dat:
- tries to be fun and weird.
- let's you interact with nostr exposing the protocol instead of abstracting it.
- tries to be minimalistic, flexible and powerful.
- doesn't do it all yet, soon™.
- is not for everyone.
- keeps changing in breaking ways.
- has bugs and bad decisions.
- is a learning tool.
- is written in vanilla js, html and css.
- is public domain, free and open-source.
- you can do whatever the fuck you want with it.
source code:
nostr:
depends on:
dev deployment:
stable deployment:
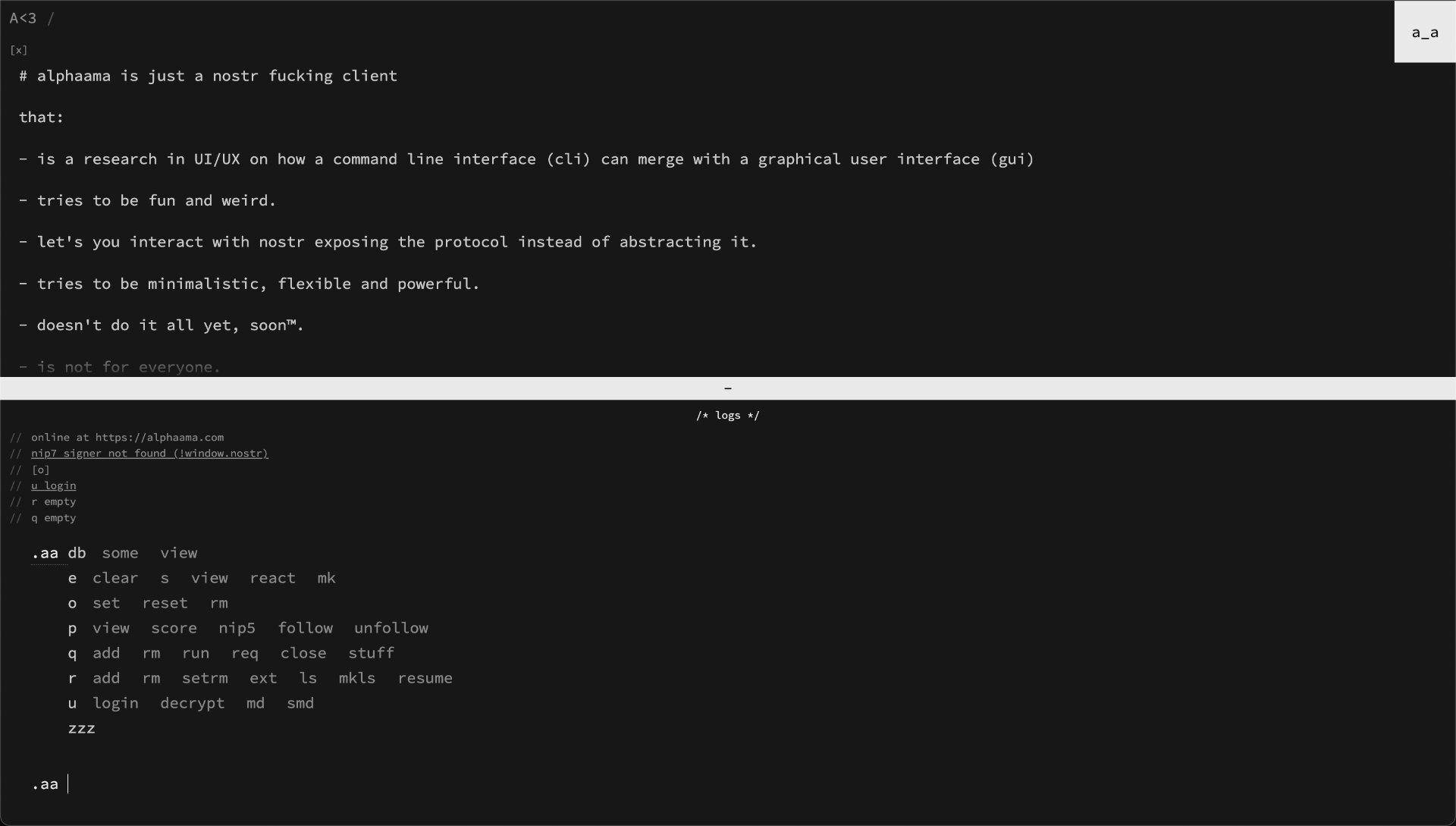
- alphaama doesn't do much on it's own, it takes commands given by the user and executes them
- it has a single input field for interaction like a Command Line Interface (CLI) wrapped in a Graphical User Interface (GUI) that can be interacted with
- commands are given by prefixing the input with a value (default is ".aa")
- if no command prefix is found at the start of the input, a kind:1 draft is created (if logged in)
- can display all event kinds using a single threaded generic event view
- can be used to create any event type and autofills the missing required fields (raw JSON)
- you can use multiple tabs with different requests
- to reset everything, type:
.aa zzz
- to set an option, type:
.aa o setfollowed bykeyandvalue - to reset options, type
.aa o resetfollowed by akey, if left empty resets all to defaults
example of how to switch theme (team) from dark to light and then setting trust to 4 so it loads stuff from your fellas:
https://v.nostr.build/w5smDlU8vMRQ1r4N.mp4
- relays are kept locally and are separate from your published relays
- relays can be added to sets
- default relay set for reading is "read"
- default relay set for writing is "write"
- default relay set for disabled is "off"
- relay sets (relset) can be used in requests or to create a list (kind:10002)
- depending from where relays were imported, sets are added automatically (ext, k3, k10002, hint)
to add a relay, type: .aa r add <url> <set_1> <set_2>
urlis a valid full URLsetis a relay set (a-z_0-9)- multiple sets can be added
- example command for adding multiple relays:
.aa r add wss://relay1.com read write, wss://relay2.org read, wss://relay3.net write
- you can use alphaama without logging in because you can read from Nostr without having to sign anything
- to sign notes, you need a signer already configured with a key (NIP7 enabled browser extension)
- make sure your signer extension is active on the current tab
