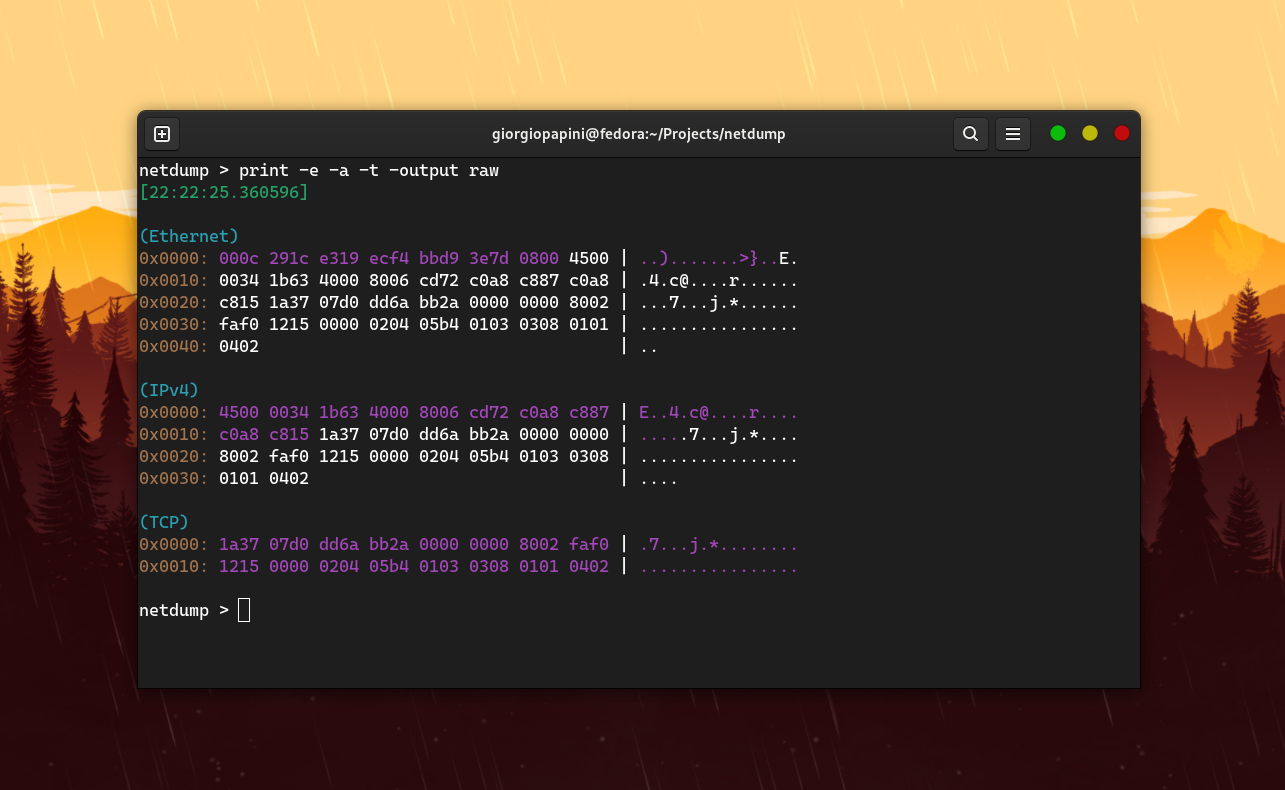
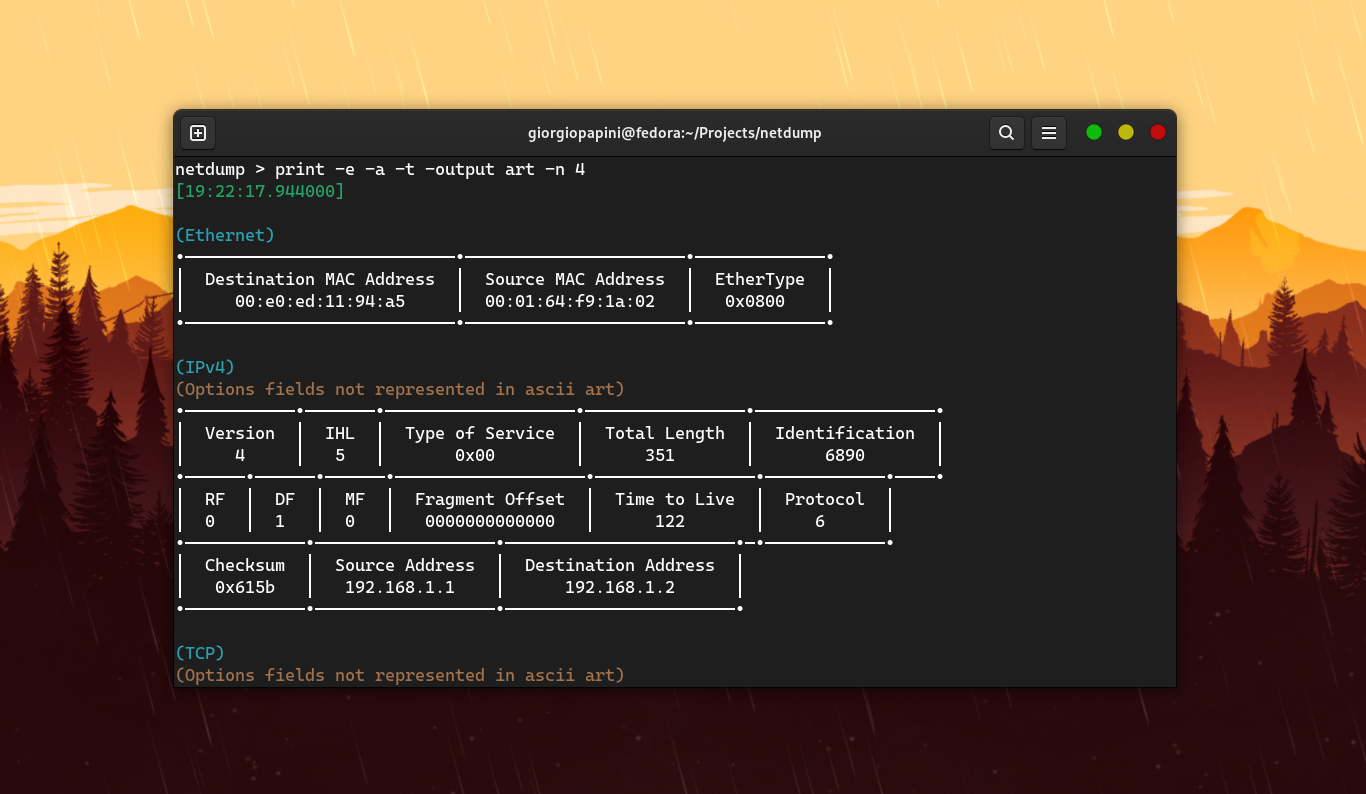
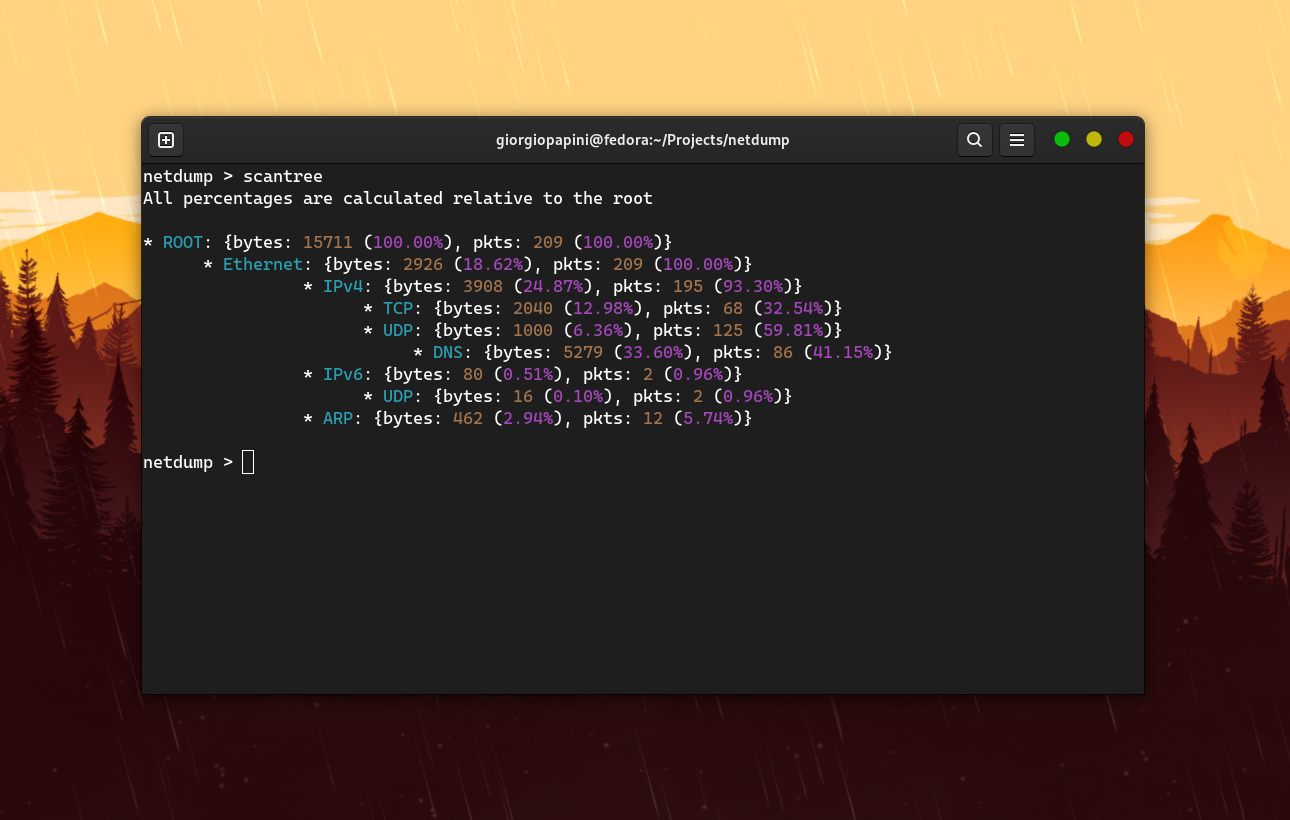
Based on libpcap and completely built in C, netdump is a free and open-source network protocol analizer. netdump is designed to cater to users with varying levels of expertise and backgrounds. It achieves this by providing an easy-to-use CLI tool, along with a straightforward netdump-devel package. This setup is ideal for users who need to analyze industry-specific protocols, those interested in building their own dissector implementations, and also for people who simply want to scan a network or a .pcap file.
