This repository is designed to help both new and experienced users get the most out of BERTopic, a powerful topic modelling library built on transformer embeddings and clustering.
It provides:
- A hands-on introduction for first-time users
- A structured approach to comparing and evaluating BERTopic model outputs
- A guide to understanding the performance trade-offs when tuning model parameters
All notebooks are Google Colab–ready to maximise accessibility — no installation required
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error Size | 52,221 | 5,298 | 41,846 | 61,754 |
| Topic 20 Size | 600 | 287 | 117 | 1,421 |
| Gini Score | 0.55 | 0.13 | 0.32 | 0.76 |
| Stability Score | 481 | 378 | 199 | 1,212 |
| Keyword Freq Score | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.20 |
| % Appearance | 56.8% | 4.38% | 48.91% | 65.38% |
These statistics are derived from over 200 BERTopic model runs using a wide range of
min_cluster_sizeandmin_topic_sizesettings.
-
📍 Estimated sweet spot:
Error_Size ≈ 56,465
Keyword_Freq_Score ≈ 0.186 -
⚠️ Suggested maximum threshold:
Error_Size ≤ 1.08 × mean(Error_Size)
This sweet spot was derived using a quadratic fit. Models beyond this range often show diminished keyword quality. This provides a normalised, model-independent threshold for selecting optimal runs.
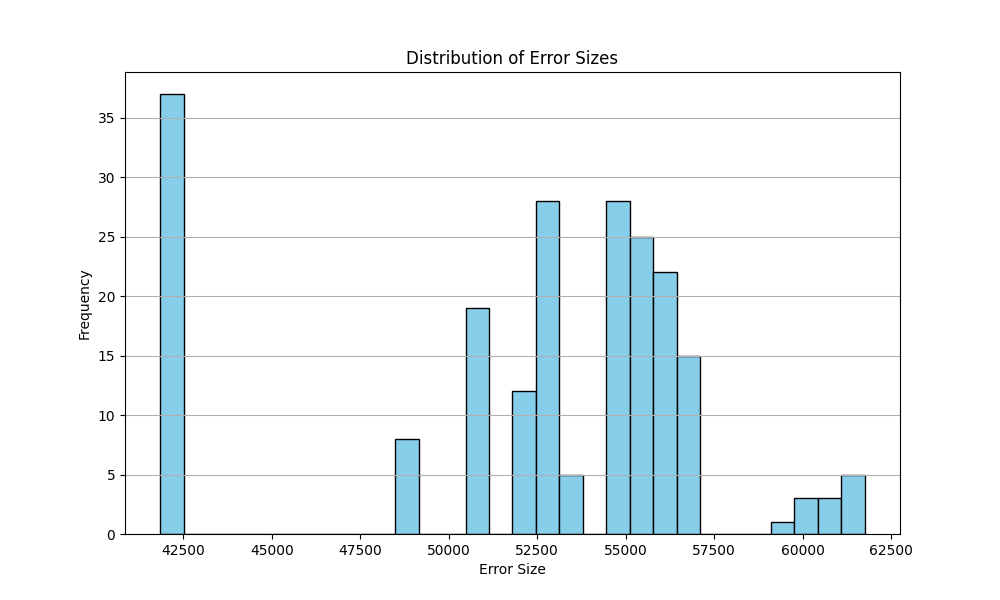
Shows the distribution of
Error_Sizeacross 211 model runs. Most cluster between 50,000–55,000.
A visualisation of the trade-off between topic balance (Gini) and coverage (% of corpus used).
A quadratic regression identifies the optimal
Error_Sizerange for maximisingKeyword_Freq_Score.
| Model | Outliers | Topics (n) | N-gram Score | Gini Score | Coherence (C_V) | Silhouette (Avg) | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| all-MiniLM-L6-v2 | 60,277 | 520 | 0.16 | 0.529 | 0.060 | 0.000 | 10.96 |
| all-mpnet-base-v2 | 62,729 | 584 | 0.16 | 0.516 | 0.090 | 0.000 | 10.22 |
| distilroberta-base | 54,131 | 922 | 0.19 | 0.391 | 0.060 | 0.000 | 11.63 |
| bge-small-en-v1.5 | 59,266 | 59 | 0.13 | 0.867 | NaN | -0.080 | 10.91 |
| mpnet-distilled | 63,041 | 384 | 0.16 | 0.706 | 0.260 | -0.040 | 10.84 |
- How to prepare and embed text for BERTopic
- How to run batch models and log metadata
- How to evaluate model outputs using statistical and visual techniques
- How to select high-quality models using a mix of lexical and structural metrics
Read the paper summarising this projected
@misc{compton2025holistic,
title={Holistic Evaluations of Topic Models},
author={Thomas Compton},
year={2025},
eprint={2507.23364},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.IR}
}This project builds on BERTopic, developed by Maarten Grootendorst.
If you use BERTopic in your work, please cite:
Grootendorst, M. (2022). BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with class-based TF-IDF. Retrieved from https://github.com/MaartenGr/BERTopic
@misc{grootendorst2022bertopic,
author = {Maarten Grootendorst},
title = {BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with class-based TF-IDF},
year = 2022,
publisher = {GitHub},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/MaartenGr/BERTopic}}
}