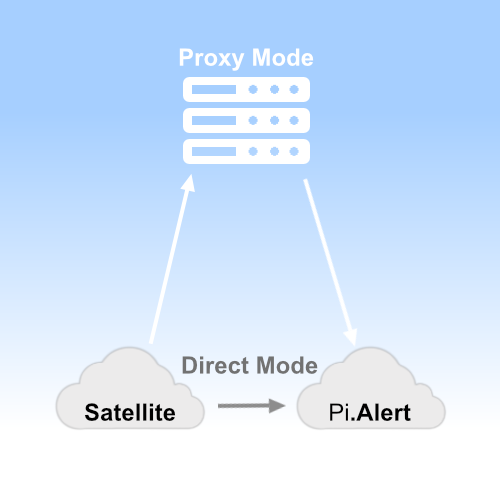
A companion script for Pi.Alert, which executes the Pi.Alert scan on an external host and sends the data as encrypted JSON to a special API.
Here the API of the Pi.Alert instance is called. This API compares the transmitted token with the Pi.Alert database to check whether the token is valid. If this is the case, the encrypted payload is decrypted and processed together with the scans of the Pi.Alert instance.
The API is installed on a separate web server. The satellite now transmits the data to the "proxy". This uses a configuration file to check whether it is a valid token and, if so, stores the data in encrypted form. Decryption on the proxy is not possible, as only the satellite and the Pi.Alert instance know the password. For Pi.Alert to retrieve the data, it must also be configured for proxy mode.
- arp-scan. The arp-scan system utility is used to search for devices on the network using arp frames.
- Fritzbox. If you use a Fritzbox (a router from the company "AVM"), it is possible to perform a query of the active hosts. This also includes hosts of the guest WLAN and Powerline devices from "AVM".
- Mikrotik. If you use Mikrotik Router as DHCP server, it is possible to read DHCP leases.
- UniFi. If you use UniFi controller, it is possible to read clients (Client Devices)
