.png"> | ||
|
|
||
| **Expressions View:** Press ‘e’ to switch to the Expressions view. This view shows all of the expressions in the current file, | ||
| sorted by score. You can move up and down the list using the up and down arrows, or the Page Up and Page Down keys. Also | ||
| note that you can toggle the sort between code location and score by pressing the ‘s’ key. Press Enter with an expression | ||
| highlighted to switch back to the Code View with that specific expression highlighted. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="675" alt="ExpressionsView" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/169103358-d4b63f25-0e2e-4eeb-90b1-c39c0eab8cdf.png"> | ||
|
|
||
| **Details View:** Press ‘d’ to switch to the Details view. This view shows the detail of the currently selected expression. The | ||
| detail lets you know how many anomalies MPCC identified within the expression, the cost, and the total score. Press ‘d’ to | ||
| return to Code View. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="675" alt="DetailsView" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/169103404-853c07a1-55bb-486f-952f-027eee1a4df8.png"> | ||
|
|
||
| **Help Pop-up:** In addition to the above views, you can press the ‘h’ key in any view to bring up the help screen which will | ||
| show you all of the hot keys and their functions. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="666" alt="Help" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/163893697-a8cd66b9-898b-4f84-8db4-92633864b4a6.png"> | ||
|
|
||
| ## Sorting/Filtering Inference Results | ||
|
|
||
| The following lists the ways MPCC’s inference results on source code data can be sorted and/or filtered. | ||
|
|
||
| ***Sort Criteria:*** | ||
|
|
||
| **Options:** | ||
| * Score (numeric value assigned by anomaly identification and complexity) | ||
| * Location (sequential code order) | ||
|
|
||
| **Default:** Score | ||
|
|
||
| **Toggle:** ‘s’ key | ||
|
|
||
| ***Class filter*** | ||
|
|
||
| **Options:** | ||
| * Trivial (minimum) | ||
| * Basic | ||
| * Complex 1 | ||
| * Complex 2 | ||
| * Max | ||
|
|
||
| **Default:** Trivial | ||
|
|
||
| **Adjust:** '1', '2', '3', '4', '5' keys | ||
|
|
||
| ***Cost filter:*** | ||
|
|
||
| **Options:** | ||
| * 0 (minimum) to 2,000 | ||
|
|
||
| **Default:** 0 | ||
|
|
||
| **Adjust:** ',' to decrease, '.' to increase, 'm' to reset to 0 (minimum) | ||
|
|
||
| ***Hide/Show Known Good:*** | ||
|
|
||
| **Options:** | ||
| * Hide Known Good | ||
| * Show Known Good | ||
|
|
||
| **Default:** Hide Known Good | ||
|
|
||
| **Toggle:** '9' key | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ## MPCC Generated Files | ||
| In addition to the live (online) user interface, you can also review the inference results offline through four MPCC generated | ||
| files. These files are re-generated each time inference is run successfully. These files will be created in the same folder that the | ||
| MPCC executable was launched and have the following naming structure. | ||
|
|
||
| **[Code Repo].by_file.txt:** This file lists all anomalous expressions (that are not nested if’s) found by MPCC. This human | ||
| readable file lists the original anomalous source and its normalized version. | ||
|
|
||
| **[Code Repo].by_file nested if.txt:** This file lists all nested if expressions that are found by MPCC to be anomalous. This | ||
| human readable file lists the original anomalous source and its normalized version. | ||
|
|
||
| **[Code Repo].mpcc.anomaly_list.json:** This file lists all expressions that are found by MPCC to be anomalous, in a machine- | ||
| readable format. | ||
|
|
||
| **[Code Repo].mpcc.summary.json:** This file contains a summary of all of the files, size, and lines of code reviewed by | ||
| MPCC. It also provides a summarized report of the number of expressions, anomalies, and scores found in the source code that | ||
| inference was performed on, in a machine-readable format. | ||
|
|
||
| ## MPCC Configuration | ||
| For users who wish to customize their MPCC experience, a JSON file is available to configure MPCC to fit your preferences. | ||
|
|
||
| The JSON file is located at the following location: | ||
|
|
||
| *%appdata%\..\local\merly.ai\debugging\MP-CodeCheck\config.json* | ||
|
|
||
| You can use any text editor to modify the colors, log file locations, and settings. Let’s take a closer look. | ||
|
|
||
| **Colors:** These are stored in the json file in hexadecimal (HEX) RGB; simply use your favorite color picker to find the | ||
| hex value of the color you’d like, and change the value of the associated item. | ||
|
|
||
| For example, you can set *anomaly_background* to RGB *ab852e* to change the highlight color of the anomalous expressions to dark orange. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="675" alt="orange_anomalies" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/169103463-9daf31dd-fb99-4138-a618-355aa8e5dae8.png"> | ||
|
|
||
| Or, set *highlight_background* to RGB *4a9de0* to change the highlight color of the non-anomalous expressions to light | ||
| blue. | ||
|
|
||
| <img width="675" alt="blue_expressions" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/92695077/169103507-c6562915-d2e7-4528-9596-47b38e24e772.png"> | ||
|
|
||
| **Log Files:** | ||
|
|
||
| You can change the model path by setting the directory associated with: local-db_root_path | ||
|
|
||
| You can change the log path by setting the directory associated with: log_path | ||
|
|
||
| **Settings:** | ||
|
|
||
| “run_training” – Determines whether or not training should be run before inference on the source code (defaults to true). | ||
|
|
||
| “filter” – Determines if items (such as nested ifs) are extracted from the json anomaly list file (defaults to true). | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|