Disclaimer: netdump is entirely independent and unrelated to any other programs named "netdump" or similar.
At this time, support is limited to GNU Make only.
Check the default Makefile variable configuration using make show-config.
If your system stores those files in different locations, you can run make install VARIABLE_NAME='/path/'
Remember that these commands might need to be run with elevated privileges.
Netdump can be executed on Unix-like operating systems conforming to the POSIX standard. It can be installed manually using make, or installed by using a package manager (RPM on Fedora, CentOS and RHEL). You can install netdump in several ways depending on your goal:
- Clone the repo and compile the program using
make. - Clone the repo and install the program inside
/usr/local/binby runningmake install. - Install the program inside
/usr/binby using a package manager.
There are several methods to execute netdump based upon the installation process you chose:
- Execute
./netdumpif you just compiled the program usingmake. - Execute
/usr/local/bin/netdump(ornetdump) if you installed the program usingmake install. - Execute
netdumpif you installed it using a package manager.
Some features, such as real-time network scanning, require netdump to be run with elevated privileges.
You can remove netdump from your system in several ways:
- Execute
make removeif you previously installed netdump usingmake install. - Uninstall netdump using the package manager you used to install it.
Remember that these commands might need to be run with elevated privileges.
The general command format is this netdump <command> -<arg_1> <value_1> ... -<arg_n> <value_n>.
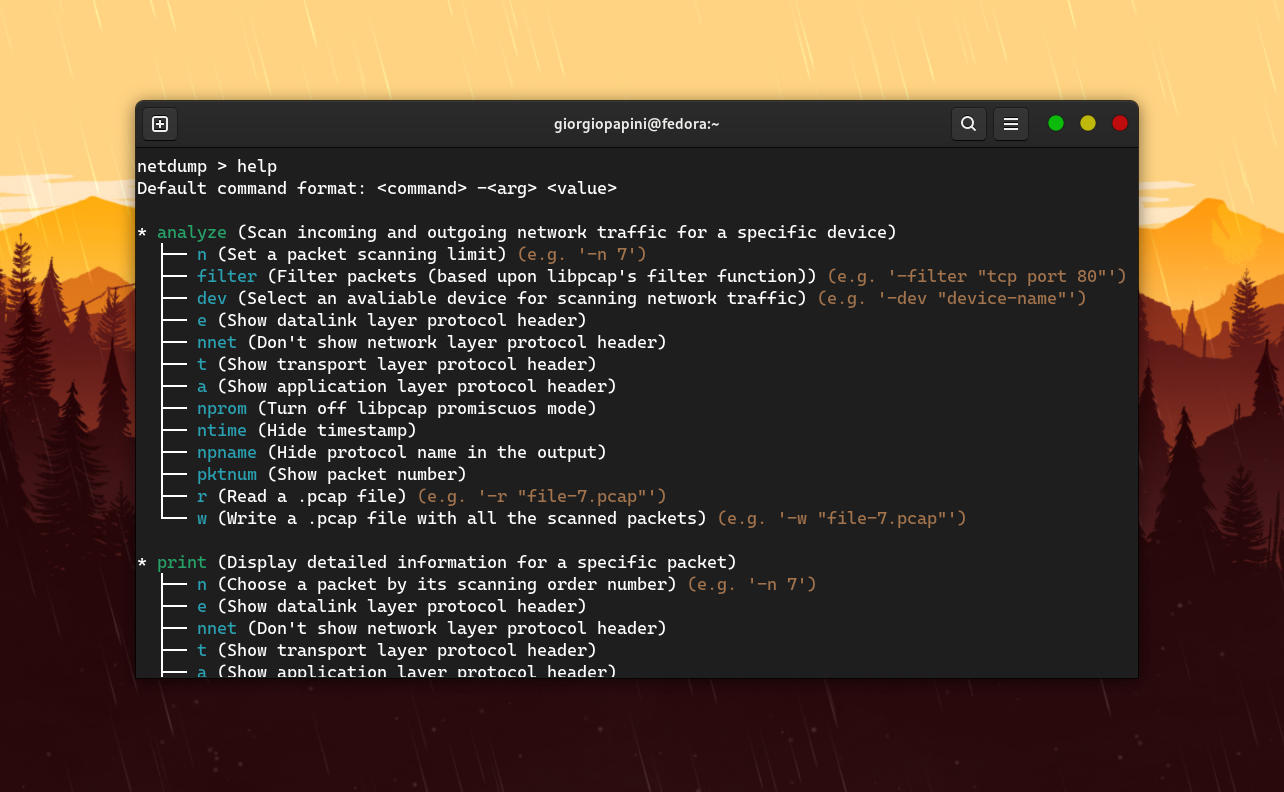
Run the help command from anywhere inside the CLI tool to get a small doc about every command and its supported arguments.
