TabBench is a new benchmark built to evaluate machine learning models on tabular data, focusing on real-world industry use cases.
TabBench addresses a critical gap: traditional benchmarks tend to rely on public, academic datasets that are clean and carefully curated. While useful for research, they fail to reflect the imperfect nature of private enterprise data.
To bridge this gap, TabBench introduces a new evaluation framework focused on real industry use cases. It enables a meaningful comparison of models specifically designed to address concrete business problems across sectors, starting with the domain of Commerce.
Commerce organizations rely heavily on tabular data that is complex, messy and highly-dimensional: structured datasets like product catalogs, transaction histories, and customer records power core business operations and decisions. TabBench is specifically designed to assess ML models on critical industry tasks that we might encounter in the Commerce sector, such as product categorization, deduplication and more. Its goal is to equip data science teams with the tools they need to identify and develop the most effective and powerful ML models tailored to their unique use cases.
With TabBench, you get:
- Industry-focused use cases with standardized workflows: Target critical production problems through streamlined workflows featuring consistent preprocessing, training, and evaluation steps allowing reproducible and fair comparison of all models.
- Evaluation on Industrial & Academic datasets:
- Assess models on proprietary industry datasets.*
- Complementary evaluation on selected academic datasets for comprehensive comparison.
- Performance tracking: Easily identify top-performing tabular models via the TabBench Dashboard.
- Neuralk Foundry: TabBench is built on top of Neuralk Foundry, a modular framework designed to help you quickly build and experiment with your own workflows.Explore here
*If you wish to become a partner company, please see the Contact section.
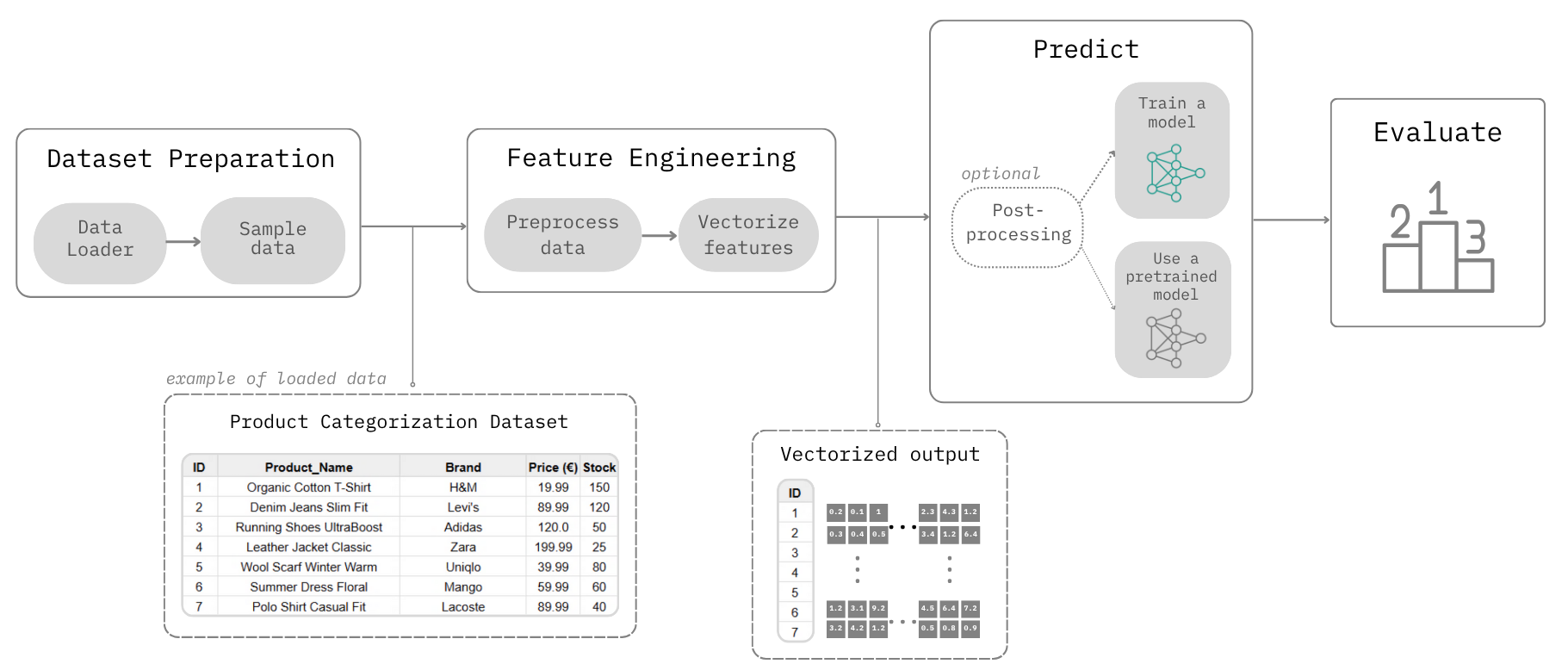
TabBench employs a modular approach to address various use cases. Each task is broken down into a sequence of steps, organized into a Workflow. Below is a visual representation of a TabBench Workflow for any given dataset and use case:
The TabBench Workflow is divided into 4 main steps:
- Load: Loads the data, defines the use case (e.g., Product Categorization), and splits the data accordingly.
