- Introduction
- What is this?
- Who made this?
- License
- Requirements
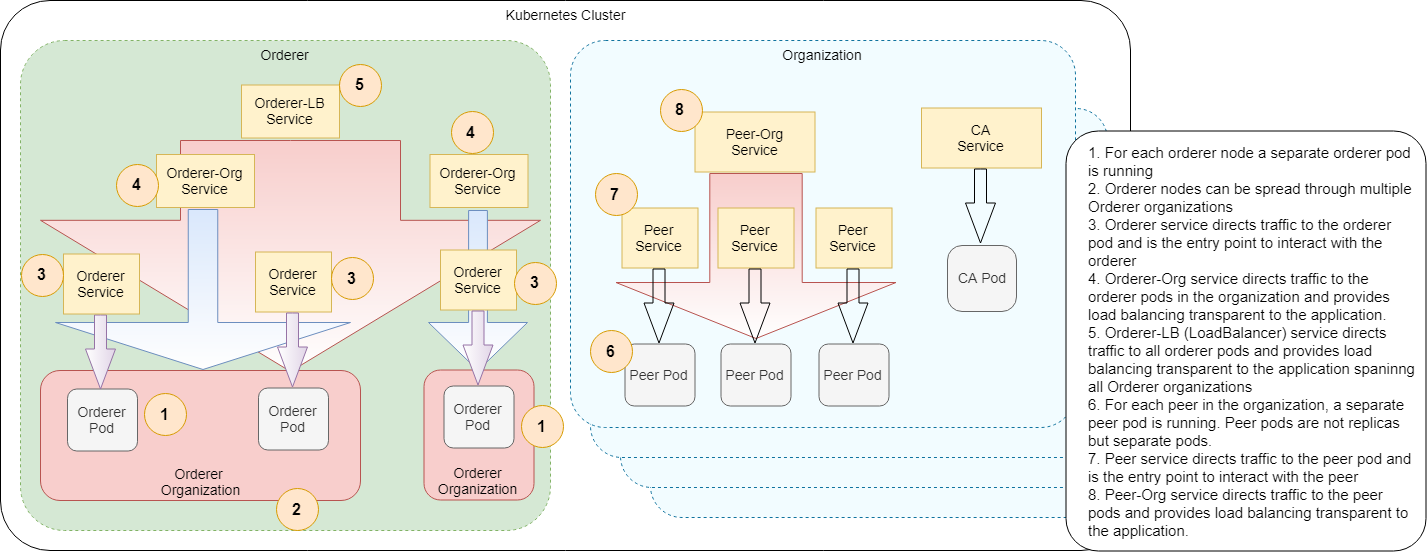
- Network Architecture
- Go over the samples
- Configuration
- TLS
- Backup-Restore
- Limitations
- Conclusion
This repository is a fork of https://github.com/APGGroeiFabriek/PIVT . I have done changes to use Fabric CA to generate certificates and private keys than using cryptogen (not recommended for production).
This repository contains a couple of Helm charts to:
- Configure and launch the whole HL Fabric network, either:
- A simple one, one peer per organization and Solo orderer
- Or scaled up one, multiple peers per organization and Kafka or Raft orderer
- Custom Network architectures (Multi cluster architectures are not supported in this release)
- Register identities with Fabric CA and generate necessary artifacts to setup up blockchain network
- Populate the network declaratively:
- Create the channels, join peers to channels, update channels for Anchor peers
- Install/Instantiate all chaincodes, or some of them, or upgrade them to newer version .
- Add new peer organizations to an already running network declaratively
- Backup and restore the state of whole network
IMPORTANT: Declarative flows use home built CLI tools based on this patch, use at your own risk!
This is a fork of https://github.com/APGGroeiFabriek/PIVT. Additional customizations are done to use Fabric CA to generate certificates and private keys than using cryptogen
This work is licensed under the same license with HL Fabric; Apache License 2.0.
