Published in Cytopathology Journal - Oct 2023
Primary Objectives:
- Develop multiple-multiclass classification models capable of diagnosing cytological image samples from diverse locations, including salivary glands, gynecological, thyroid and effussions.
- Develop an AI algorithm using single-layer cytological slide scans challenging the need for full slide multi-layer scanning with z-stack, a process that is both costly and time-consuming.
Secondary Objectives:
- Implement a web-based application using Streamlit that enables users to predict diagnoses based on their image-inputs.
- Provide informative feedback on the image features using OpenAI API.
Let´s define first a few key terms:
- Cytology: This is the study of individual cells to detect abnormalities, including cancer. It's a type of sample method that provides a less invasive alternative to biopsies, enabling early diagnosis and treatment initiation, and improving health outcomes.
- Cytopathology: A specialized field, nested in pathology, that looks at diseases on the cellular level. Professionals of cytopathology include Cytotechnologists & Cytopathologists, focusing on screening, interpretation, and diagnosis of diverse cell samples.
- Digital Pathology: This involves digitizing pathology slides, allowing the use of image-based information for diagnosis, research, and teaching. Digital Pathology includes not only the digitalization of histology and cytology slides but also the automatization, technology, and tools of all preanalytical, analytical and post-analytical processes in a pathology department
In digital cytology, we face a unique challenge. Unlike in histology, where cells maintain their flat structure (like a single layer of bricks on a wall), cytology samples can be more like a pile of bricks dumped out of a bucket. These cells in suspension no longer hold their original formation, making diagnosis more complex and time-consuming because it requires mastery of pattern recognition. Furthermore, due to these additional dimensions, digitizing these cell images requires even more storage space.
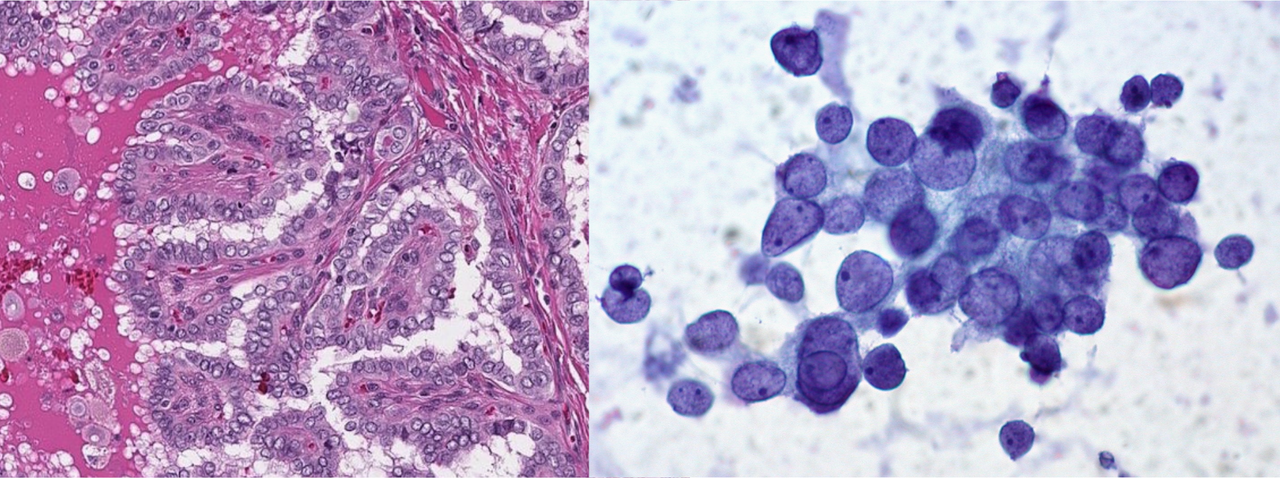
Thyroid, papillar carcinoma. Same tumor, different methods and different features. On the left, histology (1-dimensional thin layer), and on the right, cytology (three-dimensional in suspension cells).
My past 5 years of work have been all around Cytology; it involved screening and diagnosis of numerous cytology specimens, quality control, and engaging in both teaching and research, including Digital Pathology publications.
One significant barrier to the digitalization of Cytological samples is the final size. As previously explained, the cells in Cytology are not flat, unlike in Histology, but three-dimensional. This complexity typically requires a Z-stack scanning of the slides to capture all focal points, resulting in large digital files.
Despite this challenge, I firmly believe that Machine Learning and Deep Learning models can be implemented in Cytology images, bypassing the need for a complete scan, hence one of the most challenging aspects of the digitalization process.
- The convolutional neural network (CNN) model demonstrated excellent accuracy in the multiple-multiclass classification of cytology images, with a performance metric of approximately 90-95% accuracy around the 20-25 epoch mark.
- The challenge of the lack of available Data was addressed through the synthetic generation of new cytology images, an approach known as data augmentation. This technique was crucial for minimizing false negatives across all diagnostic categories.
- This model has the potential for real-world implementation, opening the door for the creation of AI algorithms using single-layer cytological slide scans or even phone-captured images, thereby challenging the need for full slide multi-layer scanning with z-stack, a process that is both costly and time-consuming.
For specific metric results, please refer to the specific Python folder:
- Pandas: Data manipulation and analysis.
- Numpy: Arrays and mathematical functions, allowing it to read images.
- Os: File managment.
- Matplotlib: 2D Data visualization.
- Seaborn: Runs on top of matplotlib, HD data visualization.
- PIL: Python Imaging Library to manipulate images.
- Warnings: Roses are red, violets are blue --> Warnings are annoying.
- Shutil: File operations (copying, deleting...).
- Random: To generate random subsets of data.
- TensorFlow: Machine Learning for Computer Vision.
- Keras: High-level neural networks API for Deep Learning, running on top of TensorFlow.
- ImageDataGenerator: To generate random data augmentation (flips, zoom...).
- Sklearn: Machine Learning metrics.
- Confusion Matrix: To evaluate true and false positives and negatives.
- Confusion Matrix Display: To easily display the matrix.
- Classification Report: For a more accurate detail of each metrics (precision, recall, f1-score, support).
- Chollet, F. Image Classification from Scratch. Keras. Retrieved from https://keras.io/examples/vision/image_classification_from_scratch/#introduction
- Chollet, F. Keras Metrics. Keras. Retrieved from https://keras.io/api/metrics/
- Nicholas Renotte. Build a Deep CNN Image Classifier with ANY Images. [Video]. YouTube. Available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jztwpsIzEGc
- OpenCV Team. Medical Multi-Label Classification. LearnOpenCV. Retrieved from https://learnopencv.com/medical-multi-label/
- Desolneux, A., Moisan, L., & Morel, J. M. (2003). Gestalt Theory and Computer Vision. In A. Desolneux, L. Moisan, & J. M. Morel (Authors), From Gestalt theory to image analysis: a probabilistic approach (pp. 1-19). Springer.
- Convolutional Neural Networks Explained. Towards Data Science. Retrieved from https://towardsdatascience.com/convolutional-neural-networks-explained-9cc5188c4939
- Different Types of CNN Architectures Explained - Examples. Vitalflux. Retrieved from https://vitalflux.com/different-types-of-cnn-architectures-explained-examples/
- CNN Architecture. InterviewBit. Retrieved from https://www.interviewbit.com/blog/cnn-architecture/
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) Architectures Explained. Medium. Retrieved from https://medium.com/@draj0718/convolutional-neural-networks-cnn-architectures-explained-716fb197b243