- OpenWRT. If you are using a router based on OpenWRT, you can import the active devices.
- Pi-hole DNS. If the Pi-hole v6 DNS server is active, Pi.Alert examines its activity looking for active devices using DNS that have not been detected by other methods.
- Pi-hole DHCP. If the Pi-hole v6 DHCP server is active, Pi.Alert examines the DHCP leases (addresses assigned) to find devices that were not discovered by the other methods.
Initially designed to run on a Debian based Linux distribution.
| One-step Automated Install |
|---|
|
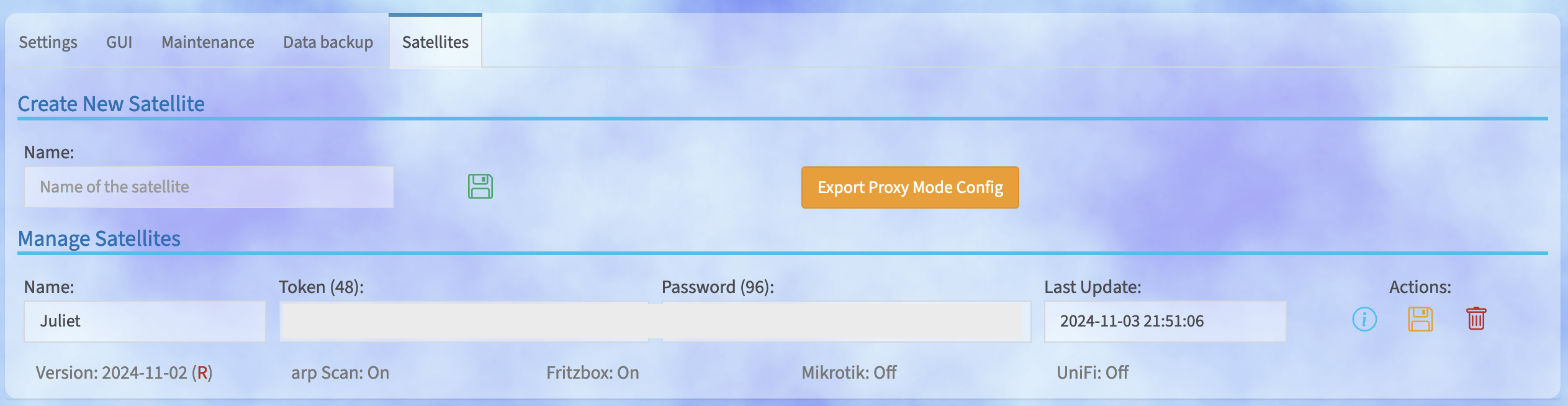
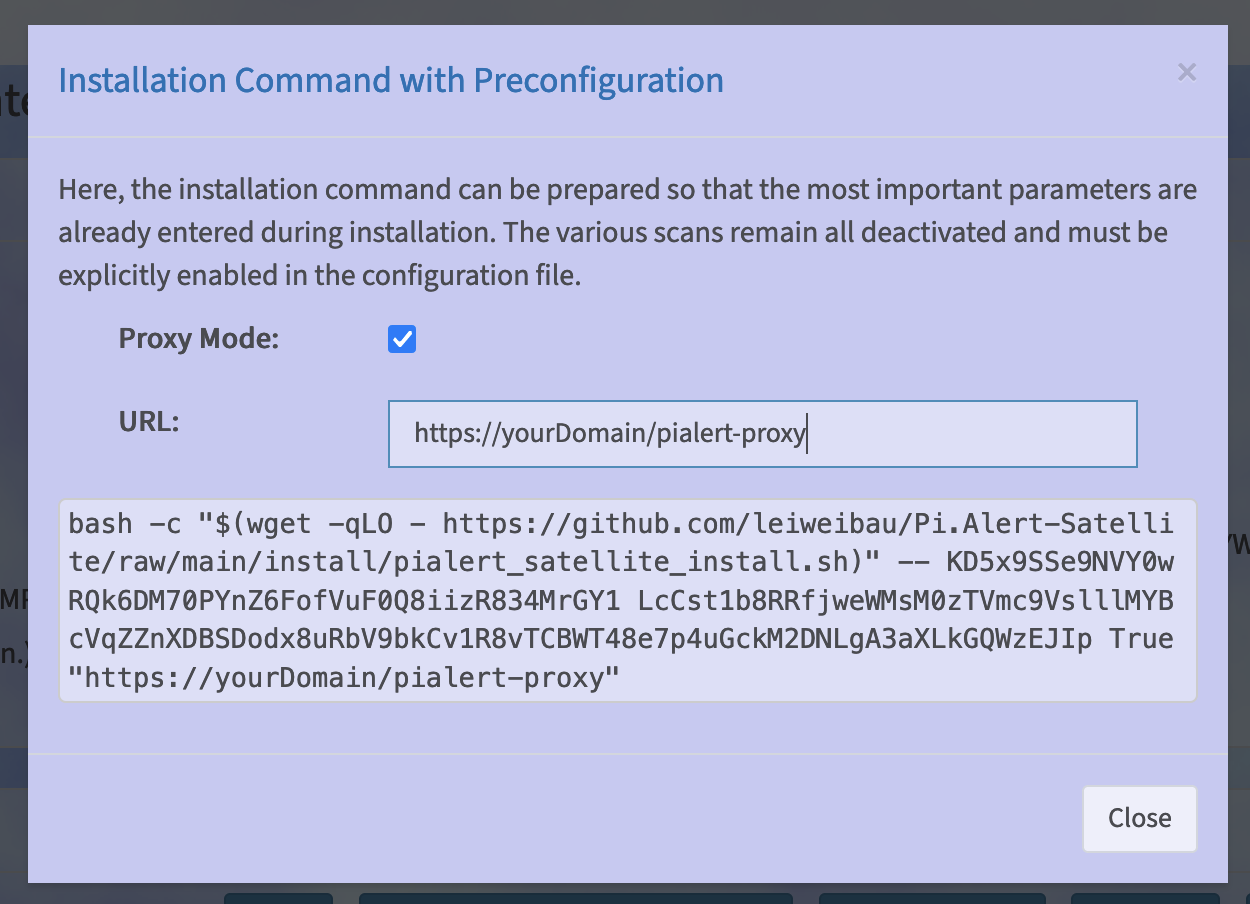
As an alternative to this installation, you can also click on the blue "i" icon on the right in the line of the corresponding satellite in the Pi.Alert instance after creating a satellite and create the installation command, which takes care of the important configuration during the installation.
 |
 |
|---|
Initially designed to run on a Debian based Linux distribution.
| One-step Automated Update |
|---|
|
An archive of older versions can be found at https://leiweibau.net/archive/pialert-satellite/. This archive contains all release notes.
In the directory "pialert-satellite/install/" there is a script called "pialert_satellite_uninstall.sh". This can be used to delete the cronjob and the "pialert-satellite" directory.
GPL 3.0 Read more here