Declaratively build a 4 node Kubernetes cluster on Proxmox using Ansible and QEMU. Optionally enable advanced features including ingress, load balancing, unattended upgrades, the Dashboard, etc.
Approximate deployment time: 25 minutes
- Proxmox server
- DNS Server*
- Ansible 2.7.0+. Known incompatibility with a previous build.
*A DNS server is not technically required, it is possible to manually add entries corresponding to your node hostnames to your Proxmox's hosts file.
Required:
- Modify the
vars.ymlfile with values specific to your environment. - Provision DNS A records for the IP Addresses & Hostnames you defined for your nodes in the
vars.ymlfile. - Modify the
inventory.inifile to reflect your chosen DNS records and the location of the SSH keys used to connect to the nodes. - Run the deployment:
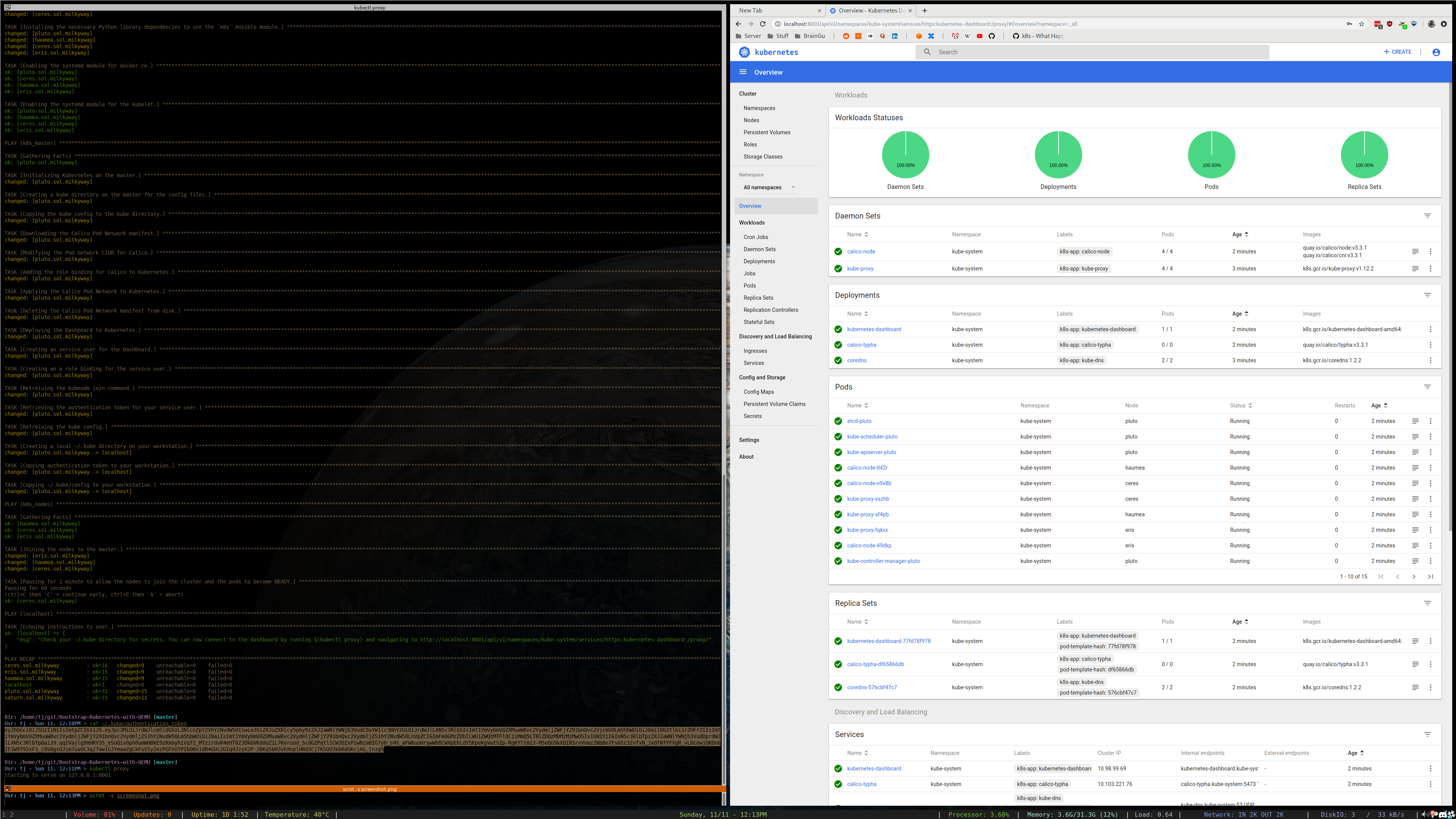
ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini site.yml - After deployment, a
~/.kubedirectory will be created on your workstation. You can use theconfigfile within to interact with your cluster.
Optional:
To enable an optional feature, fill in the additional parameters in vars.yml and execute a playbook listed below.
| Feature | Command | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Kubernetes Dashboard | ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/deploy_dashboard.yml |
|
| NFS backed persistent storage | ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/deploy_nfs_provisioner.yml |
|
| MetalLB Load Balancer | ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/deploy_metallb.yml |
|
| NGINX Ingress Controller | ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/deploy_ingress-nginx.yml |
MetalLB or other Load Balancer integration |
| DataDog agents | ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/deploy_datadog.yml |
|
| Unattended Upgrades | ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/enable_unattended_upgrades.yml |
- You can rollback the entire deployment with:
ansible-playbook -i inventory.ini playbooks/optional/delete_all_resources.yml - If Calico isn't deploying correctly it's likely the CIDR you assigned to it in
vars.ymlconflicts with your network. - There appears to be an issue with Proxmox's
cloud-initimplementation. Perhaps just with Debian? As a result, your VM might not have the correct information in/etc/resolv.confand may also have multiple IP Addresses assigned to theeth0network interfaces. Furthermore, if you do not have a DHCP server active in the network that you are provisoning the VMs to, it is entirely possible that nothing will be present at all in/etc/resolv.conf. - See this repository to do this with LXC instead. Benefits of using LXC include:
* No virtualization overhead means better performance
* Ability to directly mount volumes from your server into your containers.
- Add better support for multi-node Proxmox clusters.
- Perform security audit and enhance if necessary.
- Add info to README about updating inventory file and how to handle SSH key generation and propegation.
- Create playbook to upgrade kubernetes version for kubeadm cluster.
- The
proxmox_kvmmodule is out of date and does not support cloudinit related api calls. Meaning shell commands must be used instead to performqm createtasks. - The
k8smodule does not support applying Kubernetes Deployments from URL. Instead of usingget_urlto download them first, and then apply them withk8s, I just useshellto run akubectl apply -f. Feature Request here. - Miscellaneous
qcow2image issues:
| OS | Issue |
|---|---|
| CentOS | A nameserver is baked into /etc/resolv.conf by default. Bug Report here |
| CoreOS | Proxmix issued cloud-init does not seem to configure networking properly. |