- A running Kubernetes cluster, developed with with AKS v1.13 . Minikube should also work, but not tested
- Helm, developed with 2.11, newer 2.xx versions should also work
- jq 1.5+ and yq 2.6+
- Argo, both CLI and Controller
- Minio, only required for backup/restore and new-peer-org flows
- Persistent Volumes to store crypto data and generated assets – Developed with Azurefile as PV
- Run all the commands in fabric-kube folder
- AWS EKS users please also apply this fix
Current version uses Persistent Volumes (PV) to store all generated certificates and private keys. Utilites to create AzureFile as persistent Volume are in
- Storage/azurefile/azure-file-sc.yaml – Create Persistent Volume
- Storage/azurefile/azure-pvc-roles.yaml – Grant necessary permissions Note: PV might not be the right approach to store certificates and private keys. Future versions will use a more precise Vault (HashiCorp Vault, Azure Vault) to store all sensitive information.
First install chart dependencies, you need to do this only once:
helm repo add kafka http://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-charts-incubator
helm dependency update ./hlf-kube/
Then create necessary stuff:
./util.sh ./samples/simple/ ./samples/chaincode/
This script:
- Compresses chaincodes as
tararchives viaprepare_chaincodes.shscript - Copies created stuff and configtx.yaml into main chart folder:
hlf-init-kube
Initialize the network and start CA server
helm install ./hlf-init-kube --name hlf-init-kube -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/simple/vault.yaml
This script:
- creates PVC for all organizations (Orderer/Peer) , CA’s and peers/hosts associated to those organizations
- Start Fabric CA for each organization configured in crypto-config.yaml
Wait for all pods are up and running:
kubectl get pod --watch
In a few seconds, pods will come up:

helm template artifacts-flow/ -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml | argo submit - --watch
Screen will look somethis like this
 Now, we are ready to launch the network:
Now, we are ready to launch the network:
helm install ./hlf-kube --name hlf-kube -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml
This chart creates all the above mentioned secrets, pods, services, mount required persistent volume claims, etc. cross configures them and launches the network in unpopulated state.
Wait for all pods are up and running:
kubectl get pod --watch
In a few seconds, pods will come up:
 Congrulations you have a running HL Fabric network in Kubernetes!
Congrulations you have a running HL Fabric network in Kubernetes!
Next lets create channels, join peers to channels and update channels for Anchor peers:
helm template channel-flow/ -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml | argo submit - --watch
Wait for the flow to complete, finally you will see something like this:

Channel flow is declarative and idempotent. You can run it many times. It will create the channel only if it doesn't exist, join peers to channels only if they didn't join yet, etc.
Next lets install/instantiate/invoke chaincodes
helm template chaincode-flow/ -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml | argo submit - --watch
Wait for the flow to complete, finally you will see something like this:

Install steps may fail even many times, nevermind about it, it's a known Fabric bug, the flow will retry it and eventually succeed.
Lets assume you had updated chaincodes and want to upgrade them in the Fabric network. Firt update chaincode tar archives:
./prepare_chaincodes.sh ./samples/simple/ ./samples/chaincode/
Then make sure chaincode ConfigMaps are updated with new chaincode tar archives:
helm upgrade hlf-init-kube ./hlf-init-kube -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml
Or alternatively you can update chaincode ConfigMaps directly:
helm template -f samples/simple/network.yaml -x templates/chaincode-configmap.yaml ./hlf-init-kube/ | kubectl apply -f -
Next invoke chaincode flow again:
helm template chaincode-flow/ -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml --set chaincode.version=2.0 | argo submit - --watch
All chaincodes are upgraded to version 2.0!

Lets upgrade only the chaincode named very-simple to version 3.0:
helm template chaincode-flow/ -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml --set chaincode.version=3.0 --set flow.chaincode.include={very-simple} | argo submit - --watch
Chaincode very-simple is upgarded to version 3.0!

Alternatively, you can also set chaincode versions individually via network.chaincodes[].version
Chaincode flow is declarative and idempotent. You can run it many times. It will install chaincodes only if not installed, instatiate them only if not instantiated yet, etc.
Now, lets launch a scaled up network backed by a Kafka cluster.