- you have the option to set a mode on login, either easy or hard
- easy mode adds useful filter queries
- hard mode prevents any external connections
example for easy login type: .aa u login easy
https://v.nostr.build/OXw18vj2M8h1Mei0.mp4
to receive events from relays, you send them requests containing filters
- relays will start sending events one by one that match the request filters
- relays will keep relaying new events as they receive them until the request is closed
to send a request, type: .aa q req <relset> <JSON_filter>
relsetis either a single relay URL or a relay set idJSON_filteris a single Nostr request filter in raw JSON- you can add an extra value in the filter to close the request after all stored events have been sent:
"eose":"close"
the following variables can be used in filters:
"n_number": converts to a timestamp fromnumberof days ago. ex: "n_1" converts to 1 day ago"d_date_string": converts to a timestamp ofdate_string. ex: "d_2024-08-21""now": converts to the timestamp of now"u": converts to your pubkey (if logged in)"k3": converts to a list of pubkeys you follow (if logged in)
you can store requests so it's easier to run them
to store a request, type: .aa q add <fid> <JSON_filter>
fidis a filter identifier with the following allowed characters:a-z_0-9JSON_filteris explained above
to run a query, type: .aa q run <fid> <relset>
fidis explained aboverelsetis a single relay url or relay set; by leaving it empty, it defaults to yourreadrelay set
to close a request, type: .aa q close <fid>
- if
fidis omitted all opened requests will be closed instead
example of running the request a
https://v.nostr.build/hzQufBzjStD8L8j6.mp4
TIP => you can run multiple requests at once, separating the values with a comma (you can do this on other commands as well)
example: .aa q run f, u, n
TIP => processing a large amount of follow lists can take some time as it builds a trust score (if logged in), for example, if you are in easy mode and enter .aa q run b, then go make a coffee and let it sit for a bit..
soon™
the WoT score system used here is very primitive and consists of 2 integer values:
- a value that you can set manually (default is 0, 9 for the logged-in pubkey and 5 for it's follows) and has influence in displaying content (renders image, video, etc). this value relates to the
trustoption - a generated value from the number of followers a pubkey has that you also follow. this is only used as a visual hint
soon™
soon™
soon™