-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
Metadata API data structures
TODO
- add logical/domain model (updated version of https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S0167642314002925-gr004.jpg)
- describe namespaces (from https://app.assembla.com/spaces/crce/wiki/Metadata_API_model)
- list existing defined namespaces (from https://app.assembla.com/spaces/crce/wiki/Metadata_logical_definition_overview)
CRCE metadata API represents basic objects which are used and maintained inside of CRCE. Logical relations between those artefacts can be seen on this diagram (for more informations about implementation, please see javadoc which could be generated during build):
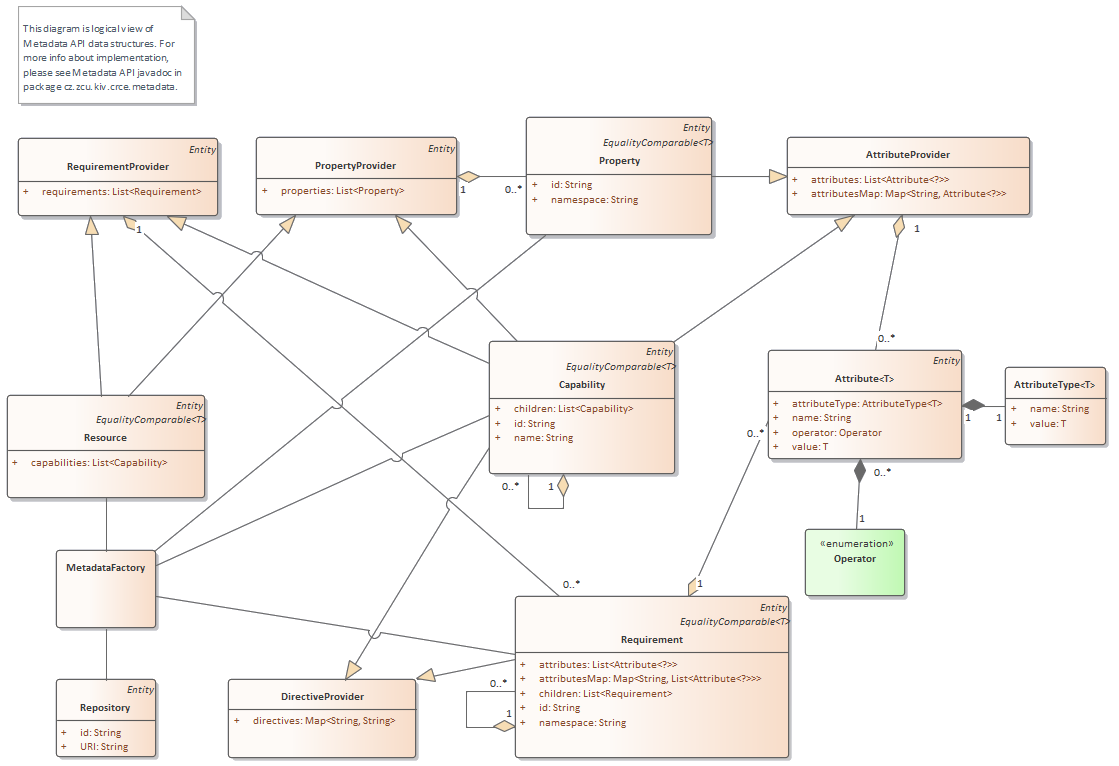
All objects marked with label Entity extends Entity interface.
Property, Capability, Requirement and Resource also implement EqualityComparable interface which enables deeper comparation.
-
Resource- artifact which is uploaded, indexed and stored inside of CRCE -
Property- property of given Resource -
Capability- properties which are provided by given Resource -
Requirement- properties which are required by given Resource -
Attribute- represents one attribute of given metadata type-
AttributeType- information about data type ofAttribute
-
-
Store- object which stores all metadatas -
MetadataFactory- object which provides creation of metadatas
If plugin has to be able to store metadata, it has to implement MetadataDao interface from core/crce-metadata-dao-api. There is currently primarly used MongoDB database engine as storage unit which has DAO implementation in core/crce-metadata-dao-mongodb module. MetadataDao interface is implemented by class BaseMongoDao. This class handles all work with the database. Mapping between stored format and system format is handled by mappers in mapper package. These mappers are using objects from db package to map results from DB to system objects or system objects to DB queries.
[ CRCE wiki ]