Strings should be enclosed in "" to prevent netdump from misinterpreting uppercase letters, -, and other symbols.
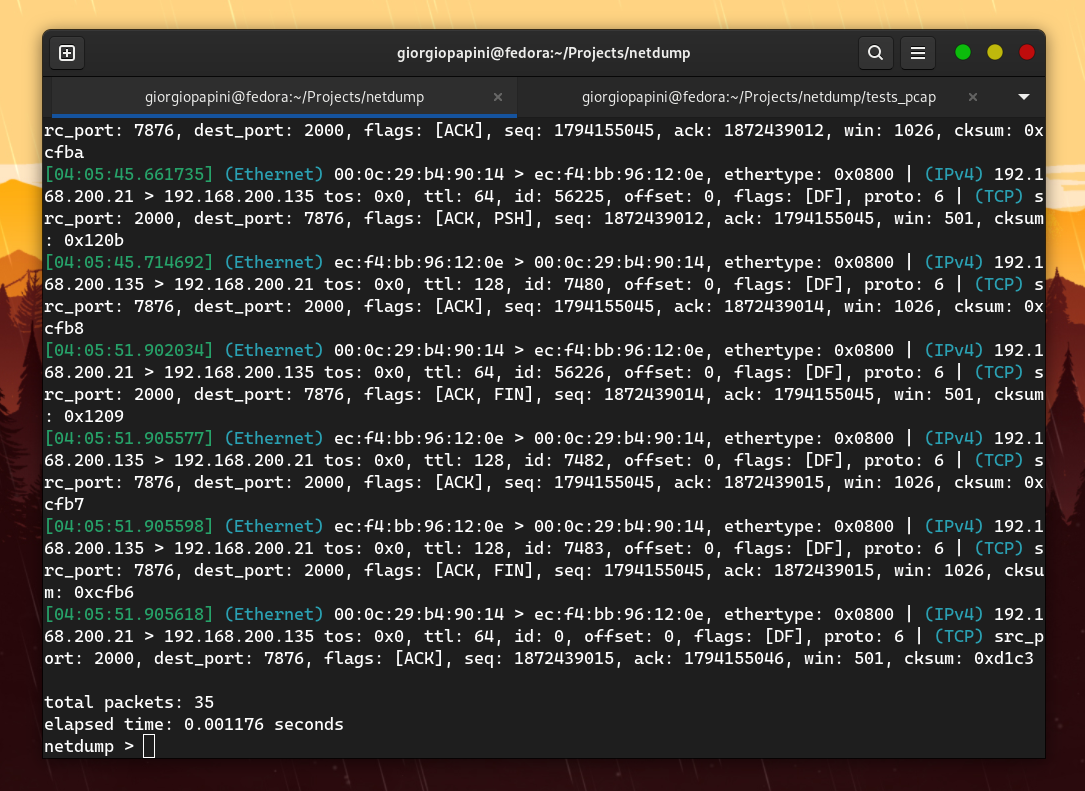
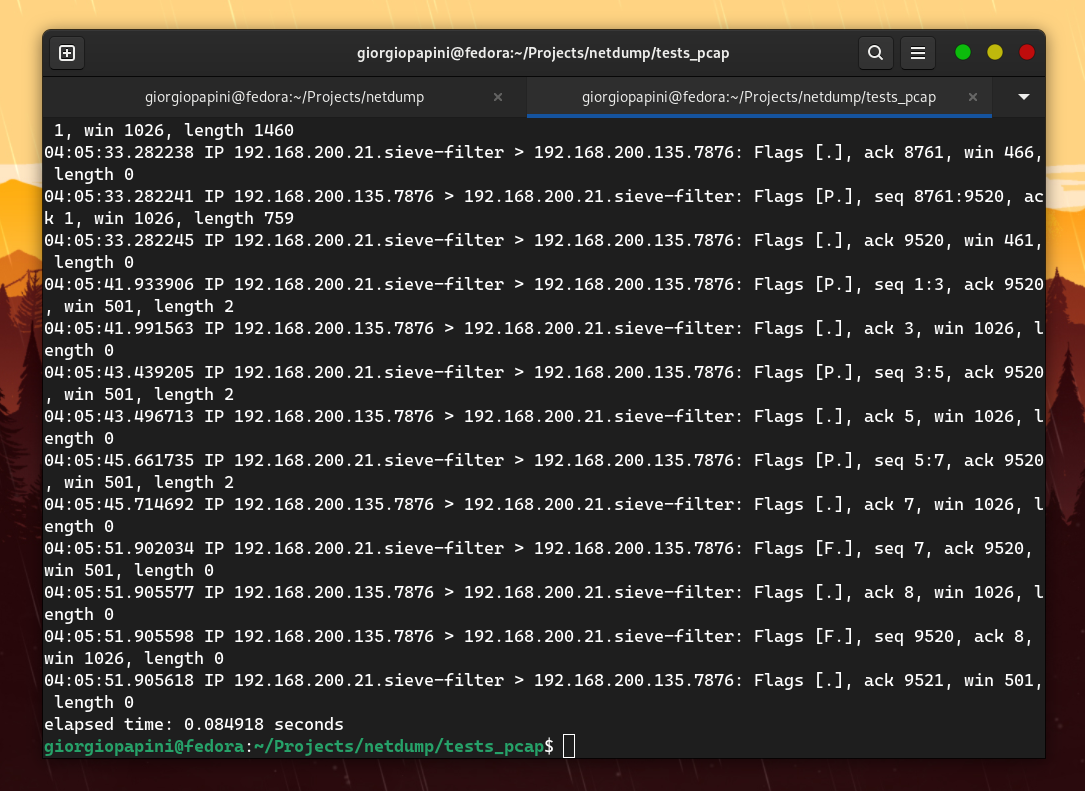
This command is used to scan incoming and outgoing network traffic for a selected device. The following table lists the allowed arguments for this command.
| Arg | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
-n |
int | Set a packet scanning limit |
-filter |
str | Filter packets (based upon libpcap's filter function) |
-dev |
str | Select an avaliable device for scanning network traffic |
-e |
none | Show datalink layer protocol header |