First tear down everything:
argo delete --all
helm delete hlf-init-kube --purge
helm delete hlf-kube --purge
Wait a bit until all pods are terminated:
kubectl get pod --watch
Then create necessary stuff:
./util.sh ./samples/scaled-kafka/ ./samples/chaincode/
Intialize and start Fabric CA
helm install ./hlf-init-kube --name hlf-init-kube -f samples/scaled-kafka/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-kafka/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-kafka/values.yaml -f samples/scaled-kafka/vault.yaml
Generate artifacts from Fabric CA
helm template artifacts-flow/ -f samples/scaled-kafka/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-kafka/crypto-config.yaml | argo submit - --watch
Lets launch our scaled up Fabric network:
helm install ./hlf-kube --name hlf-kube -f samples/scaled-kafka/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-kafka/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-kafka/values.yaml
Again lets wait for all pods are up and running:
kubectl get pod --watch
This time, in particular wait for 4 Kafka pods and 3 ZooKeeper pods are running and ready count is 1/1.
Kafka pods may crash and restart a couple of times, this is normal as ZooKeeper pods are not ready yet,
but eventually they will all come up.
Congrulations you have a running scaled up HL Fabric network in Kubernetes, with 3 Orderer nodes backed by a Kafka cluster and 2 peers per organization. Your application can use them without even noticing there are 3 Orderer nodes and 2 peers per organization.
Lets create the channels:
helm template channel-flow/ -f samples/scaled-kafka/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-kafka/crypto-config.yaml | argo submit - --watch
And install chaincodes:
helm template chaincode-flow/ -f samples/scaled-kafka/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-kafka/crypto-config.yaml | argo submit - --watch
Now, lets launch a scaled up network based on three Raft orderer nodes spanning two Orderer organizations. This sample also demonstrates how to enable TLS and use actual domain names for peers and orderers instead of internal Kubernetes service names. Enabling TLS globally is mandatory as of Fabric 1.4.2. This is resolved but not released yet.
For TLS, we need hostAliases support in Argo workflows and also in Argo CLI, which is implemented but not released yet. You can install Argo controller from Argo repo with the below command. We have built Argo CLI binary from Argo repo for Linux which can be downloaded from here. Use at your own risk!
kubectl apply -n argo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo/master/manifests/install.yaml
Compare scaled-raft-tls/configtx.yaml with other samples, in particular it uses actual domain names like peer0.atlantis.com instead of internal Kubernetes service names like hlf-peer--atlantis--peer0. This is necessary for enabling TLS since otherwise TLS certificates won't match service names.
Also in network.yaml file, there are two additional settings. As we pass this file to all Helm charts, it's convenient to put these settings into this file.
tlsEnabled: true
useActualDomains: true
First tear down everything:
argo delete --all
helm delete hlf-init-kube --purge
helm delete hlf-kube --purge
Wait a bit until all pods are terminated:
kubectl get pod --watch
Then create necessary stuff:
./util.sh ./samples/scaled-raft-tls/ ./samples/chaincode/
Intialize and start Fabric CA
helm install ./hlf-init-kube --name hlf-init-kube -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/vault.yaml
Generate artifacts from Fabric CA
helm template artifacts-flow/ -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml | argo submit - --watch
Lets launch our Raft based Fabric network in broken state:
helm install ./hlf-kube --name hlf-kube -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml
The pods will start but they cannot communicate to each other since domain names are unknown. You might also want to use the option --set peer.launchPods=false --set orderer.launchPods=false to make this process faster.
Run this command to collect the host aliases:
kubectl get svc -l addToHostAliases=true -o jsonpath='{"hostAliases:\n"}{range..items[*]}- ip: {.spec.clusterIP}{"\n"} hostnames: [{.metadata.labels.fqdn}]{"\n"}{end}' > samples/scaled-raft-tls/hostAliases.yaml
Or this one, which is much convenient:
./collect_host_aliases.sh ./samples/scaled-raft-tls/
Let's check the created hostAliases.yaml file.
