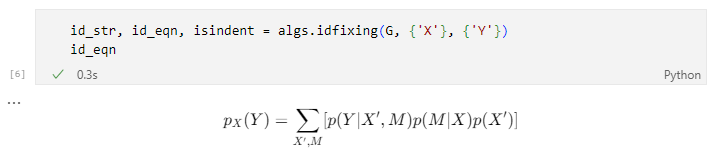GRAPL: A computational library for nonparametric structural causal modelling, analysis and inference
Structural causal models (SCMs) provide a probabilistic language for describing directed relationships between random variables. SCMs are widely used in science and engineering to capture causal relationships between quantitative, measured phenomena in the real world. Two SCM formalisms, directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) and acyclic directed mixed graphs (ADMGs) have been extensively studied. In these formalisms, the conditions under which causal dependence between variables occurs is well understood. Furthermore, analytical techniques have been developed which allow manipulation of the model so as to perform causal adjustment, that is, the isolation of desired causal relationships from the SCM. The GRAPL library brings together the most important and useful of such algorithms in one convenient software package. Using this library it is possible to represent, analyze and manipulate DAGs and ADMGs of arbitrary complexity.
- A simple text-based domain-specific language for representing both directed acyclic (DAG) and mixed, directed acyclic models (ADMGs) of interacting variables
- Derivation of factorized, marginalized nonparametric distributional models for arbitrary DAGs
- Computation of nonparametric, causal interventional distributions in arbitrarily complex models with (ADMG) and without (DAG) hidden variables, where such an interventional distribution can be computed in principle
- Various algorithms for the analysis of causal influence in DAGs/ADMGs (e.g. c-components/districts, node interventions, local Markov conditional independence relations, d-separation, topological sorting)
- Latex format output distributions and DOT (Graphviz) graph drawings, which can be easily dropped into documents for publication
- Inline IPython/Jupyter Latex equation and DAG/ADMG rendering (using Graphviz)
We currently offer seamless installation with pip.
Simply:
pip install grapl-causal
Alternatively, download the current distribution of the package, and run:
pip install .
in the root directory of the decompressed package.
IPython/Jupyter tutorials are included as part of the package in increasing order of complexity. These can be found in grapl/tutorials.
For example, see Tutorial 5.
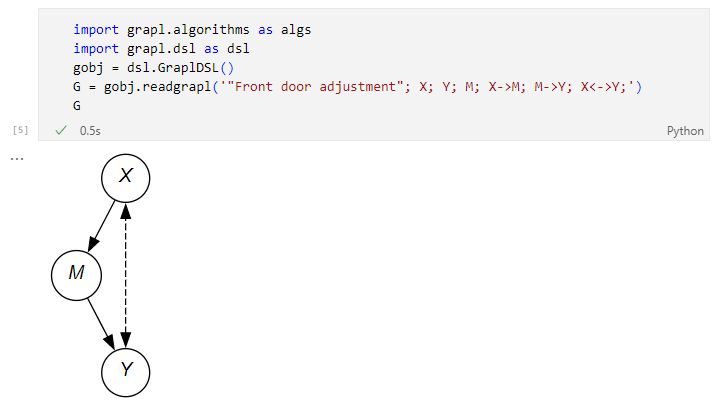
Computing the front-door adjusted distribution of the causal effect of X on Y with mediator M (e.g. X → M → Y) with hidden/latent confounding back-door path X — Y.
First, create a GRAPL DSL object, then the GRAPL description of the graph in a string, and parse the string using grapl.dsl.readgrapl to create the graph object G. This can then be rendered directly in IPython/Jupyter notebooks:
Next, invoke the grapl.algorithms.idfixing algorithm to find the interventional distribution (if it can be identified). This can be rendered directly in Latex form:
>>> import grapl.test.unit_tests as tests
>>> tests.run_all()- Implementation of m-separation and m-connection algorithms.