Install Guide | Documentation | Examples | Paper | Leaderboard | Baselines
⚠️ This branch contains the beta of version 1.2.0It contains the latest changes planned for the release of DeepOBS 1.2.0, including support for PyTorch. Not all features are implemented and most notably we currently don't provide baselines for this version. We continuously make changes to this version, so things can break if you update. If you want a more stable preview, check out our pre-releases.
DeepOBS is a python framework for automatically benchmarking deep learning optimizers. Its goal is to drastically simplify, automate and improve the evaluation of deep learning optimizers.
It can:
- evaluate the performance of new optimizers on more than 25 real-world test problems, such as training Residual Networks for image classification or LSTMs for character prediction.
- automatically compare the results with realistic baselines (without having to run them again!)
DeepOBS automates several steps when benchmarking deep learning optimizers:
- Downloading and preparing data sets.
- Setting up test problems consisting of contemporary data sets and realistic deep learning architectures.
- Running the optimizers on multiple test problems and logging relevant metrics.
- Comparing your results to the newest baseline results of other optimizers.
- Reporting and visualizing the results of the optimizer benchmark as ready-to-include
.texfiles.
The code for the current implementation working with TensorFlow can be found on Github. A PyTorch version is currently developed (see News section below).
The documentation of the beta version is available on readthedocs.
The paper describing DeepOBS has been accepted for ICLR 2019.
If you find any bugs in DeepOBS, or find it hard to use, please let us know. We are always interested in feedback and ways to improve DeepOBS.
We are currently working on a new and improved version of DeepOBS, version 1.2.0. It will support PyTorch in addition to TensorFlow, has an easier interface, and many bugs ironed out. You can find the latest version of it in this branch.
A pre-release is currently available and a full release will be available in the coming weeks.
Many thanks to Aaron Bahde for spearheading the development of DeepOBS 1.2.0.
You can install DeepOBS by simply running
pip install deepobs
This will install the latest proper release (currently 1.1.2).
You can also get the latest stable (pre-release) by running
pip install 'git+https://github.com/fsschneider/DeepOBS.git@v1.2.0-beta0#egg=DeepOBS'
to get the preview of DeepOBS 1.2.0. Note, this version also includes support for PyTorch.
If you want to create a local and modifiable version of DeepOBS, you can do this directly from this repo via
pip install -e 'git+https://github.com/fsschneider/DeepOBS.git@develop#egg=deepobs'
which would give you the latest development version of DeepOBS.
If you use TensorFlow, you have to download the data sets for the test problems. This can be done by simply running the Prepare Data script:
deepobs_prepare_data.sh
The easiest way to use DeepOBS with your new optimizer is to write a run script for it. You will only need to write 6 lines of code, specifying which optimizer you want to use and what hyperparameters it has. That is all.
Here is an example using the momentum optimizer in PyTorch:
"""Example run script for PyTorch and the momentum optimizer."""
from torch.optim import SGD
from deepobs import pytorch as pt
optimizer_class = SGD
hyperparams = {"lr": {"type": float},
"momentum": {"type": float, "default": 0.99},
"nesterov": {"type": bool, "default": False}}
runner = pt.runners.StandardRunner(optimizer_class, hyperparams)
runner.run(testproblem='quadratic_deep', hyperparams={'lr': 1e-2}, num_epochs=10)Now you are ready to run your optimzier on all test problems of DeepOBS, for example to run it on a simple noisy quadratic problem try
python example_runner.py quadratic_deep --learning_rate 1e-2
The next steps in the tutorial and a full recommended step-by-step protocol for benchmarking deep learning optimizers can be found in the documentation.
