Stop just unlocking the UI. Start proving the identity.
Typical biometric plugins (such as local_auth) return only a boolean indicating whether authentication succeeded.
biometric_signature goes significantly further by generating a verifiable cryptographic signature using a private key stored in hardware (Secure Enclave / StrongBox).
Even if an attacker bypasses or hooks biometric APIs, your backend will still reject the request because the attacker cannot forge a hardware-backed signature without the private key.
- Cryptographic Proof Of Identity: Hardware-backed RSA (Android) or ECDSA (all platforms) signatures that your backend can independently verify.
- Decryption Support:
- RSA: RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding (Android native, iOS/macOS via wrapped software key)
- EC: ECIES (
eciesEncryptionStandardX963SHA256AESGCM)
- Hardware Security: Uses Secure Enclave (iOS/macOS) and Keystore/StrongBox (Android).
- Hybrid Architectures:
- Android Hybrid EC: Hardware EC signing + software ECIES decryption. Software EC private key is AES-wrapped using a Keystore/StrongBox AES-256 master key that requires biometric authentication for every unwrap.
- iOS/macOS Hybrid RSA: Software RSA key for both signing and decryption, wrapped using ECIES with Secure Enclave EC public key. Hardware EC is only used for wrapping/unwrapping.
- Key Invalidation: Keys can be bound to biometric enrollment state (fingerprint/Face ID changes).
- Device Credentials: Optional PIN/Pattern/Password fallback on Android.
The plugin supports different operational modes depending on the platform:
Android supports three key modes:
-
RSA Mode (
SignatureType.rsa):- Hardware-backed RSA-2048 signing (Keystore/StrongBox)
- Optional RSA decryption (PKCS#1 padding)
- Private key never leaves secure hardware
-
EC Signing-Only (
SignatureType.ecdsa,enableDecryption: false):- Hardware-backed P-256 key in Keystore/StrongBox
- ECDSA signing only
- No decryption support
-
Hybrid EC Mode (
SignatureType.ecdsa,enableDecryption: true):- Hardware EC key for signing
- Software EC key for ECIES decryption
- Software EC private key encrypted using AES-256 GCM master key (Keystore/StrongBox)
- Per-operation biometric authentication required for decryption
Apple platforms support two key modes (Secure Enclave only supports EC keys natively):
-
EC Mode (
SignatureType.ecdsa):- Hardware-backed P-256 key in Secure Enclave
- ECDSA signing
- Native ECIES decryption (
eciesEncryptionStandardX963SHA256AESGCM) - Single key for both operations
-
RSA Mode (
SignatureType.rsa) - Hybrid Architecture:- Software RSA-2048 key for both signing and decryption
- RSA private key wrapped using ECIES with Secure Enclave EC public key
- Hardware EC key is only used for wrapping/unwrapping the RSA key
- Wrapped RSA key stored in Keychain as
kSecClassGenericPassword - Per-operation biometric authentication required to unwrap RSA key
-
Enrollment
User authenticates → hardware generates a signing key.
Hybrid modes additionally generate a software decryption key, which is then encrypted using secure hardware.
-
Signing
Biometric prompt is shown
Hardware unlocks the signing key, and a verifiable signature is produced.
-
Decryption
A biometric prompt is shown again.
Hybrid modes unwrap the software private key using hardware-protected AES-GCM, then decrypt the payload.
-
Backend Verification
The backend verifies signatures using the registered public key.
Verification must not be performed on the client.
Perform verification on the server. Below are reference implementations.