cat samples/scaled-raft-tls/hostAliases.yaml
The output will be something like:
hostAliases:
- ip: 10.0.110.93
hostnames: [orderer0.groeifabriek.nl]
- ip: 10.0.32.65
hostnames: [orderer1.groeifabriek.nl]
- ip: 10.0.13.191
hostnames: [orderer0.pivt.nl]
- ip: 10.0.88.5
hostnames: [peer0.atlantis.com]
- ip: 10.0.88.151
hostnames: [peer1.atlantis.com]
- ip: 10.0.217.95
hostnames: [peer10.aptalkarga.tr]
- ip: 10.0.252.19
hostnames: [peer9.aptalkarga.tr]
- ip: 10.0.64.145
hostnames: [peer0.nevergreen.nl]
- ip: 10.0.15.9
hostnames: [peer1.nevergreen.nl]
The IPs are internal ClusterIPs of related services. Important point here is, as opposed to pod ClusterIPs, service ClusterIPs are stable, they won't change if service is not deleted and re-created.
Next, let's update the network with this host aliases information. These entries goes into pods' /etc/hosts file via Pod hostAliases spec.
helm upgrade hlf-kube ./hlf-kube -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/hostAliases.yaml
Again lets wait for all pods are up and running:
kubectl get pod --watch
Congrulations you have a running scaled up HL Fabric network in Kubernetes, with 3 Raft orderer nodes spanning 2 Orderer organizations and 2 peers per organization. But unfortunately, due to TLS, your application cannot use them with transparent load balancing, you need to connect to relevant peer and orderer services separately.
Lets create the channels:
helm template channel-flow/ -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/hostAliases.yaml | argo submit - --watch
And install chaincodes:
helm template chaincode-flow/ -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/hostAliases.yaml | argo submit - --watch
First tear down and re-launch and populate the simple network as described in launching the network, creating channels and installing chaincodes.
At this point we can update the original configtx.yaml, crypto-config.yaml and network.yaml for the new organizations. First take backup of the originals:
rm -rf tmp && mkdir -p tmp && cp samples/simple/configtx.yaml samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml samples/simple/network.yaml tmp/
Then override with extended ones:
cp samples/simple/extended/* samples/simple/ && cp samples/simple/configtx.yaml hlf-kube/
Update configtx
helm upgrade hlf-init-kube ./hlf-init-kube -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/simple/vault.yaml
create artifacts for new organization
helm template artifacts-flow/ -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml | argo submit - --watch
Then update hlf-kube and launch the new peers:
helm upgrade hlf-kube ./hlf-kube -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml
Then lets create new peer organizations:
helm template peer-org-flow/ -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/simple/configtx.yaml | argo submit - --watch
This flow:
- Parses consortiums from
configtx.yamlusinggenesisProfiledefined innetwork.yaml - Adds missing organizations to consortiums
- Adds missing organizations to existing channels as defined in
network.yaml - Emits an error for non-existing consortiums
- Skips non-existing channels (they will be created by channel flow later)
When the flow completes the output will be something like this:

By default, peer org flow updates all existing channels and consortiums as necessary. You can limit this behaviour by setting flow.channel.include and flow.consortium.include variables respectively.
At this point make sure new peer pods are up and running. Then run the channel flow to create new channels and populate existing ones regarding the new organizations:
helm template channel-flow/ -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml | argo submit - --watch
Finally run the chaincode flow to populate the chaincodes regarding new organizations:
helm template chaincode-flow/ -f samples/simple/network.yaml -f samples/simple/crypto-config.yaml --set chaincode.version=2.0 | argo submit - --watch
Please note, we increased the chaincode version. This is required to upgrade the chaincodes with new policies. Otherwise, new peers' endorsements will fail.
Peer org flow is declarative and idempotent. You can run it many times. It will add peer organizations to consortiums only if they are not already in consortiums, add peer organizations to channels only if not already in channels.
Restore the original files
cp tmp/configtx.yaml tmp/crypto-config.yaml tmp/network.yaml samples/simple/
Adding new peer organizations to a network which utilizes Raft orderer is similar. But there is one point to be aware of: After adding new organizations we need to update the rest of the network with new host aliases information. This means existing pods will be restarted and will lose all the data. That's why persistence should be enabled.
