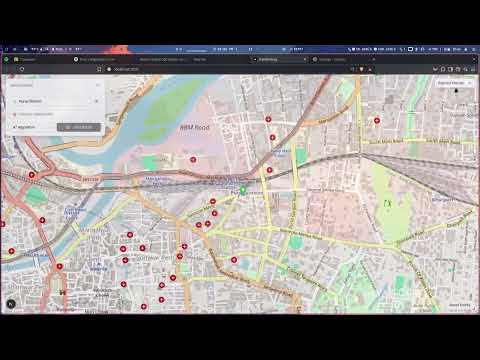
This project implements a Shortest Pathfinding System using Dijkstra's Algorithm and A*. The backend is built with Django, the frontend with Next.js, and the shortest path computation is performed efficiently using file-based caching. The project integrates OpenStreetMap (OSM) data for geospatial mapping and visualization.
project_root/
│── backend/ # Django Backend
│ ├── shortest_path/ # Django Project
│ │ ├── manage.py # Django project manager
│ │ ├── shortest_path/ # Main Django app
│ │ ├── maps/ # Django routes app
│ │ │ ├── models.py # Database models
│ │ │ ├── views.py # API views
│ ├── utils/ # Utils to populate the data into the database
│── frontend/ # Next.js Frontend
│ ├── components/ # React components
│ ├── pages/ # Next.js pages
│ ├── public/ # Static assets
│ ├── styles/ # Global styles
│ ├── utils/ # Helper functions
│ ├── services/ # API calls and integrations
│── docs/ # Documentation
│── README.md # Project documentation
pip install venv
python -m venv venvWindows:
venv\Scripts\activateLinux/macOS:
source venv/bin/activatecd backend
pip install -r requirements.txtDownload PostgreSQL from the official site: https://www.postgresql.org/download/
- Open pgAdmin and create a new database named
pathfindingdb. - Set up environment variables in
.env:
DB_NAME=pathfindingdb
DB_USER=your_username
DB_PASSWORD=your_password
DB_HOST=localhost
DB_PORT=5432- Apply migrations:
python manage.py migrateRun the following utility script:
python backend/utils/util_pune.pyThis will populate the database with geospatial data.
Download and install Node.js from https://nodejs.org/.
cd frontend
npm installCreate a .env.local file in the frontend directory:
NEXT_PUBLIC_API_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8000/apinpm run devThe Next.js application will be available at http://localhost:3000/.
- Interactive Map: Displays OpenStreetMap with path visualization.
- Shortest Path Calculation: Users can select two points, and the shortest path is computed and displayed.
- Live Updates: The frontend dynamically fetches routes from the backend API.
- Custom Markers: Start and end points are marked on the map.
- Mobile-Friendly UI: Responsive design for mobile and desktop users.
We use Django’s file-based caching to cache graph data and prevent repeated database reads, speeding up the algorithm.
- Graph Data Caching:
- An adjacency list representation of the graph is cached in the filesystem.
- If cache is missing or expired, data is loaded from the database and cached again.
# settings.py
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.filebased.FileBasedCache',
'LOCATION': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'graph_cache'),
}
}Make sure the graph_cache/ directory exists and is writable.
from django.core.cache import cache
def load_graph():
graph = cache.get("graph_data")
if graph:
return graph
# Load graph from DB if not cached
nodes = Node.objects.all()
edges = Edge.objects.all()
graph = {node.id: [] for node in nodes}
for edge in edges:
graph[edge.start_node_id].append((edge.end_node_id, edge.weight))
graph[edge.end_node_id].append((edge.start_node_id, edge.weight))
cache.set("graph_data", graph)
return graph- Optimizing pathfinding by integrating Dijkstra directly into PostgreSQL using recursive SQL queries.
- Implementing an API to fetch routes dynamically from the frontend.
- Enhancing UI with interactive map features using MapLibre GL JS.
- Backend: Django, Django REST Framework
- Frontend: Next.js, React, MapLibre GL JS
- Database: PostgreSQL + PostGIS
- Pathfinding: Dijkstra’s Algorithm, A*
- Geospatial Data: OpenStreetMap (OSM), GeoJSON
- Caching: Django File-Based Caching
- Prasangeet Dongre (B23CH1033) - Project Lead
- Prakhar Chauhan (B23BB1032)
- Rajas Kadu (B23CH1039)
- Mayuri R. Pujari (B23ES1026)