const crypto = require('crypto');
function verifySignature(publicKeyPem, payload, signatureBase64) {
const verify = crypto.createVerify('SHA256');
verify.update(payload); // The original string you sent to the plugin
verify.end();
// Returns true if valid
return verify.verify(publicKeyPem, Buffer.from(signatureBase64, 'base64'));
}from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import padding
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import serialization
import base64
def verify_signature(public_key_pem_str, payload_str, signature_base64_str):
public_key = serialization.load_pem_public_key(public_key_pem_str.encode())
signature = base64.b64decode(signature_base64_str)
try:
# Assuming RSA (For EC, use ec.ECDSA(hashes.SHA256()))
public_key.verify(
signature,
payload_str.encode(),
padding.PKCS1v15(),
hashes.SHA256()
)
return True
except Exception:
return Falseimport (
"crypto"
"crypto/rsa"
"crypto/sha256"
"crypto/x509"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/pem"
"fmt"
)
func verify(pubPemStr, payload, sigBase64 string) error {
block, _ := pem.Decode([]byte(pubPemStr))
pub, _ := x509.ParsePKIXPublicKey(block.Bytes)
rsaPub := pub.(*rsa.PublicKey)
hashed := sha256.Sum256([]byte(payload))
sig, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(sigBase64)
return rsa.VerifyPKCS1v15(rsaPub, crypto.SHA256, hashed[:], sig)
}To get started with Biometric Signature, follow these steps:
- Add the package to your project by including it in your
pubspec.yamlfile:
dependencies:
biometric_signature: ^9.0.1| Android | iOS | macOS | Windows | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Support | SDK 24+ | 13.0+ | 10.15+ | 10+ |
This plugin works with Touch ID or Face ID. To use Face ID in available devices, you need to add:
<dict>
<key>NSFaceIDUsageDescription</key>
<string>This app is using FaceID for authentication</string>
</dict>to your Info.plist file.
This plugin requires the use of a FragmentActivity instead of Activity. Update your MainActivity.kt to extend FlutterFragmentActivity:
import io.flutter.embedding.android.FlutterFragmentActivity
class MainActivity : FlutterFragmentActivity() {
}Update your project's AndroidManifest.xml file to include the
USE_BIOMETRIC permission.
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.app">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.USE_BIOMETRIC" />
</manifest>This plugin works with Touch ID on supported Macs. To use Touch ID, you need to:
- Add the required entitlements to your macOS app.
Open your macOS project's entitlements file (typically located at macos/Runner/DebugProfile.entitlements and macos/Runner/Release.entitlements) and ensure it includes:
<key>com.apple.security.device.usb</key>
<false/>
<key>com.apple.security.device.bluetooth</key>
<false/>
<key>keychain-access-groups</key>
<array>
<string>$(AppIdentifierPrefix)com.yourdomain.yourapp</string>
</array>Replace com.yourdomain.yourapp with your actual bundle identifier.
- Ensure CocoaPods is properly configured in your
macos/Podfile. The plugin requires macOS 10.15 or later:
platform :osx, '10.15'This plugin uses Windows Hello (Windows.Security.Credentials.KeyCredentialManager) for biometric authentication on Windows 10 and later. Keys are typically backed by the device's TPM (Trusted Platform Module) for hardware-grade security.
Platform Limitations:
- Key Type: Windows Hello only supports RSA-2048 keys (ECDSA requests are automatically promoted to RSA).
- Authentication: Windows Hello always authenticates during key creation (
enforceBiometricis effectively alwaystrue). - Configuration:
setInvalidatedByBiometricEnrollmentanduseDeviceCredentialsarguments are ignored on this platform. - Decryption: Not supported. The Windows Hello API is designed primarily for authentication (signing) and does not expose general decryption capabilities for these keys.
No additional configuration is required. The plugin will automatically use Windows Hello when available.
- Import the package in your Dart code:
import 'package:biometric_signature/biometric_signature.dart';- Initialize the Biometric Signature instance:
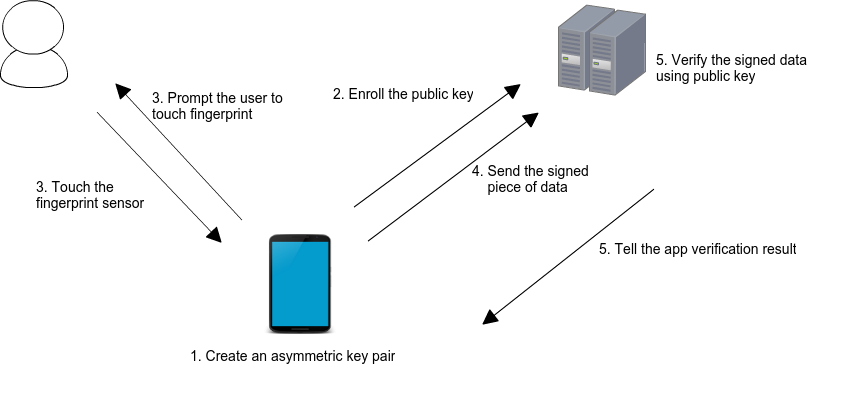
final biometricSignature = BiometricSignature();This package simplifies server authentication using biometrics. The following image from Android Developers Blog illustrates the basic use case:
When a user enrolls in biometrics, a key pair is generated. The private key is securely stored on the device, while the public key is sent to a server for registration. To authenticate, the user is prompted to use their biometrics, unlocking the private key. A cryptographic signature is then generated and sent to the server for verification. If the server successfully verifies the signature, it returns an appropriate response, authorizing the user.
