中文 | English
Etl-engine is a lightweight, robust, and extensible Headless ETL library designed for developers. It focuses on high-concurrency and high-performance data synchronization, serving as the ideal code-level alternative to heavy, GUI-based ETL tools like Kettle (PDI).
Etl-engine provides the following three core features:
Significant improvement in data processing and database I/O speeds through batch operations and a non-blocking, cached pipeline design.
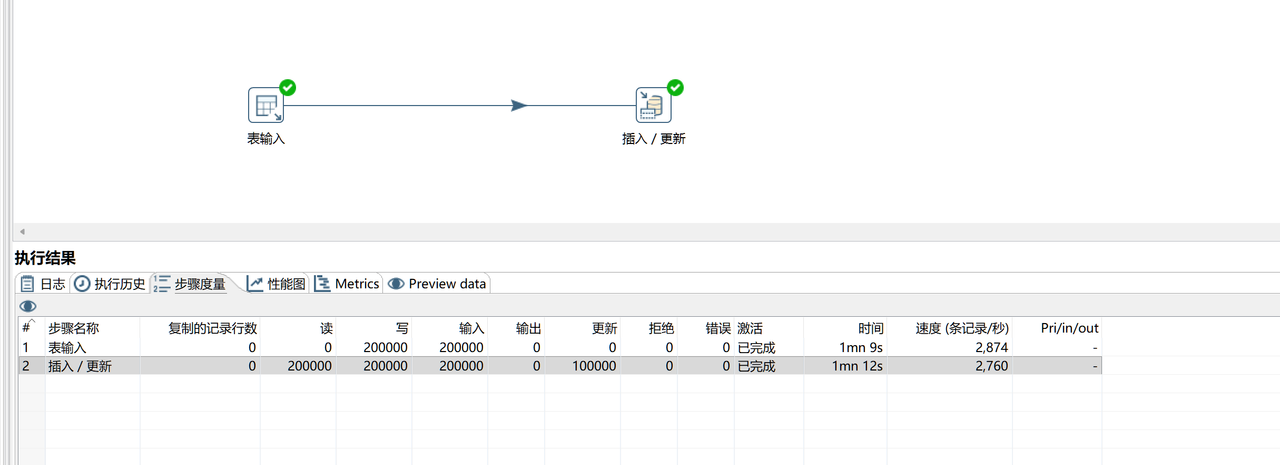
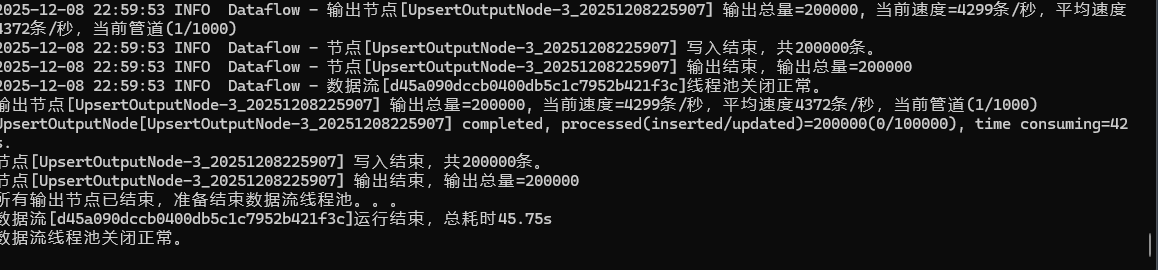
📊 Real-World Test: For an insert/update task involving etl-engine is
-
Self-Healing: Tasks do not crash on individual data errors; it supports automatic retries and error handling to ensure stable long-running jobs.
-
Full-Link Logging: Provides detailed execution metrics for debugging.
The core consists of only three main components: Node, Pipe, and Dataflow . All data loading logic is abstracted into extensible Nodes. In addition to the built-in JDBC data source Node, users can easily inherit the base class to quickly develop new data sources (such as Http, Redis) or custom transformation logic to meet specific business requirements.
The following code demonstrates how to quickly build an ETL task that extracts data from Oracle and synchronizes (Upsert) it to PostgreSQL (Load).
flowchart LR
sqlInputNode --pipe--> upsertOutputNode
//Create Oracle data source
DataSource dataSourceOracle = DataSourceUtil.getOracleDataSource();
//Create talbe output node
SqlInputNode sqlInputNode = new SqlInputNode(dataSourceOracle, "select * from t_resident_info");
//Create Postgres data source
DataSource dataSourcePG = DataSourceUtil.getPostgresDataSource();
//Create upsert output node
UpsertOutputNode upsertOutputNode = new UpsertOutputNode(dataSourcePG, "t_resident_info", 1000);
//Set the unique identifier (primary key) mapping, used to determine Insert or Update.
upsertOutputNode.setIdentityMapping(Arrays.asList(new Tuple2<>("ID", "ID")));
//Create a pipe and set the buffer size to 1,000 data rows.
