-
Couldn't load subscription status.
- Fork 0
High Level Design Overview
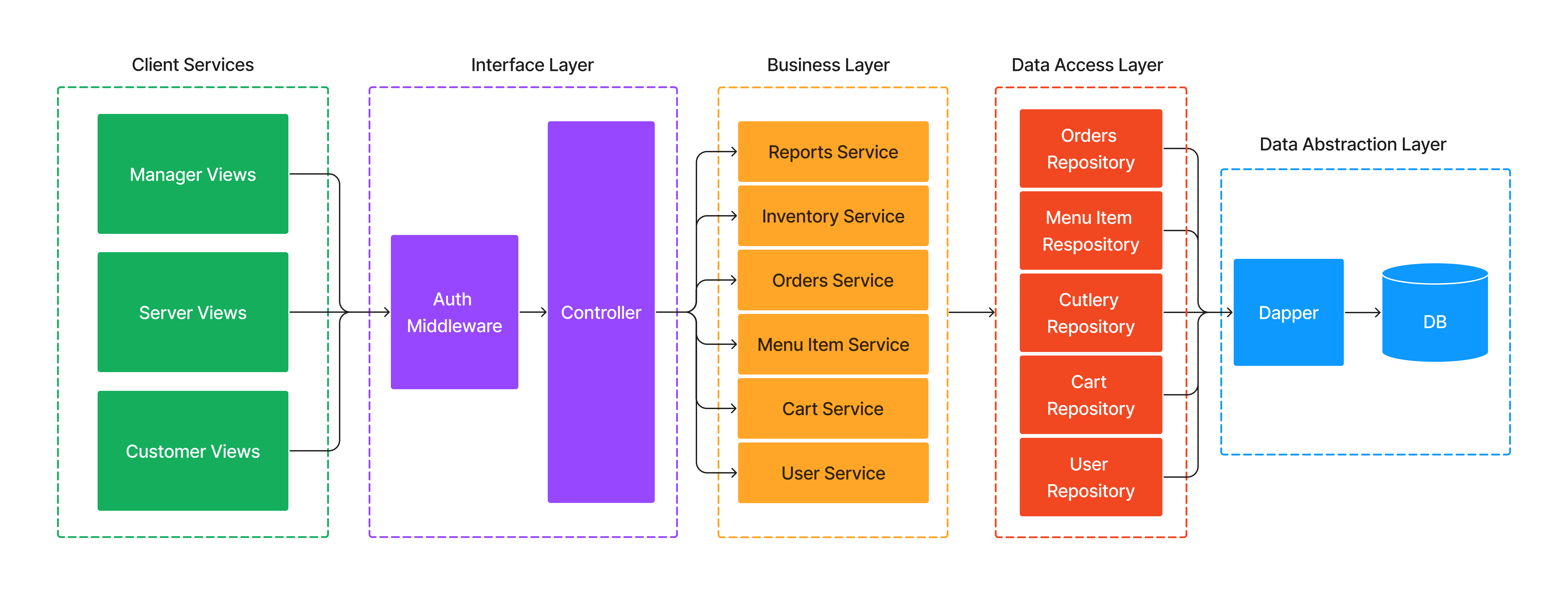
The backend solution follows a standard MVC pattern that includes four layers in the backend: a controller, a business layer/services, a data access layer/repository, and a data abstraction layer with Dapper and PostgresSQL. Together, these layers help create less coupled, more modular, more flexible, and more reusable code. Change is the enemy of perfect design, and we want to make sure that our API is ready to handle any changes thrown at it.
The controller layer acts as an interface and is responsible for handling incoming requests and sending responses back to the client. It receives input from the user and passes it to the business layer, which performs the necessary operations.
To reinforce the contracts with the View, the Controller uses request / response objects for each Model (i.e. MenuItemRequest, CutleryReponse, etc.) They are responsible for encapsulating the input and output parameters for a specific operation. By using request objects, the Controller can ensure that the input parameters are valid and meet the expected format before passing them to the Model. This helps to reduce errors and improve the overall reliability of the application.
By using request objects, the Controller can ensure that the input parameters are valid and meet the expected format before passing them to the Model. This helps to reduce errors and improve the overall reliability of the application.
The business layer/services are responsible for implementing business logic and processing data. They receive input from the controller layer and use the data access layer/repository to perform data operations. The business layer also validates data and enforces business rules.
The data access layer/repository is responsible for interacting with the database. It provides a simplified interface to perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on the database. It uses the Data Abstraction layer to communicate with the database.
The Data Abstraction layer is responsible for providing an abstraction over the database. It uses Dapper, an object-relational mapping (ORM) tool, to interact with the PostgreSQL database. Dapper simplifies database access by allowing developers to write SQL queries and map the results to C# objects.
Authentication will be handles by OAuth2 and a User's table will reinforce the creation of users with different permissions.