-nnet |
none | Don't show network layer protocol header |
-t |
none | Show transport layer protocol header |
-a |
none | Show application layer protocol header |
-nprom |
none | Turn off libpcap promiscuos mode |
-ntime |
none | Hide timestamp |
-npname |
none | Hide protocol name in the output |
-pktnum |
none | Show packet number |
-r |
str | Read a .pcap file |
-w |
str | Write a .pcap file with all the scanned packets |
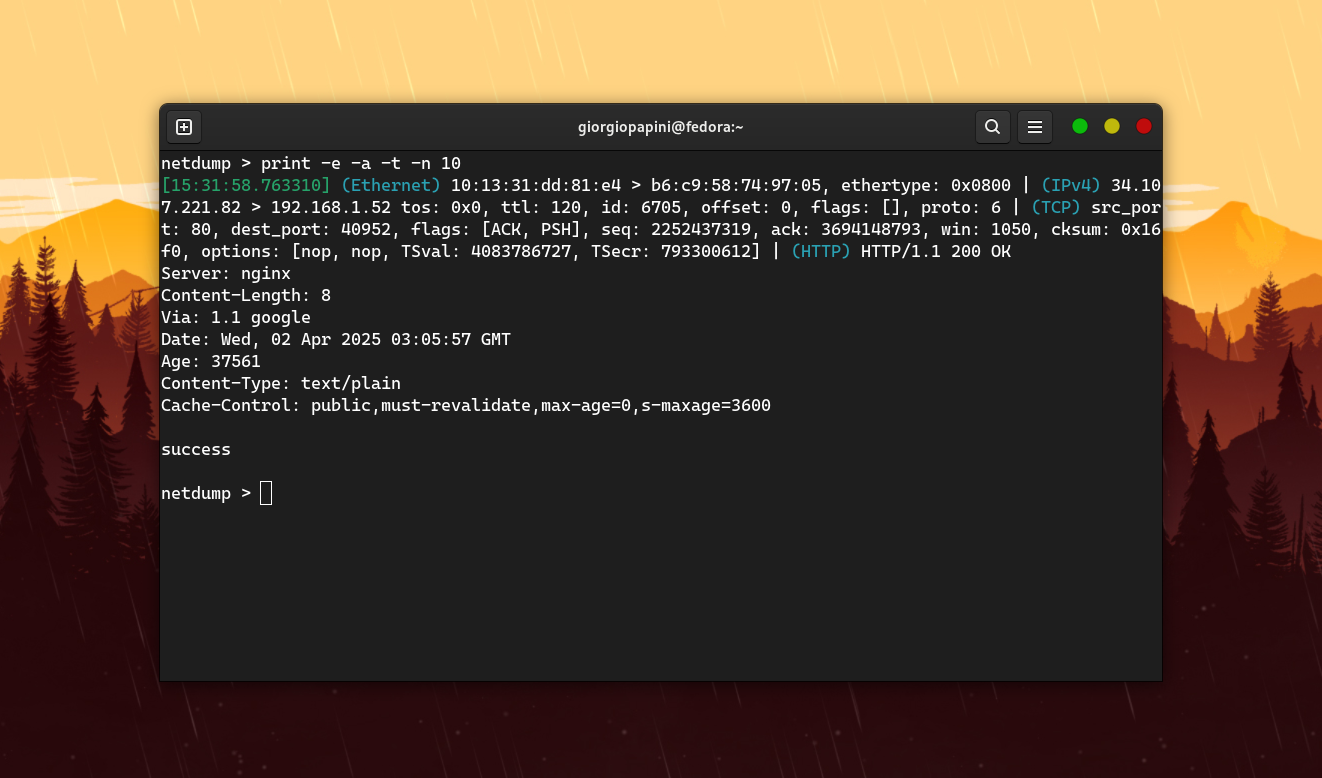
This command is used to display detailed informations for a specific packet. The following table lists the allowed arguments for this command.
