This project is a deep learning implementation using TensorFlow to analyze audio files and recognize the language being spoken in them. The model is based on a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture that has proven to be effective in audio signal processing tasks.
Use the following command lines in order to clone the repository and create a virtual environment.
git clone github.com/Zoko91/DeepLanguage
cd DeepLanguage
python3 -m venv venvThen, activate the virtual environment and install the required packages.
# Windows
venv\Scripts\activate
# Linux and Mac
source venv/bin/activateFinally, install the required packages and run the program.
pip install -r requirements.txtIMPORTANT:
- The data used for both the traning and the testing of the model is not included in the repository. It can be downloaded from the Common Voice website.
- The scripts up to date are located in the workingDirectory folder. Others might be deprecated (see: oldScripts).
The data collected to feed the model is from Common Voice by Mozilla. I used 11 000 audios of 5 seconds for each language is the traning process. I used 2 000 audios for testing and validating.$
The Common Voice dataset: This dataset, which was released by Mozilla in 2017, contains over 500 hours of voice data from more than 20,000 contributors, in a variety of languages. The dataset can be downloaded from the Common Voice website:
<a href="https://voice.mozilla.org/en/datasets">Link</a>Using tensorflow and librosa librairies in Python, the feature extracted from each audio files are the Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCS).
MFCCs are a compact representation of the spectral envelope of an audio signal, which captures important information about the frequency content of the signal in a way that is less sensitive to noise and irrelevant variations in the signal. MFCCs are computed by taking the Fourier transform of the signal, mapping it onto the Mel frequency scale, and then taking the logarithm of the magnitudes, followed by a Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT).
The model choosen for the language identification task was a Convolutional Neural Network, also called CNN.
CNNs are particularly well-suited to tasks like language identification because they are able to automatically learn relevant features from the raw input data. In the case of audio signals, this means that a CNN can learn to identify patterns in the frequency content of the signal that are characteristic of specific languages, without the need for manual feature engineering.
The model has been trained on 4 different languages.
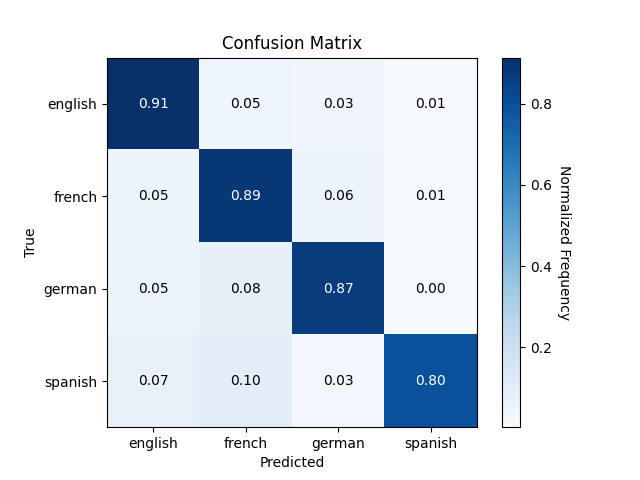
Here are the results of the latest model presented with a Confusion Matrix.
The model repository cannot be cloned as many files are ignored in the versioning process. However a website had been created, cf: DeepLanguage Website and will soon be available free to use online.