- Vectorize: Performs necessary preprocessing and converts data entries into vector embeddings.
- Predict: Applies a model to the vectorized data. This step can involve training a new model or using a pre-trained one from a selection of choices. Post-processing may also occur depending on the selected model.
- Evaluate: Assesses the accuracy and performance of the Predict step.
To get quickly started with a TabBench Workflow, you can jump straight into our example notebooks:
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 - Getting Started with TabBench | Discover how TabBench works and train your first tabular model on a Product Categorization task. |
| 2 - Adding a local or internet dataset | How to add your own datasets for evaluation (local, downloadable, or OpenML). |
| 3 - Use a custom model | How to integrate a new model in TabBench and use it on different use cases. |
| 4 - Tackle the categorisation challenge | A pipeline similar to our private task for you to train your model before submitting it. |
Driven by the above Workflow approach, TabBench is able to handle diverse industry use cases such as:
- Product Categorization: Accurately assigning categories to products coming from catalogs often filled with typos, missing fields, and inconsistent formats.
- (More use cases coming soon!)
With TabBench you can benchmark traditional and state-of-the-art tabular models on:
- Industrial Datasets: Proprietary industry datasets.
- Academic Datasets: Starting with a selection of OpenML datasets, with more academic benchmarks coming soon for fair comparison.
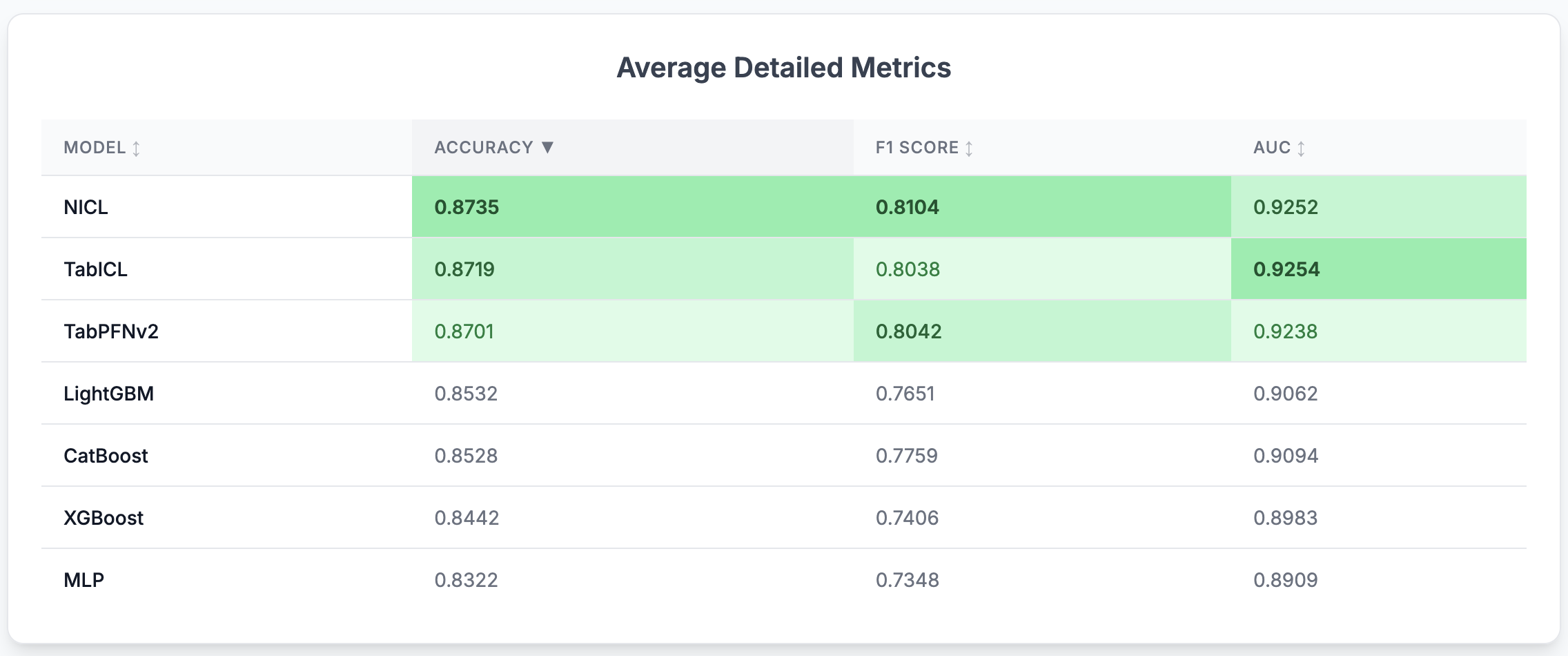
TabBench currently supports the following models, with more additions planned:
- NICL (Neuralk In-Context-Learning): Our in-house foundation model.
- TabICL (Tabular In-Context Learning): A transformer-based model that performs feature compression before doing in-context learning on tabular data by conditioning on labeled support examples to predict unseen queries without task-specific training.
- TabPFNv2: A Transformer-based model that performs in-context learning by approximating Bayesian inference for tabular classification on small datasets.
- XGBoost: An optimized distributed gradient boosting library designed to be highly efficient, flexible, and portable.
- CatBoost: A gradient boosting on decision trees library, particularly strong with categorical features.
- LightGBM: A fast, efficient gradient boosting framework that builds decision trees using histogram-based learning for scalable, high-performance tabular modeling.