| Arg | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
-n |
int | Choose a packet by its scanning order number |
-e |
none | Show datalink layer protocol header |
-nnet |
none | Don't show network layer protocol header |
-t |
none | Show transport layer protocol header |
-a |
none | Show application layer protocol header |
-ntime |
none | Hide timestamp |
-npname |
none | Hide protocol name in the output |
-output |
(std, raw, art) | Select output format |
-pktnum |
none | Show packet number |
This command is used to manage custom dissectors. The following table lists the allowed arguments for this command.
| Arg | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
-list |
none | Show custom dissectors list |
-add |
str | Add custom dissector |
-on |
str | Activate custom dissector (empty = all) |
-off |
str | Deactivate custom dissector (empty = all) |
This command is used to retrieve a list of supported protocols. The following table lists the allowed arguments for this command.
| Arg | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
-tables |
none | Show supported protocol tables |
-from |
str | Show supported protocols from the specified tables |
-search |
int | Looks up a protocol by number. If 'from' is set, the search is limited to the specified tables |
This command is used to save scanned packets to a .pcap file. The following table lists the allowed arguments for this command.
| Arg | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
-to |
str | Specify the destination file for saving scanned data |
-n |
int | Choose the single packet to save by its scanning order number |
This command is used to obtain the hierarchical structures of the protocols currently being scanned.
This command is used to reset stored packets.
This command is used to retrieve a list of all available devices for scanning.
This command is used to clear screen output.
This command is used to exit program.
To create a custom dissector, refer to the netdump-devel repo (https://github.com/giorgiopapini/netdump-devel).
The netdump-devel package allows you to compile your custom dissector as a shared library. Once compiled as a shared lib, you can add it to netdump using the following command:
netdump dissectors -add "path-to-dissector.so" (.so if your system is Linux or *BSD. Otherwise, adjust it according to your system).
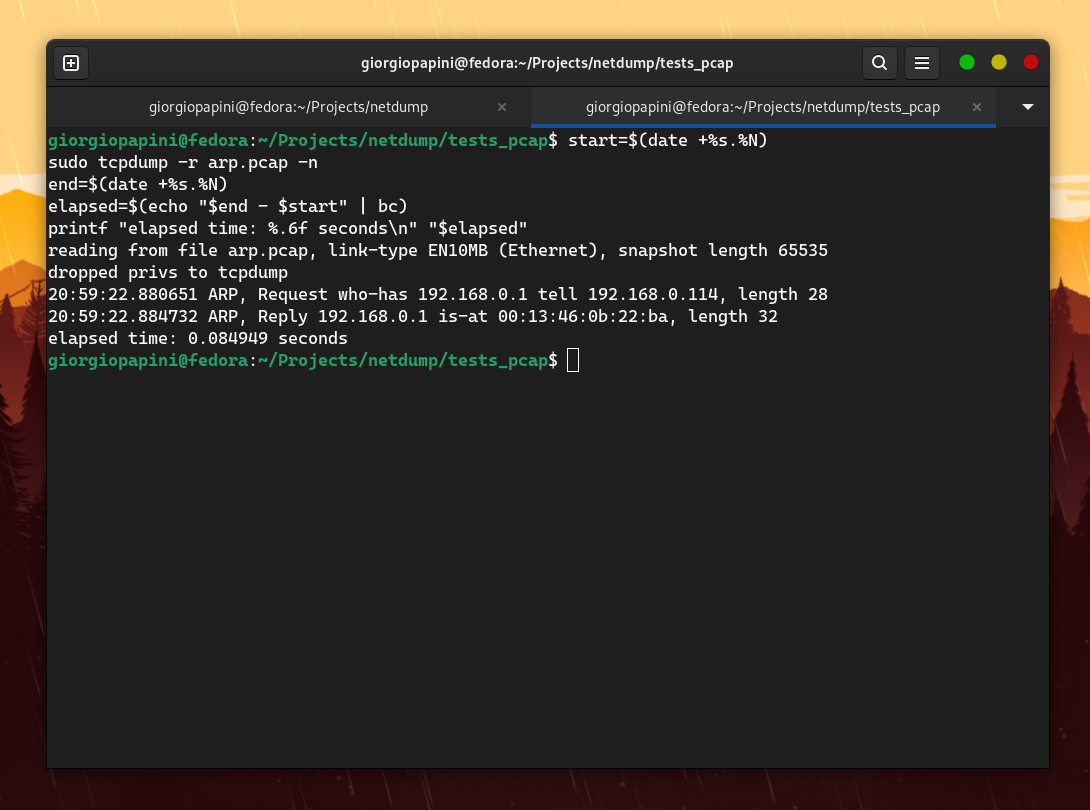
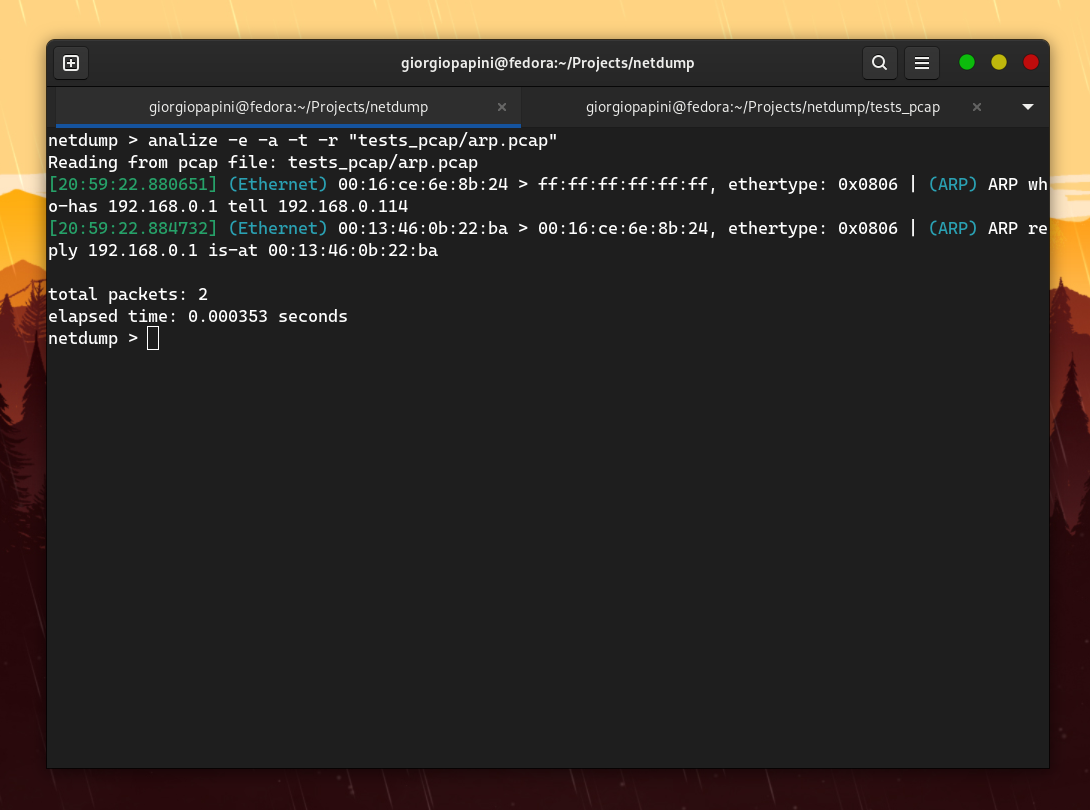
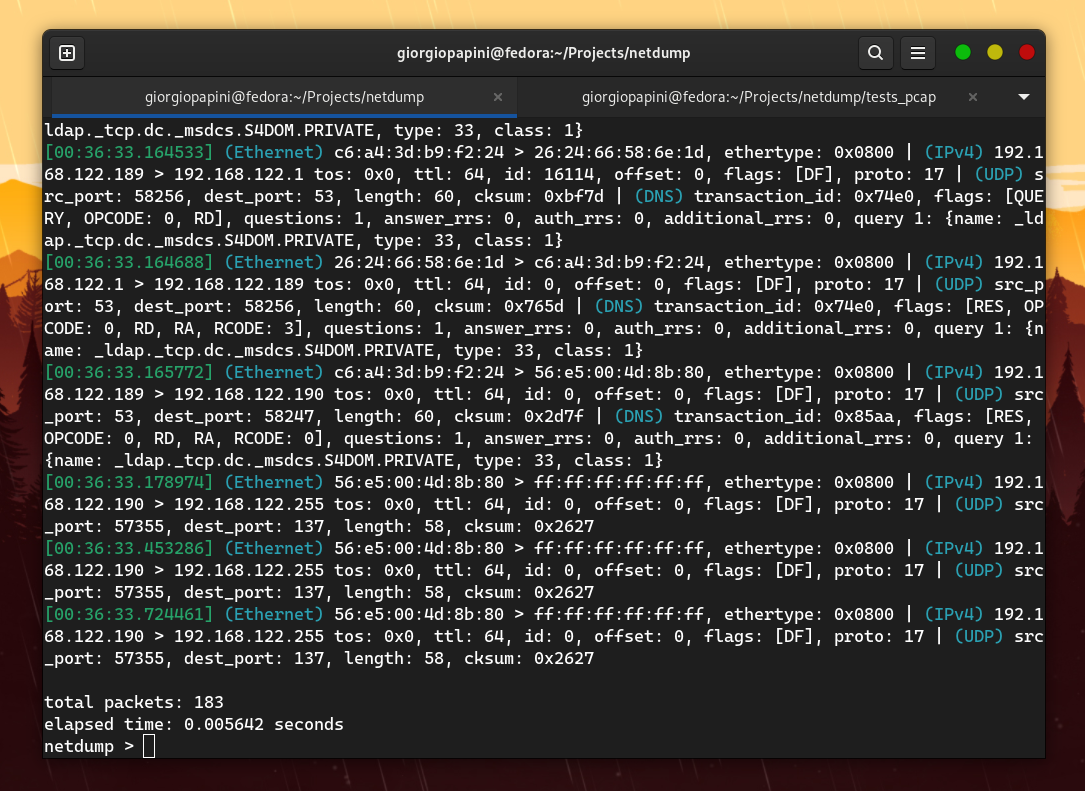
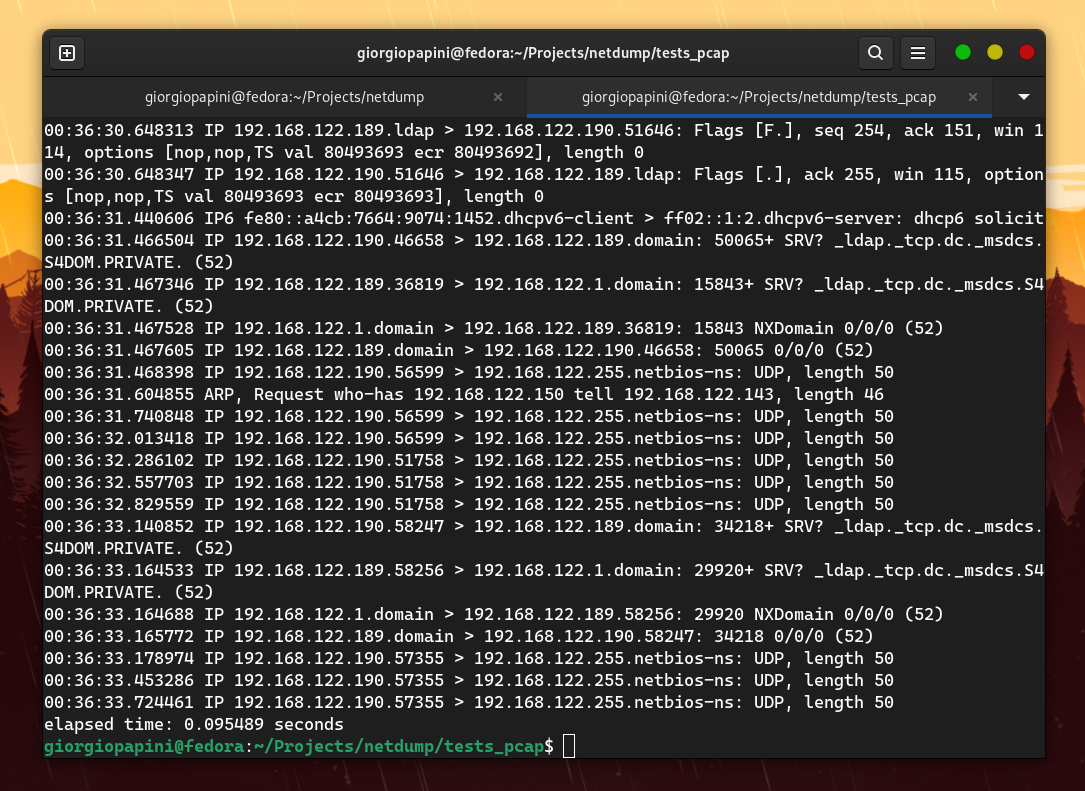
I compared netdump with tcpdump in terms of speed, and these are the results I obtained (I disabled hostname resolution in tcpdump to make it faster). The following are some of the comparisons I made. For others, check the assets folder.
However, the problem is that netdump does not support the extensive range of protocols that tcpdump does. Therefore, I focused on measuring TCP packets by adding "dummy" protocol handlers to the proto_tables that netdump queries while dissecting a TCP packet. The result is still amazing. Watch the video
Contributions are welcome and really appreciated. To increase the popularity and usefulness of netdump, support for additional protocols is highly encouraged. Contributions of new protocol dissectors are especially welcome and appreciated, though all types of contributions are valued. The following is a quick start guide explaining how to practically contribute to the project:
Click the fork button to create your own fork of the project
git clone git@github.com:YOUR-USERNAME/netdump.git
cd netdumpgit checkout -b your-branch-nameMake your improvements or bug fixes than commit and push.
git add .
git commit -m "Describe your changes precisely"
git push origin your-branch-nameGo to the original repository and open a pull request from your fork.