-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
Automated Testing
Controllers are a central part of any REST API service. As such, we should have confidence they behave as intended for our application. Automated tests can provide us with this confidence and can detect errors before they reach production.
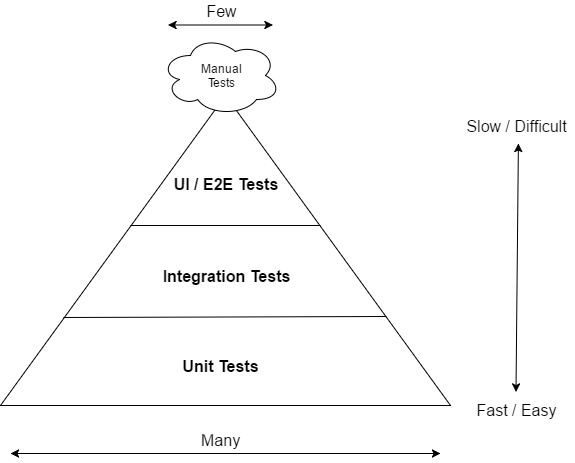
- UI Testing — These tests ensure that proper testing coverage for business logic, corner cases and component interactions with unit and integration tests.
- Integration Testing — These tests ensure that component interactions work as expected against external artifacts like databases and file system.
- Unit Testing — These tests ensure that individual components of the application work as expected.
Integration testing sits in the middle of the automated test pyramid and ensures individual modules and components in our code can be successfully connected to produce the expected behavior. For eg. we have a testRegisterValid method in AccountResourceIT class which located at /src/test/java/com.springboot.rest.web.rest and for that we have validate the user requirement like login,firstname,lastname,password etc.
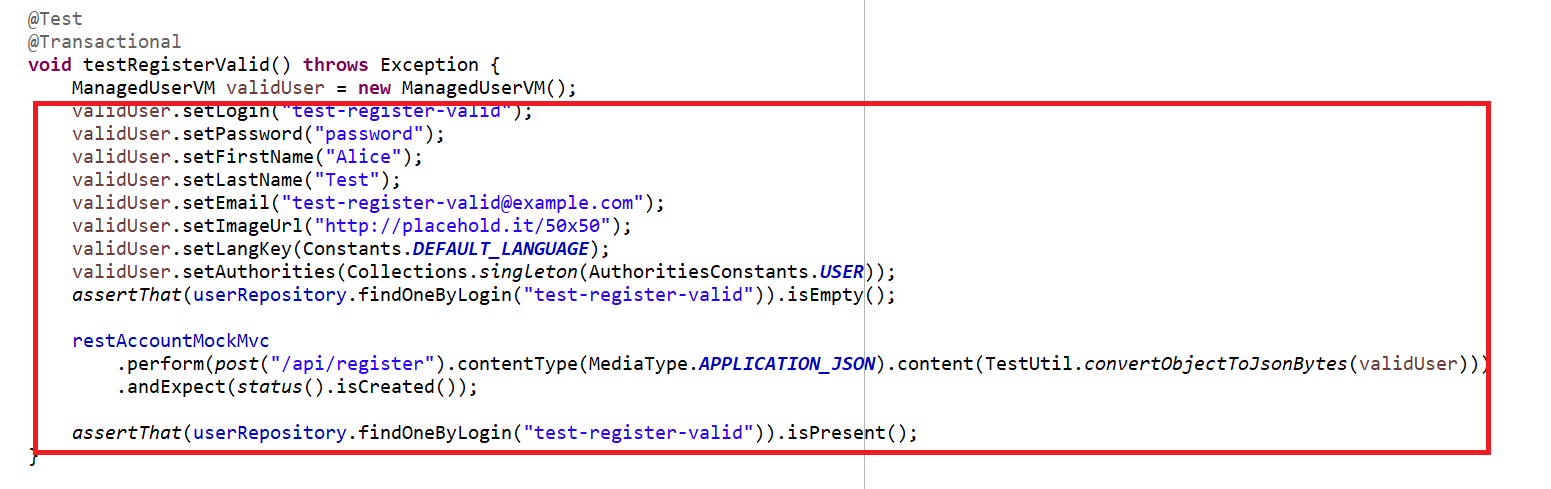
We have add plugins into the build.gradle file
task integrationTest(type: Test) {
useJUnitPlatform()
description = "Execute integration tests."
group = "verification"
include "**/*IT*", "**/*IntTest*"
testLogging {
events 'FAILED', 'SKIPPED'
}
jvmArgs += '-Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -Xmx256m'
if (project.hasProperty('testcontainers')) {
environment 'spring.profiles.active', 'testcontainers'
}
reports.html.enabled = false
}
For Integration Testing You need to run command on terminal
./gradlew test integrationTest jacocoTestReport
Unit testing plays a very important role in making the software more maintainable. Unit tests involve testing a part of an application in isolation from its infrastructure and dependencies. It tests one small piece of functionality in a microservice. The unit represents a unit of work – usually a single method in our code.
The purposes of unit testing are:
- To segregate and test that each part of a program is working as expected.
- To increase confidence while modifying logic when maintaining code.
- To easily identify the defects in an application since unit testing data is closed to production.
- To verify the accuracy of each program unit.