Pipe pipe = new Pipe(1000);
//Connect the sql input node and table upsert node.
pipe.connect(sqlInputNode, upsertOutputNode);
//Create dataflow instance
Dataflow dataflow = new Dataflow(sqlInputNode);
//Start the data flow and set the timeout after 5 minutes.
dataflow.syncStart(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);flowchart LR
SqlInputNode --pipe-->ValueConversionNode --pipe--> UpsertOutputNode
package io.github.add2ws.node;
import lombok.NonNull;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.liuneng.base.MiddleNode;
import org.liuneng.base.Row;
import org.liuneng.exception.NodeException;
@Slf4j
public class ValueConversionNode extends MiddleNode {
@Override
protected @NonNull Row process(@NonNull Row row) throws NodeException {
// Converting values from column 'gender' to 'gender_name'.
if ("1".equals(row.get("gender"))) {
row.put("gender_name", "male");
} else {
row.put("gender_name", "female");
}
// Masking values of column 'address'.
String address = String.valueOf(row.get("address"));
if (address != null) {
String masked = address.replaceAll("^(.).*(.)$", "$1***$2");
row.put("address", masked);
}
return row;
}
@Override
public String[] getColumns() throws NodeException {
//Adding column 'gender_name' for subsequent nodes.
return new String[]{"gender_name"};
}
@Override
public @NonNull Type getType() {
//MiddleNode type: When connecting to multiple downstream nodes,
// determines whether the data stream is copied or distributed.
return Type.COPY;
}
}// Create Oracle data source and SQL input node
DataSource dataSourceOracle = DataSourceUtil.getOracleDataSource();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM ETL_BASE.T_RESIDENT_INFO WHERE 1=1 AND ROWNUM < 50000";
SqlInputNode sqlInputNode = new SqlInputNode(dataSourceOracle, sql);
// Create Postgres data source and table output node
DataSource dataSourcePG = DataSourceUtil.getPostgresDataSource();
UpsertOutputNode upsertOutputNode = new UpsertOutputNode(dataSourcePG, "t_resident_info", 1000);
upsertOutputNode.setIdentityMapping(Arrays.asList(new Tuple2<>("ID", "ID")));
// Create value conversion node
ValueConversionNode valueConversionNode = new ValueConversionNode();
// Connect Oracle input node to value conversion node
Pipe pipe = new Pipe(10000);
pipe.connect(sqlInputNode, valueConversionNode);
// Connect value conversion node to Postgres output node
pipe = new Pipe(10000);
pipe.connect(valueConversionNode, upsertOutputNode);
// Start dataflow
Dataflow dataflow = new Dataflow(sqlInputNode);
dataflow.syncStart(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);3. One SQL input node distributes the data stream to multiple output nodes based on column value evaluation.
flowchart LR
SqlInputNode --Pipe--> ConditionNode
ConditionNode --"Pipe[0](gender=1)"--> UpsertOutputNode
ConditionNode --"Pipe[1](gender=2)"--> FileOutputNode
package io.github.add2ws.node;
import lombok.NonNull;
import org.liuneng.base.MiddleNode;
import org.liuneng.base.Row;
import org.liuneng.exception.NodeException;
public class ConditionNode extends MiddleNode {
@Override
protected @NonNull Row process(@NonNull Row row) throws NodeException {
Object gender = row.get("gender");
if ("1".equals(gender)) {
// Distribute data where gender=1 to the first downstream pipe
row.setPipeIndex(0);
return row;
} else {
// Otherwise, distribute to the second downstream pipe
row.setPipeIndex(1);
return row;
}
}
@Override
public String[] getColumns() throws NodeException {
// No additional columns added
return new String[0];
}
@Override
public @NonNull Type getType() {
// MiddleNode type: When connected to multiple downstream nodes,
// determines whether the data stream is copied or distributed.
return Type.SWITCH;
}
} // Create Oracle data source and SQL input node
DataSource dataSourceOracle = DataSourceUtil.getOracleDataSource();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM ETL_BASE.T_RESIDENT_INFO WHERE 1=1 AND ROWNUM < 50000";
SqlInputNode sqlInputNode = new SqlInputNode(dataSourceOracle, sql);
// Create Postgres data source and table output node
DataSource dataSourcePG = DataSourceUtil.getPostgresDataSource();
UpsertOutputNode upsertOutputNode = new UpsertOutputNode(dataSourcePG, "t_resident_info", 1000);
upsertOutputNode.setIdentityMapping(Arrays.asList(new Tuple2<>("ID", "ID")));
// Create CSV file output node
FileOutputNode fileOutputNode = new FileOutputNode("D:/t_resident_info_female_" + System.currentTimeMillis() +".csv", FileOutputNode.Format.CSV);
// Create middle node
ConditionNode conditionNode = new ConditionNode();
// Connect Oracle input node
Pipe pipe = new Pipe(10000);
pipe.connect(sqlInputNode, conditionNode);
// Connect middle node to Postgres output node
pipe = new Pipe(10000);
pipe.connect(conditionNode, upsertOutputNode);
// Connect middle node to CSV file output node
pipe = new Pipe(10000);
pipe.connect(conditionNode, fileOutputNode);
// Start dataflow
Dataflow dataflow = new Dataflow(sqlInputNode);
dataflow.syncStart(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);The core of Etl-engine consists of only the following three main components :
- Node The starting point, ending point, and carrier for data transformation logic.
- Pipe A non-blocking, cached queue responsible for transferring data between Nodes.
- Dataflow The orchestrator and execution entry point for the task.