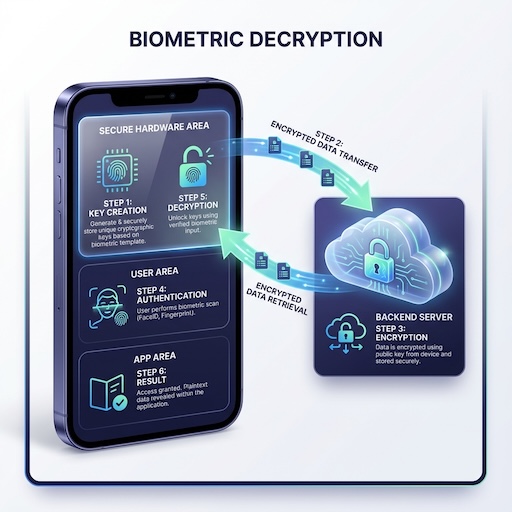
The plugin also supports secure decryption, ensuring that sensitive data transmitted from the server can only be accessed by the authenticated user on their specific device.
- Key Creation: The device generates a key pair (EC or RSA) in secure hardware.
- Registration: The public key is sent to the backend server.
- Encryption: The server encrypts the sensitive payload using the public key.
- Authentication: The encrypted payload is sent to the device. The user must authenticate biometrically to proceed.
- Decryption: Once authenticated, the secure hardware uses the private key to decrypt the payload, revealing the plaintext data to the app.
This class provides methods to manage and utilize biometric authentication for secure server interactions. It supports both Android and iOS platforms.
Generates a new key pair (RSA 2048 or EC) for biometric authentication. The private key is securely stored on the device.
-
Parameters:
config:CreateKeysConfigwith platform options (see below)keyFormat: Output format (KeyFormat.base64,pem,hex)promptMessage: Custom authentication prompt message
-
Returns:
Future<KeyCreationResult>.publicKey: The formatted public key string (Base64 or PEM).code:BiometricErrorcode (e.g.,success,userCanceled).error: Descriptive error message.
| Option | Platforms | Description |
|---|---|---|
signatureType |
Android/iOS/macOS | SignatureType.rsa or SignatureType.ecdsa |
enforceBiometric |
Android/iOS/macOS | Require biometric during key creation |
setInvalidatedByBiometricEnrollment |
Android/iOS/macOS | Invalidate key on biometric changes |
useDeviceCredentials |
Android/iOS/macOS | Allow PIN/passcode fallback |
enableDecryption |
Android | Enable decryption capability |
promptSubtitle |
Android | Subtitle for biometric prompt |
promptDescription |
Android | Description for biometric prompt |
cancelButtonText |
Android | Cancel button text |
final result = await biometricSignature.createKeys(
keyFormat: KeyFormat.pem,
promptMessage: 'Authenticate to create keys',
config: CreateKeysConfig(
signatureType: SignatureType.rsa,
enforceBiometric: true,
setInvalidatedByBiometricEnrollment: true,
useDeviceCredentials: false,
enableDecryption: true, // Android only
),
);
if (result.code == BiometricError.success) {
print('Public Key: ${result.publicKey}');
}Prompts the user for biometric authentication and generates a cryptographic signature.
