Orchestration project with Vagrant and Kubernetes 3d & 3s
- Bonus - Gitlab, ArgoCD and K3D
- Part 1 - Vagrant, K3s Server and Agent
- Part 2 - K3s Apps and Ingress
- Part 3 - K3d + Argo CD
- Kubernetes Objects - Declarative management using config files
- Kubernetes Glossary
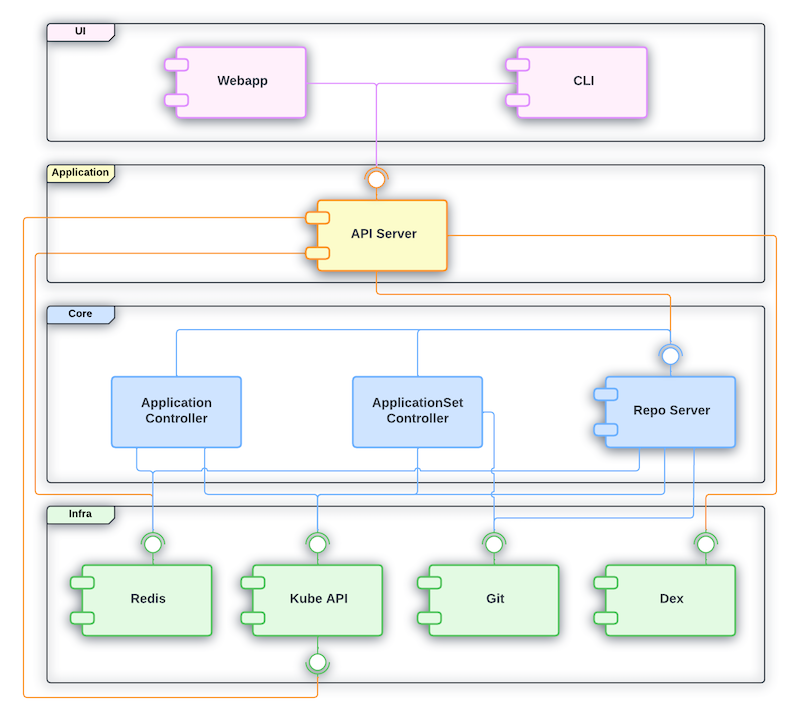
- Kubernetes - Reference
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It provides a robust framework for running distributed systems resiliently, allowing for load balancing, service discovery, and self-healing capabilities.
# Create Kubernetes Objects
kubectl apply -f <directory>Namespaces are a way to divide cluster resources between multiple users via resource quota. They provide a mechanism for isolating groups of resources within a single cluster. Namespaces are intended for use in environments with many users spread across multiple teams, or projects.
graph TD;
subgraph Cluster
subgraph nsA[Namespace A]
direction LR
rsr_a@{shape: "display", label: "Resources A"}
svc_a[Service A] --> pod_a1[Pod A1]
svc_a --> pod_a2[Pod A2]
end
subgraph nsB[Namespace B]
direction LR
rsr_b@{shape: "display", label: "Resources B"}
svc_b[Service B] --> pod_b1[Pod B1]
svc_b --> pod_b2[Pod B2]
end
end
classDef k8s fill:#326ce5,stroke:#fff,stroke-width:4px,color:#fff;
classDef cluster fill:#fff,stroke:#bbb,stroke-width:2px,color:#326ce5;
class svc_a,pod_a1,pod_a2,svc_b,pod_b1,pod_b2 k8s;
class Cluster,nsA,nsB cluster;
[!NOTE]
Ingress dev is frozen. New features are being added to Gateway API.
Ingress is a Kubernetes resource that manages external access to services within a cluster, typically HTTP and HTTPS traffic. It provides a way to define rules for routing incoming requests to the appropriate services based on hostnames, paths, or other criteria.
Ingress use an Ingress Controller to fulfill the Ingress rules. The Ingress Controller is responsible for processing the Ingress resource and configuring the underlying load balancer or proxy to route the traffic accordingly (like ingress-nginx).
graph LR;
client([client])-. Ingress-managed <br> load balancer .->ingress[Ingress];
ingress-->|routing rule|service[Service];
subgraph cluster
ingress;
service-->pod1[Pod];
service-->pod2[Pod];
end
classDef plain fill:#ddd,stroke:#fff,stroke-width:4px,color:#000;
classDef k8s fill:#326ce5,stroke:#fff,stroke-width:4px,color:#fff;
classDef cluster fill:#fff,stroke:#bbb,stroke-width:2px,color:#326ce5;
class ingress,service,pod1,pod2 k8s;
class client plain;
class cluster cluster;
K3S is a lightweight Kubernetes distribution designed for resource-constrained environments and edge computing. It simplifies the deployment and management of Kubernetes clusters by reducing the complexity and resource requirements typically associated with standard Kubernetes installations.
Flannel is a virtual network that connects containers across multiple hosts. It is often used as a network fabric for Kubernetes clusters, providing a layer 3 network that enables pods to communicate with each other regardless of the host they are running on.
K3D is a lightweight wrapper around K3s that allows you to run K3s clusters in Docker containers. It simplifies the process of creating and managing local Kubernetes clusters for development and testing purposes.
# Create a K3D cluster with 1 server and 2 agents
k3d cluster create mycluster --servers 1 --agents 2Argo CD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes. It automates the deployment and management of applications by synchronizing the desired state defined in Git repositories with the actual state in the Kubernetes cluster.
# Install Argo CD in the argocd namespace
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yamlGitLab Deployment Components:
- GitLab Rails app (main web UI + API).
- PostgreSQL (database).
- Redis (caching & job queues).
- Gitaly (handles Git repository storage & access).
- Sidekiq (background jobs, e.g., sending emails, cleaning data).
- Workhorse (smart reverse proxy, handles Git pushes/pulls efficiently).
- NGINX (optional, used for web serving).
- Prometheus & Grafana (monitoring stack, optional).
- Registry (Docker image storage).
- Runner (separate component, not bundled by default).
Vagrant is a tool for building and managing virtualized development environments. It allows developers to create reproducible and portable development environments using simple configuration files. Vagrant can work with various virtualization providers, such as VirtualBox, VMware, and cloud providers like AWS and Azure.
When you use vagrant up, Vagrant looks for a file named Vagrantfile in the following order:
[home]/[current_user]/[parent_dir]/[current_directory]/Vagrantfile
[home]/[current_user]/[parent_dir]/Vagrantfile
[home]/[current_user]/Vagrantfile
[home]/Vagrantfile
/VagrantfileTo create a vagrant file, simply create a file named Vagrantfile in the desired directory and define your virtual machine configuration using the Vagrant configuration syntax.
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "ubuntu/bionic64"
config.vm.network "forwarded_port", guest: 80, host: 8080
config.vm.provision "shell", inline: <<-SHELL
apt-get update
apt-get install -y apache2
SHELL
endvagrant up
vagrant halt
vagrant destroyvagrant ssh <vm_name># Remove a VM
vagrant destroy <vm_name>
# Force removal
vagrant destroy <vm_name> --force# List of runnings VMs
VBoxManage list runningvms# Kernel-based Virtual Machine: conflict resolution - unload KVM modules
sudo modprobe -r kvm_intel kvm