- MLP (Multi-Layer Perceptron): A feedforward neural network that models tabular data by learning non-linear interactions between numerical and embedded categorical features.
TabBench currently focuses exclusively on classification and categorization tasks. Academic classification benchmarks are optimized for ROC-AUC, while categorization tasks prioritize the more practical F1-score.
Preprocessing steps vary depending on the model type, following each model’s recommended practices:
- TabPFN, TabICL, and NICL: These models include their own preprocessing pipelines, which we use as-is.
- Tree-based models (XGBoost, CatBoost, LightGBM): Since these models support native handling of categorical features, we apply ordinal encoding to categorical columns and leave numerical values unchanged.
- MLPs: Categorical features are embedded via learned embeddings, while numerical features are standardized using z-score normalization.
Performance is evaluated using a 5-fold stratified shuffle split. For models that require hyperparameter tuning (i.e., tree-based models and MLPs), we conduct 100 Optuna trials on a 5-fold shuffle split of the training set.
Use this option if you just want to run TabBench or use it in your own pipelines without modifying its source code.
$ pip install tabbenchUse this option if you want to explore, modify, or contribute to the codebase, or run local notebooks and experiments.
git clone https://github.com/Neuralk-AI/TabBench
cd TabBenchIt is recommended to build a custom environment. Example with conda:
conda create -n tabbench python=3.10
conda activate tabbenchInstalling the packages in the conda environment (in editable mode):
pip install -e . For those who wish to understand the underlying mechanics, contribute to the development of the industry workflows, or build their own custom solutions, we encourage you to explore Neuralk Foundry. This is the modular framework that powers key aspects of TabBench. You can find the Neuralk Foundry repository and more detailed information here.
If you incorporate any part of this repository into your work, please reference it using the following citation:
@article{neuralk2025tabench,
title={TabBench: A Tabular Machine Learning Benchmark},
author={Neuralk-AI},
year={2025},
publisher = {GitHub},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/Neuralk-AI/TabBench}},
}If you have any questions or wish to propose new features please feel free to open an issue or contact us at alex@neuralk-ai.com.
For collaborations please contact us at antoine@neuralk-ai.com.