- Parameters:
payload: The data to signconfig:CreateSignatureConfigwith platform optionssignatureFormat: Output format for signaturekeyFormat: Output format for public keypromptMessage: Custom authentication prompt
| Option | Platforms | Description |
|---|---|---|
allowDeviceCredentials |
Android | Allow PIN/pattern fallback |
promptSubtitle |
Android | Subtitle for biometric prompt |
promptDescription |
Android | Description for biometric prompt |
cancelButtonText |
Android | Cancel button text |
shouldMigrate |
iOS | Migrate from legacy keychain storage |
- Returns:
Future<SignatureResult>.signature: The signed payload.publicKey: The public key.code:BiometricErrorcode.
final result = await biometricSignature.createSignature(
payload: 'Data to sign',
promptMessage: 'Please authenticate',
signatureFormat: SignatureFormat.base64,
keyFormat: KeyFormat.base64,
config: CreateSignatureConfig(
allowDeviceCredentials: false,
),
);Decrypts the given payload using the private key and biometrics.
- Parameters:
payload: The encrypted datapayloadFormat: Format of encrypted data (PayloadFormat.base64,hex)config:DecryptConfigwith platform optionspromptMessage: Custom authentication prompt
| Option | Platforms | Description |
|---|---|---|
allowDeviceCredentials |
Android | Allow PIN/pattern fallback |
promptSubtitle |
Android | Subtitle for biometric prompt |
promptDescription |
Android | Description for biometric prompt |
cancelButtonText |
Android | Cancel button text |
shouldMigrate |
iOS | Migrate from legacy keychain storage |
Note: Decryption is not supported on Windows.
- Returns:
Future<DecryptResult>.decryptedData: The plaintext string.code:BiometricErrorcode.
final result = await biometricSignature.decrypt(
payload: encryptedBase64,
payloadFormat: PayloadFormat.base64,
promptMessage: 'Authenticate to decrypt',
config: DecryptConfig(
allowDeviceCredentials: false,
),
);Deletes all biometric key material (signing and decryption keys) from the device's secure storage.
- Returns:
Future<bool>.true: Keys were successfully deleted, or no keys existed (idempotent).false: Deletion failed due to a system error.
Note: This operation is idempotent—calling
deleteKeys()when no keys exist will still returntrue. This allows safe "logout" or "reset" flows without checking key existence first.
final deleted = await biometricSignature.deleteKeys();
if (deleted) {
print('All biometric keys removed');
}Checks if biometric authentication is available on the device and returns a structured response.
- Returns:
Future<BiometricAvailability>.canAuthenticate:boolindicating if auth is possible.hasEnrolledBiometrics:boolindicating if user has enrolled biometrics.availableBiometrics:List<BiometricType>(e.g.,fingerprint,face).reason: String explanation if unavailable.
final availability = await biometricSignature.biometricAuthAvailable();
if (availability.canAuthenticate) {
print('Biometrics available: ${availability.availableBiometrics}');
} else {
print('Not available: ${availability.reason}');
}Retrieves detailed information about existing biometric keys without prompting for authentication.
- Parameters:
checkValidity: Whether to verify the key hasn't been invalidated by biometric changes. Default isfalse.keyFormat: Output format for public keys (KeyFormat.base64,pem,hex). Default isbase64.
- Returns:
Future<KeyInfo>.exists: Whether any biometric key exists.isValid: Key validity status (only populated whencheckValidity: true).algorithm:"RSA"or"EC".keySize: Key size in bits (e.g., 2048, 256).isHybridMode: Whether using hybrid signing/decryption keys.publicKey: The signing public key.decryptingPublicKey: Decryption key (hybrid mode only).
final info = await biometricSignature.getKeyInfo(
checkValidity: true,
keyFormat: KeyFormat.pem,
);
if (info.exists && (info.isValid ?? true)) {
print('Algorithm: ${info.algorithm}, Size: ${info.keySize}');
print('Hybrid Mode: ${info.isHybridMode}');
}Convenience method that wraps getKeyInfo() and returns a simple boolean.
- Parameters:
checkValidity: Whether to check key validity. Default isfalse.
- Returns:
Future<bool>-trueif key exists and is valid.
final exists = await biometricSignature.biometricKeyExists(checkValidity: true);