Code implementation of various algorithms and DS concepts with explanations.
- ANALYSIS
- SORTING ALGORITHMS
- DATA STRUCTURE
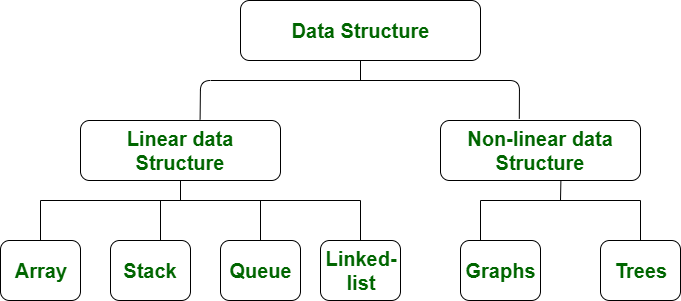
Data Structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data.
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization, management, and storage format that enables efficient access and modification.
An algorithm is a set of well-defined instructions in sequence to solve a problem. In an easy saying, an algorithm is nothing but a mention of steps to solve a problem. They are essentially a solution.
- Input and output should be defined precisely.
- Each step in the algorithm should be clear and unambiguous.
- Algorithms should be most effective among many different ways to solve a problem.
- An algorithm shouldn't include computer code. Instead, the algorithm should be written in such a way that it can be used in different programming languages.
Its the amount of memory space required by the algorithm, during the course of its execution. Space complexity must be taken seriously for multi-user systems and in situations where limited memory is available.
Time Complexity is a way to represent the amount of time required by the program to run till its completion. It's generally a good practice to try to keep the time required minimum, so that our algorithm completes it's execution in the minimum time possible.
Note: Space and time complexity is well discussed as comments in the code(few are left, will be done soon)
Sorting refers to arranging data in a particular format, ascending or descending. There are various type of sorting techniques, few of them are:
- Quick Sort
- Bubble Sort
- Merge Sort
- Counting Sort
- Insertion Sort
- Selection Sort
- Heap Sort
- Radix Sort
- Bucket Sort