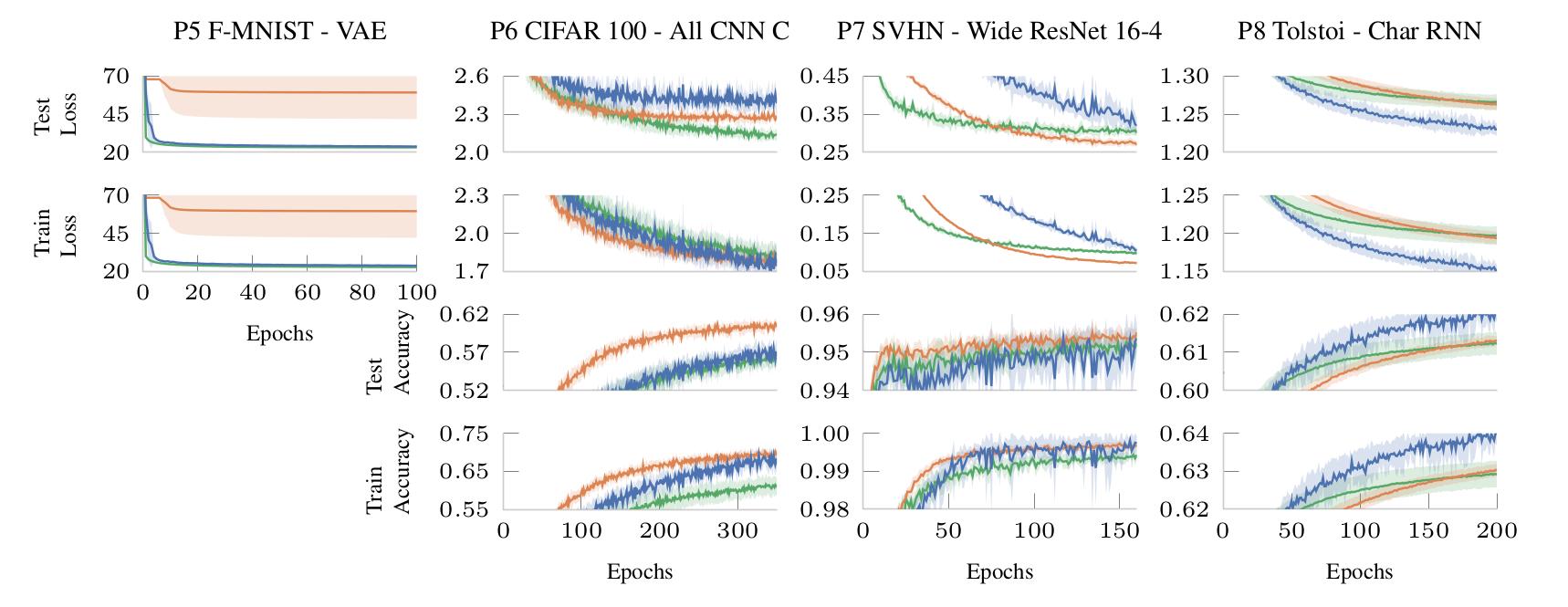
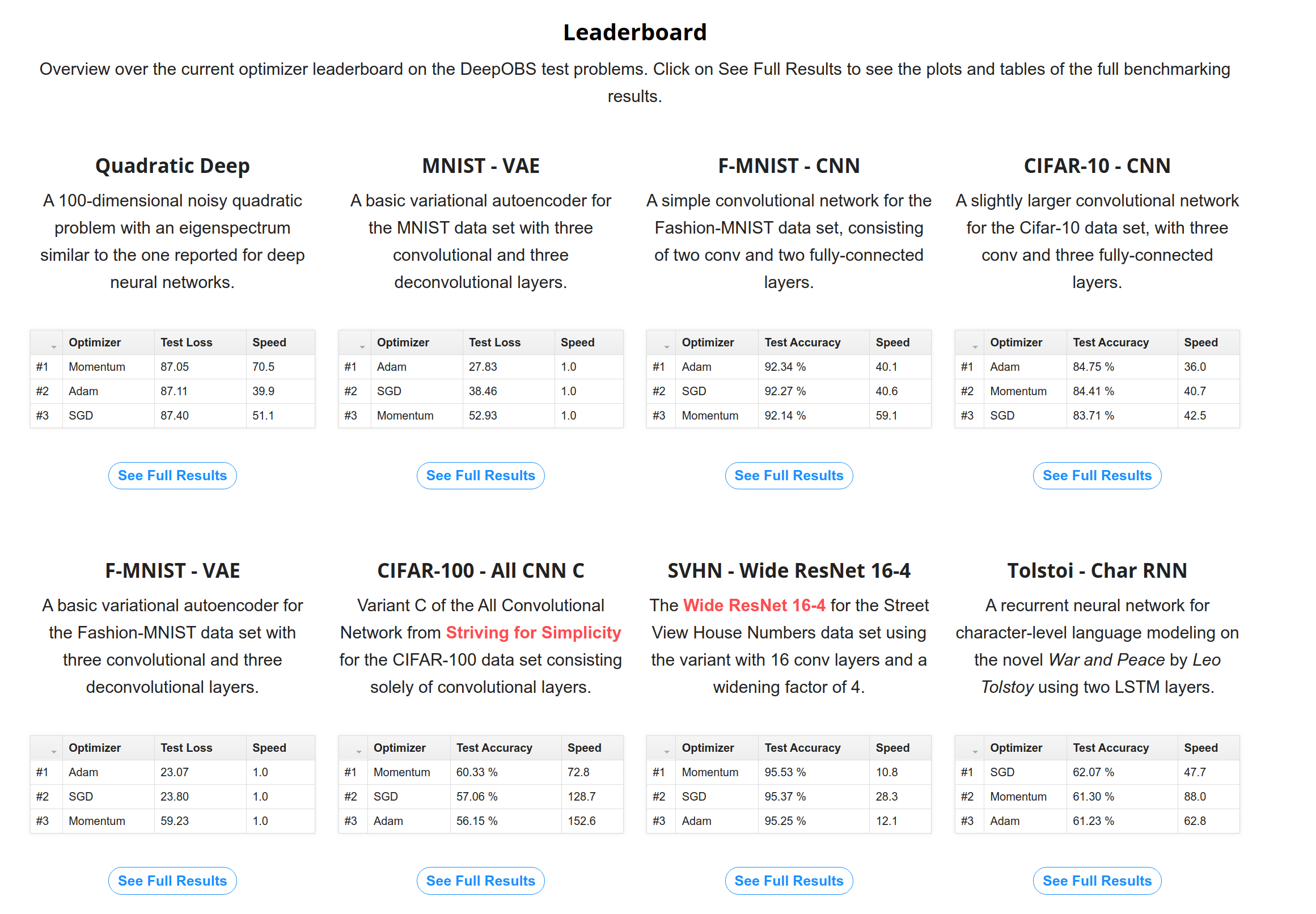
We keep an online leaderboard of our benchmark sets. All entries in the leaderboard are automatically available for comparisons via our baselines.
ℹ️ If you have an optimizer that you believe should be in the leaderboard let us know!
ℹ️ We are always looking for additional support. We hope that DeepOBS is the start of a community effort to improve the quality of deep learning optimizer benchmarks. If you find any bugs, stumbling blocks or missing interesting test problems feel free to contact us, create an issue or add a pull request. If you created a new optimizer and tested it with DeepOBS please notify us, so that we can include your results in the leaderboard and our baselines.
Many people have contributed to DeepOBS and were essential during its development. The list is roughly in chronological order and does not represent the amount of effort put in.
If you use DeepOBS in your work, we would appreciate a reference to our ICLR paper:
BibTeX entry:
@InProceedings{schneider2018deepobs,
Title = {Deep{OBS}: A Deep Learning Optimizer Benchmark Suite},
Author = {Frank Schneider and Lukas Balles and Philipp Hennig},
Booktitle = {International Conference on Learning Representations},
Year = {2019},
Url = {https://openreview.net/forum?id=rJg6ssC5Y7}
}