First tear down and re-launch and populate the Raft network as described in scaled-up-raft-network but pass the following additional flag: -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/persistence.yaml
At this point we can update the original configtx.yaml, crypto-config.yaml and network.yaml for the new organizations. First take backup of the originals:
rm -rf tmp && mkdir -p tmp && cp samples/scaled-raft-tls/configtx.yaml samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml tmp/
Then override with extended ones:
cp samples/scaled-raft-tls/extended/* samples/scaled-raft-tls/ && cp samples/scaled-raft-tls/configtx.yaml hlf-kube/
Update configtx
helm upgrade hlf-init-kube ./hlf-init-kube -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/vault.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/persistence.yaml
create artifacts for new organization
helm template artifacts-flow/ -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml | argo submit - --watch
Update the network and launch new peers
helm upgrade hlf-kube ./hlf-kube -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/persistence.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/hostAliases.yaml
Collect extended host aliases:
./collect_host_aliases.sh ./samples/scaled-raft-tls/
Upgrade host aliases in pods and wait for all pods are up and running:
helm upgrade hlf-kube ./hlf-kube -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/hostAliases.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/persistence.yaml
kubectl get pod --watch
Let's create the new peer organizations:
helm template peer-org-flow/ -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/configtx.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/hostAliases.yaml | argo submit - --watch
Then run the channel flow to create new channels and populate existing ones regarding the new organizations:
helm template channel-flow/ -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/hostAliases.yaml | argo submit - --watch
Finally run the chaincode flow to populate the chaincodes regarding new organizations:
helm template chaincode-flow/ -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/network.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/scaled-raft-tls/hostAliases.yaml --set chaincode.version=2.0 | argo submit - --watch
Please note, we increased the chaincode version. This is required to upgrade the chaincodes with new policies. Otherwise, new peers' endorsements will fail.
Restore original files
cp tmp/configtx.yaml tmp/crypto-config.yaml tmp/network.yaml samples/scaled-raft-tls/
Update the Template.Count value for relevant PeerOrgs in crypto-config.yaml and run the sequence
in adding new peer organizations.
No need to run peer-org-flow in this case as peer organizations didn't change.
But running it won't hurt anyway, remember it's idempotent ;)
There are basically 2 configuration files: crypto-config.yaml and network.yaml.
This is Fabric's native configuration for cryptogen tool. We use it to define the network architecture. We honour OrdererOrgs,
PeerOrgs, Template.Count at PeerOrgs (peer count) and Specs.Hostname[] at OrdererOrgs.
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "OrdererOrgs" - Definition of organizations managing orderer nodes
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OrdererOrgs:
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Orderer
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Name: AreteOrderer
Domain: arete.com
Specs:
- Hostname: orderer0
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "PeerOrgs" - Definition of organizations managing peer nodes
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
PeerOrgs:
- Name: AreteCorporate
Domain: corporate.arete.com
EnableNodeOUs: true
Template:
Count: 2
Users:
Count: 1
- Name: ABCVendor
Domain: vendor.abc.com
EnableNodeOUs: true
Template:
Count: 1
Users:
Count: 1This file defines how network is populated regarding channels and chaincodes.
network:
# used by init script to create genesis block and by peer-org-flow to parse consortiums
genesisProfile: OrdererGenesis
# used by init script to create genesis block
systemChannelID: aretechainid
# defines which organizations will join to which channels
channels:
- name: common
# all peers in these organizations will join the channel
orgs: [AreteCorporate, ABCVendor]
- name: private-arete
# all peers in these organizations will join the channel
orgs: [AreteCorporate]
# defines which chaincodes will be installed to which organizations
chaincodes:
- name: very-simple
# if defined, this will override the global chaincode.version value
version: # "2.0"
# chaincode will be installed to all peers in these organizations
orgs: [AreteCorporate, ABCVendor]
# at which channels are we instantiating/upgrading chaincode?
channels:
- name: common
# chaincode will be instantiated/upgraded using the first peer in the first organization
# chaincode will be invoked on all peers in these organizations
orgs: [AreteCorporate, ABCVendor]
policy: OR('AreteCorporateMSP.member','ABCVendorMSP.member')
- name: even-simpler
orgs: [AreteCorporate]
channels:
- name: private-arete
orgs: [AreteCorporate]
policy: OR('AreteCorporateMSP.member')
For chart specific configuration, please refer to the comments in the relevant values.yaml files.