- Right click on application and click on Run as after that click on JUnit Test as shown in below,
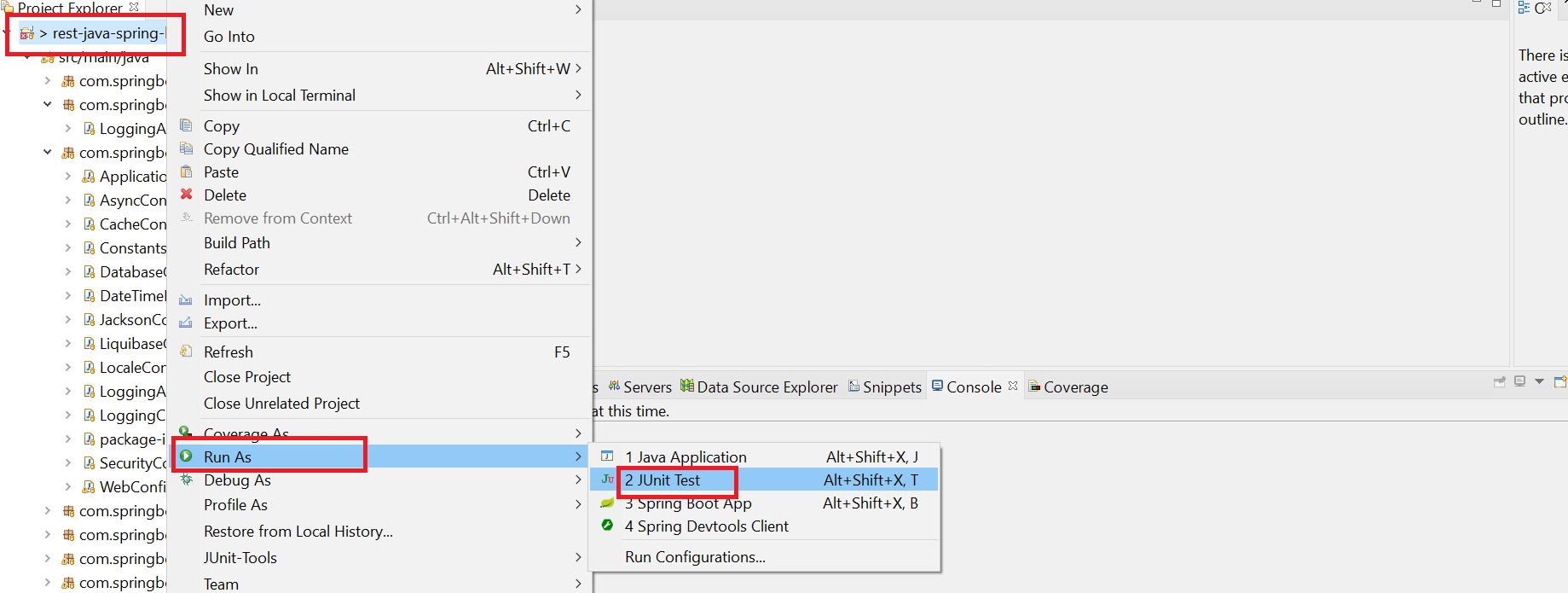
- This will display the list of test case methods.
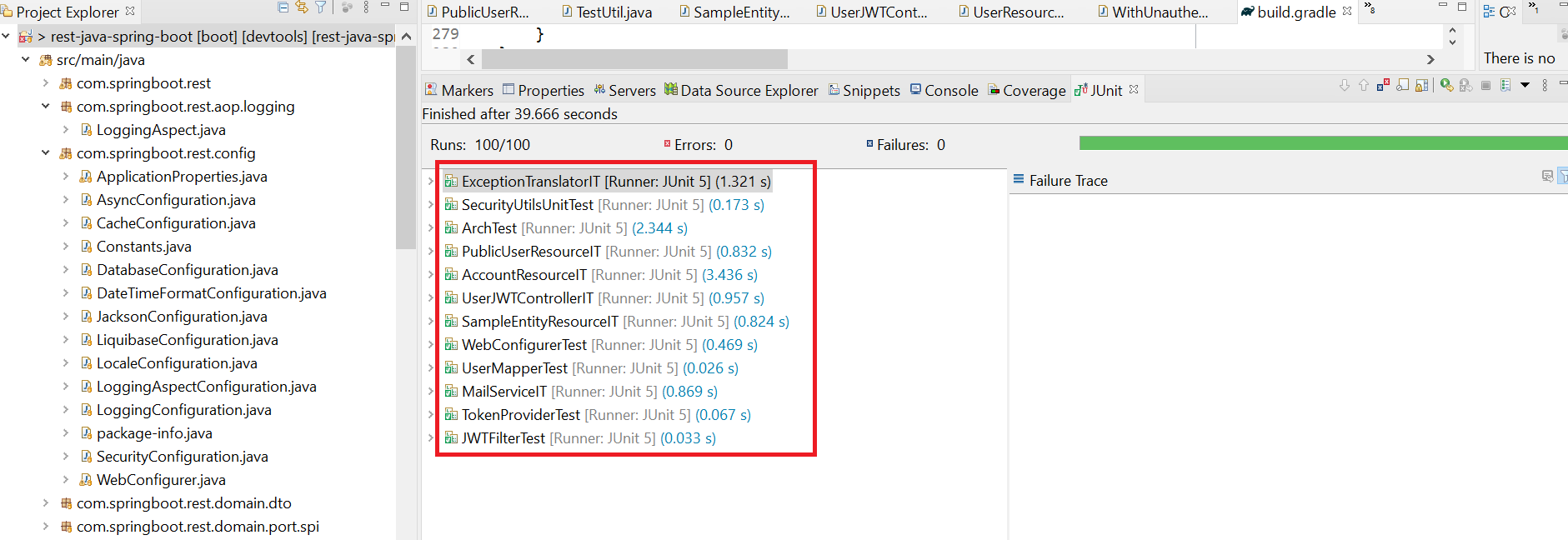
We have also integrated it with sonarCloud. Click here to sign-in(through github account credentials) to sonarCloud and go to Coverage.
It will show code coverage for that test case.