🦾💻🌐 distributed training & serverless inference at scale (https://podplex.run)
built in < 24 hours at the Runpod hackathon (co-hosted by Etched, Nomic, Replit, and vLLM)
🏆 UPDATE: This project won the $10,000 prize from Runpod at the hackathon! We feel humbled and are excited for the new things we can build with the credits.
- train & inference on RunPod serverless, RunPod pods, RunPod network storage
- data visualizations on Nomic
- frontend on Vercel
- built with Replit
The world isn’t facing a GPU supply problem, it’s facing a GPU under-utilization problem. For comparison, there’s 20-40 million GPUs on the Ethereum blockchain, 3 orders of magnitude more than the amount of GPUs used to train Llama 3, one of the largest open source training experiments of all time.
However, tapping into this compute is tricky. Most individual provisioners of GPUs don’t have A100s or H100s connected with Nvlink and InfiniBand.
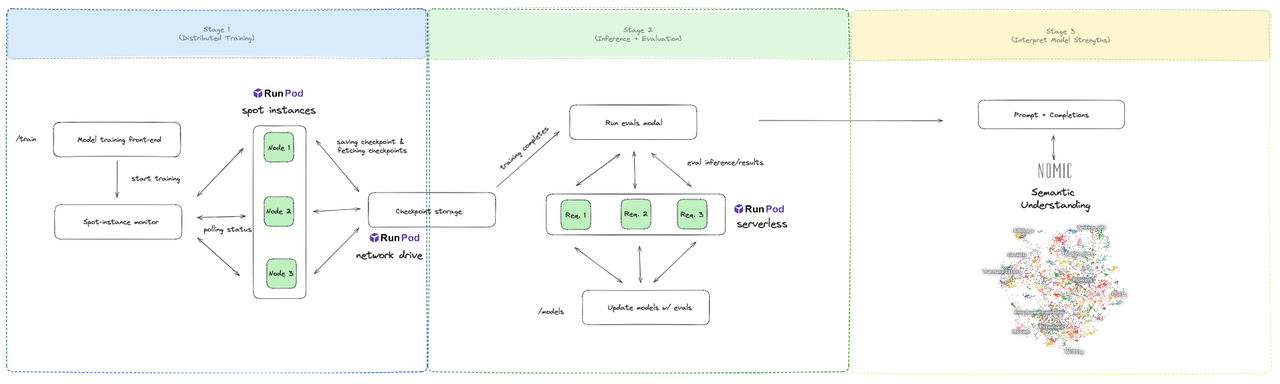
That’s where PodPlex comes in. We integrate with decentralized cloud servers like RunPod and use distribution schemes like fully sharded data parallel to partition large models into shards, which can effectively fit and train on smaller devices. At TreeHacks, our team made an earlier prototype of this on a 4-layer DNN, where he hand-computed gradients and network connections. This past weekend, we focused on scaling this approach to natively integrate with PyTorch, allowing us to expand to more architectures without rewriting symbolics ourselves.
- Train machine learning models across distributed spot instances with FSDP (Answer.AI implementation).
- Automatic orchestration of Runpod pods for training via a custom Docker image
- Uses Runpod Spot instances + Community Cloud to reduce cloud costs by up to 76% (benchmarked on GTX 4090’s).
- Automatically handles restarts/failed nodes by using checkpoint backups.
- Run eval benchmarks against trained models using Runpod serverless
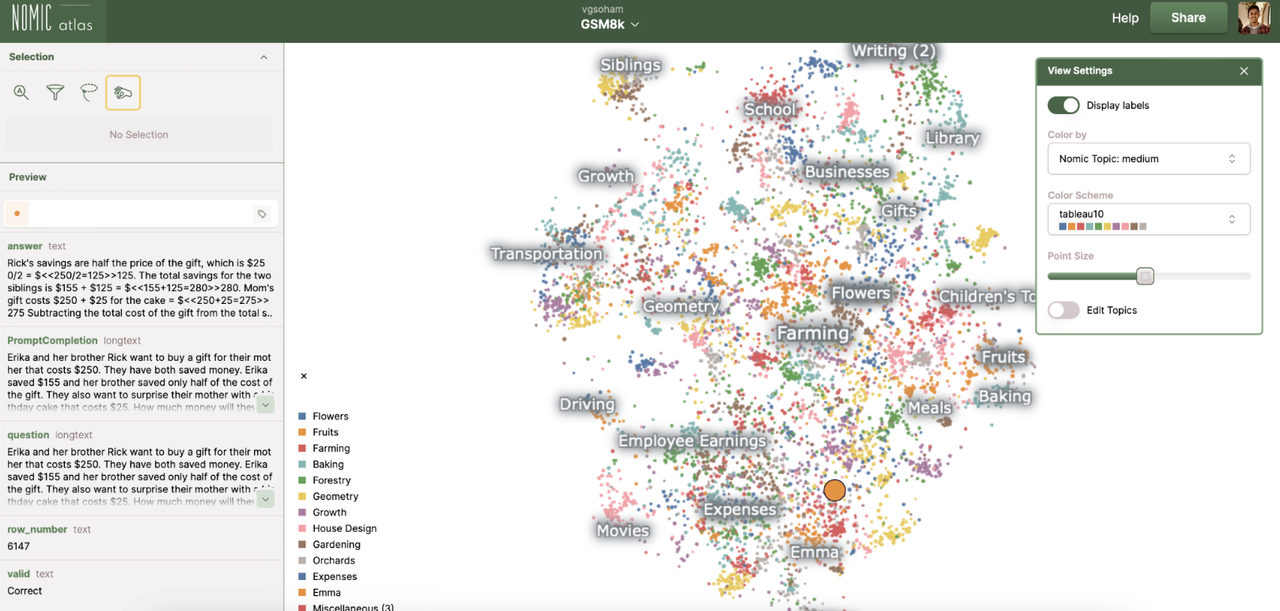
- Visualize evals in Nomic for quick feedback loops
This contains the frontend for podplex, where you can start training and evaluation jobs. Uses Runpod GraphQL API to spin up pods. These pods then use custom docker images (defined by the Dockerfile) to train the model.
AWS lambda code for checking spot instance health and restarting pods if any shut down.
Uses Fully Sharded Data Parallel methodology to train across multiple GPUs (see AnswerDotAI implementation). These pods use custom docker images to train the model.
AWS lambda code that determines whether or not the fault_tolerance lambda should run. It accomplishes this by enabling and disabling an EventBridge rule.
Runpod Serverless endpoint with vLLM’s for inference
Runpod Serverless endpoint with torch inference + experiments
Start training with fsdp/train_llama.py. Sample training command:
python train_llama.py \
--model_name meta-llama/Meta-Llama-Guard-2-8B \
--batch_size 2 \
--context_length 512 \
--precision bf16 \
--train_type qlora \
--use_gradient_checkpointing true \
--use_cpu_offload true \
--dataset alpaca \
--reentrant_checkpointing true
Note, that you need to request access from the Llama Page on HuggingFace to access the model.