Using TLS is a two step process. We first launch the network in broken state, then collect ClusterIPs of services and attach them to pods as DNS entries using pod hostAliases spec.
Important point here is, as opposed to pod ClusterIPs, service ClusterIPs are stable, they won't change if service is not deleted and re-created.
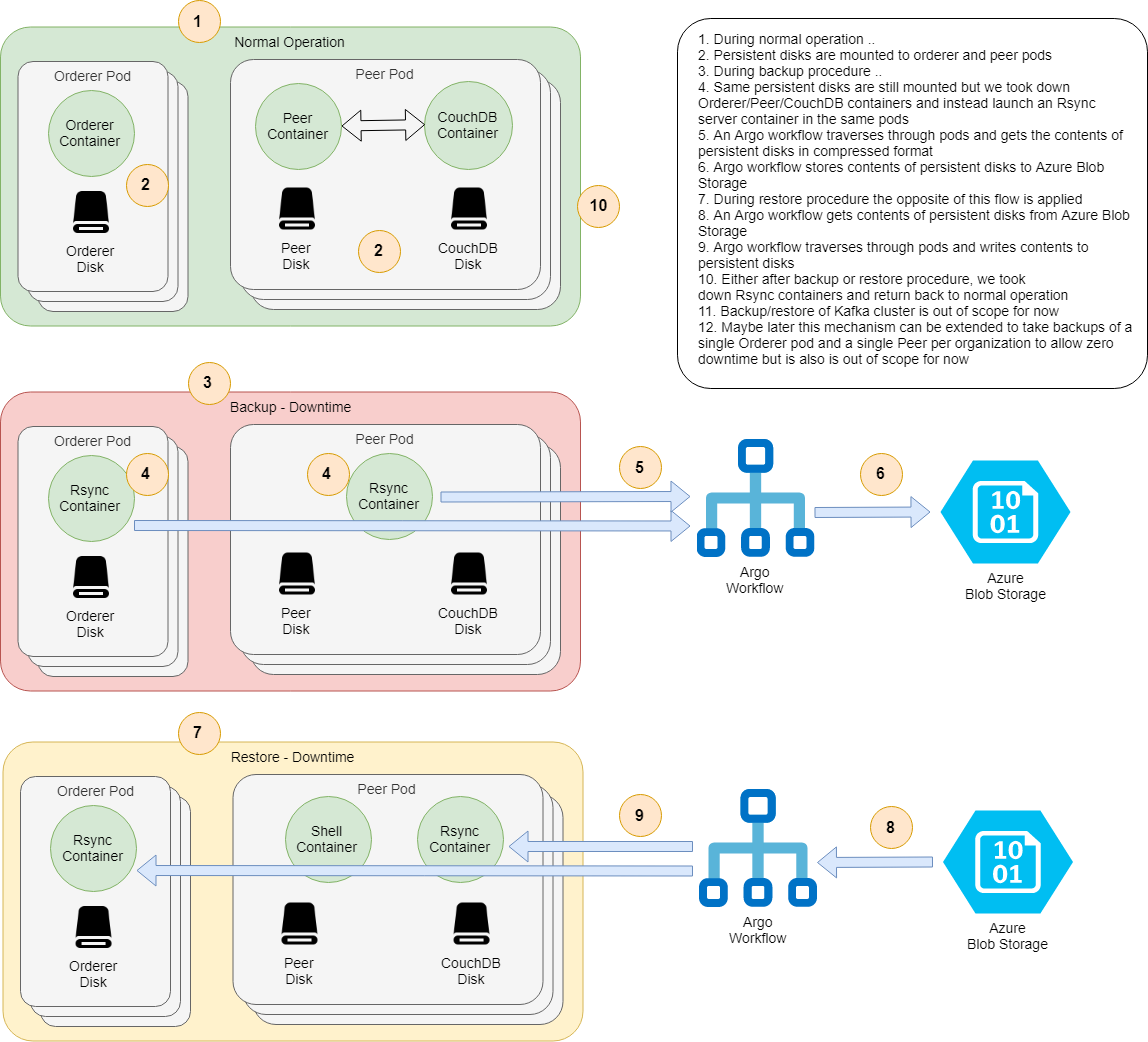
- Persistence should be enabled in relevant components (Orderer, Peer, CouchDB)
- Configure Argo for some artifact repository. Easiest way is to install Minio
- An Azure Blob Storage account with a container named
hlf-backup(configurable). ATM, backups can only be stored at Azure Blob Storage but it's quite easy to extend backup/restore flows for other mediums, like AWS S3. See bottom of backup-workflow.yaml
IMPORTANT: Backup flow does not backup contents of Kafka cluster, if you are using Kafka orderer you need to manually back it up. In particular, Kafka Orderer with some state cannot handle a fresh Kafka installation, see this Jira ticket, hopefully Fabric guys will fix this soon.
