This is a Machine Learning Project made by team Neophytes (313) for Code Off Duty by DSC WOW.
Fake news spreads like a wildfire and this is a big issue nowadays. We need learn how to distinguish fake news from a real one. We can use supervised learning to implement a model like this.
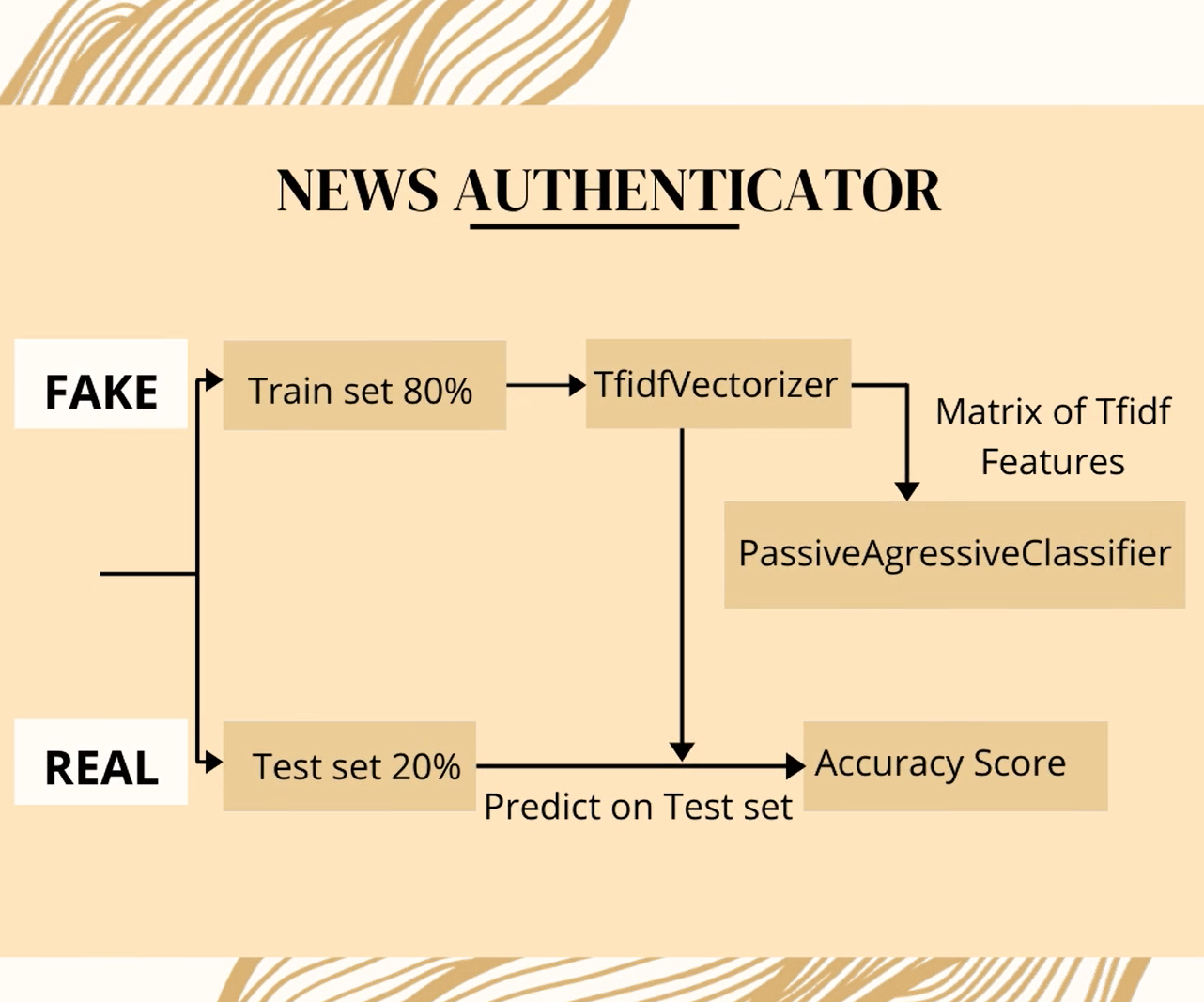
We made this project in python with objective to build a model to accurately classify a piece of news as REAL or FAKE.
This python project of news authenticator deals with fake news and real news. Using sklearn (scikit), we build a TfidfVisualizer on our dataset. Then, we initialize a PassiveAgressive Classifier and fit the model. In the end, the accuracy score and the confusion matrix tell us how well our model fares.
Fake news is a type of yellow journalism that encapsulates pieces of news that may be hoaxes and is generally spread through social media and other online media. This is often done to impose certain ideas and is often achieved with political agendas. Such news items may contain false and/or exaggerated claims, and may end up being viralized by algorithms, and users may end up in a filter bubble.
The number of times a word appears in a document is its Term Frequency. A higher value means a term appears more often than others, and so, the document is a good match when the term is part of the search terms.
Words that occur many times a document, but also occur many times in many others, may be irrelevant. IDF is a measure of how significant a term is in the entire corpus.
The TfidfVectorizer converts a collection of raw documents into a matrix of TF-IDF features.