First lets create a persistent network:
./util.sh ./samples/simple-persistent/ ./samples/chaincode/
helm install --name hlf-init-kube -f samples/simple-persistent/network.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/values.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/vault.yaml ./hlf-init-kube
helm template artifacts-flow/ -f samples/simple-persistent/network.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/crypto-config.yaml | argo submit - --watch
helm install --name hlf-kube -f samples/simple-persistent/network.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/values.yaml ./hlf-kube
Again lets wait for all pods are up and running, this may take a bit longer due to provisioning of disks.
kubectl get pod --watch
Then populate the network, you know how to do it :)
Start backup procedure and wait for pods to be terminated and re-launched with Rsync containers.
helm upgrade hlf-kube --set backup.enabled=true -f samples/simple-persistent/network.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/values.yaml ./hlf-kube
kubectl get pod --watch
Then take backup:
helm template -f samples/simple-persistent/crypto-config.yaml --set backup.target.azureBlobStorage.accountName=<your account name> --set backup.target.azureBlobStorage.accessKey=<your access key> backup-flow/ | argo submit - --watch
This will create a folder with default backup.key (html formatted date yyyy-mm-dd),
in Azure Blob Storage and hierarchically store backed up contents there.
Finally go back to normal operation:
helm upgrade hlf-kube -f samples/simple-persistent/network.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/values.yaml ./hlf-kube
kubectl get pod --watch
Start restore procedure and wait for pods to be terminated and re-launched with Rsync containers.
helm upgrade hlf-kube --set restore.enabled=true -f samples/simple-persistent/network.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/values.yaml ./hlf-kube
kubectl get pod --watch
Then restore from backup:
helm template --set backup.key='<backup key>' -f samples/simple-persistent/crypto-config.yaml --set backup.target.azureBlobStorage.accountName=<your account name> --set backup.target.azureBlobStorage.accessKey=<your access key> restore-flow/ | argo submit - --watch
Finally go back to normal operation:
helm upgrade hlf-kube -f samples/simple-persistent/network.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/crypto-config.yaml -f samples/simple-persistent/values.yaml ./hlf-kube
kubectl get pod --watch
Transparent load balancing is not possible with TLS as of Fabric 1.4.2. So, instead of Peer-Org, Orderer-Org or Orderer-LB services, you need to connect to individual Peer and Orderer services.
This is possible but they should be run in different namespaces. We do not use Helm release name in names of components, so if multiple instances of Fabric network is running in the same namespace, names will conflict.
Currently this is not supported.
Currently this is not supported.
Backup & Restore might not work with recent changes. This feature is in prgress
This is forked from https://github.com/APGGroeiFabriek/PIVT. credits to https://github.com/APGGroeiFabriek/PIVT/commits?author=raftAtGit
- Vault support (Hashicorp / Azure vault)
- Operating HLF network spanned acrosss multiple clusters
- Support for Intermediate CAs
Stay tuned