Passive Aggressive algorithms are online learning algorithms. Such an algorithm remains passive for a correct classification outcome, and turns aggressive in the event of a miscalculation, updating and adjusting. Unlike most other algorithms, it does not converge. Its purpose is to make updates that correct the loss, causing very little change in the norm of the weight vector.
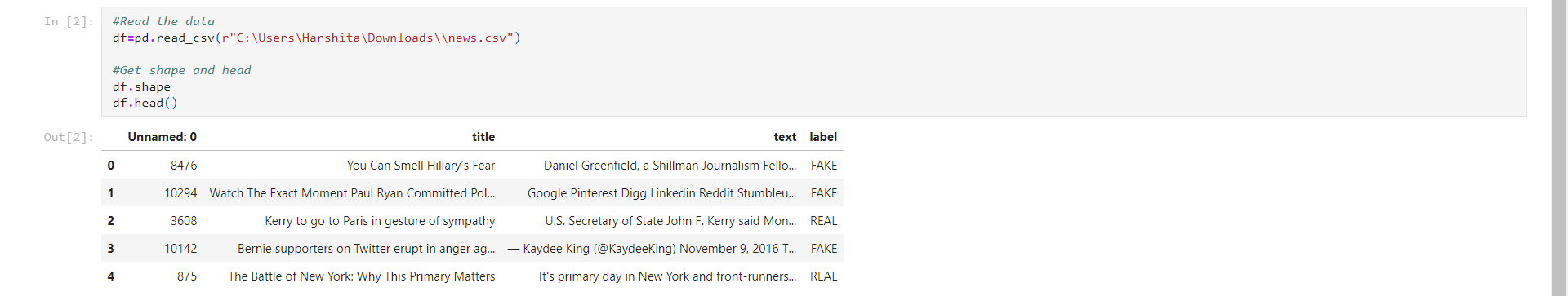
The dataset we've used for this python project is news.csv. This dataset has a shape of 7796x4. The first column identifies the news, the second and third are the title and text, and the fourth column has labels denoting whether the news is REAL or FAKE.
Make necessary imports
Read the data into a DataFrame, and get the shape of the data and the first 5 records.
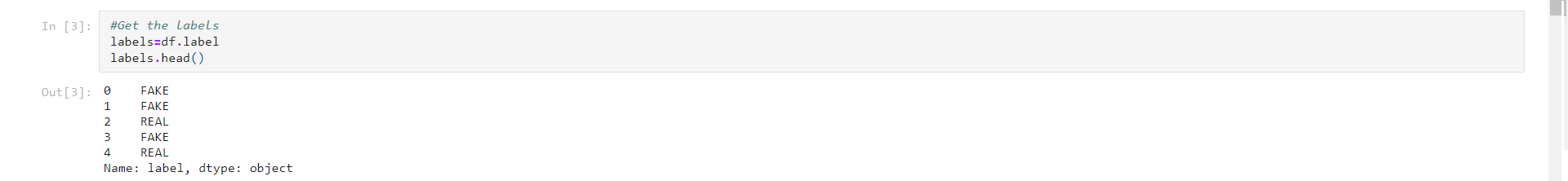
Get the labels from the DataFrame.
Split the dataset into training and testing sets.
Initialize a TfidfVectorizer with stop words from the English language and a maximum document frequency of 0.7 (terms with a higher document frequency will be discarded). Stop words are the most common words in a language that are to be filtered out before processing the natural language data. And a TfidfVectorizer turns a collection of raw documents into a matrix of TF-IDF features.
Now, fit and transform the vectorizer on the train set, and transform the vectorizer on the test set.
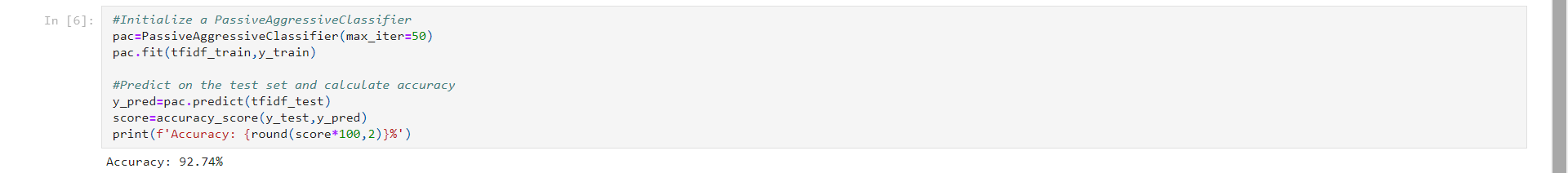
Next, we’ll initialize a PassiveAggressiveClassifier. That is we’ll fit this on tfidf_train and y_train.
Then, we’ll predict on the test set from the TfidfVectorizer and calculate the accuracy with accuracy_score() from sklearn.metrics.
We got an accuracy of 92.74% with this model.
Now we'll print out a confusion matrix to gain insight into the number of false and true negatives and positives.
So with this model, we have 588 true positives, 587 true negatives, 42 false positives, and 50 false negatives. We took a political dataset, implemented a TfidfVectorizer, initialized a PassiveAggressiveClassifier, and fit our model. We ended up obtaining an accuracy of 92.74% in magnitude.
On clicking the "Predict" button following output can be seen: