Spark Structured Streaming stream to stream joins and aggregations can be complicated to reason about and implement. In addition, you need to take into account watermarks to ensure streaming state is cleaned up appropriately and avoid runaway state growth. However, if we land streaming data in Delta tables first, we can then use Change Data Feed (CDF) to perform incremental stream to stream joins and incremental aggregations without needing watermarks and reducing complexity in reasoning about these operations. This framework provides an API which looks like a familiar pyspark dataframe API, and implements such capability. Using standard Databricks Delta Medallion architecture, you can start by landing streaming data in bronze a table at a time and then perform incremental joins and aggregations downstream in silver and/or gold tables.
StreamJoin is a framework for running incremental joins and aggregation over structured streaming CDF feeds from Delta tables. It allows you to have data streaming in from anywhere and landing as tables in Databricks Delta and then have streaming incremental joins and aggregation happening downstream from Delta Bronze or Silver layers.
An example in python:
%run "StreamJoin"
c = (
Stream.fromPath(f'{silver_path}/customers')
.primaryKeys('customer_id')
.sequenceBy('customer_operation_date')
)
t = (
Stream.fromPath(f'{silver_path}/transactions')
.primaryKeys('transaction_id')
.sequenceBy('operation_date')
)
j = (
t.join(c, 'left')
.onKeys('customer_id')
.groupBy("customer_id")
.agg(F.sum("amount").alias("total_amount"))
.writeToPath(f'{gold_path}/aggs')
.option("checkpointLocation", f'{checkpointLocation}/gold/aggs')
.queryName(f'{gold_path}/aggs')
.start()
)
or
%run "StreamJoin"
c = (
Stream.fromPath(f'{silver_path}/customers')
.primaryKeys('customer_id')
.sequenceBy('customer_operation_date')
)
t = (
Stream.fromPath(f'{silver_path}/transactions')
.primaryKeys('transaction_id')
.sequenceBy('operation_date')
)
j = (
t.join(c, 'left')
.on(t['customer_id'] == c['customer_id'])
.groupBy("customer_id")
.agg(F.sum("amount").alias("total_amount"))
.writeToPath(f'{gold_path}/aggs')
.option("checkpointLocation", f'{checkpointLocation}/gold/aggs')
.queryName(f'{gold_path}/aggs')
.start()
)
Unique primary keys (.primaryKeys()) are required per table for joins to ensure incremental merges have unique keys to merge on.
Sequence columns (.sequenceBy()) is optional to ensure correct ordered processing/merging on rows from CDF, with the same primary key, based on order of sequence column, if not provided one of the rows is randomly picked for duplicate primary keys.
To use it put
%run "StreamJoin"
at the top of your Notebook.
The diagram below depicts the operation steps assuming the following conceptual example:
c = (
Stream.fromPath(f'{silver_path}/customers')
.primaryKeys('customer_id')
.sequenceBy('customer_operation_date')
)
t = (
Stream.fromPath(f'{silver_path}/transactions')
.primaryKeys('transaction_id')
.sequenceBy('operation_date')
)
o = (
Stream.fromPath(f'{silver_path}/orders')
.primaryKeys('order_id')
.sequenceBy('order_operation_date')
)
p = (
Stream.fromPath(f'{silver_path}/products')
.primaryKeys('product_id')
.sequenceBy('product_operation_date')
)
j = (
c.join(t, 'right')
.onKeys('customer_id')
.join(o, 'left')
.onKeys('transaction_id')
.join(p)
.onKeys('product_id')
.groupBy("customer_id")
.agg(F.sum("amount").alias("total_amount"))
.writeToPath(f'{gold_path}/aggs')
.option("checkpointLocation", f'{checkpointLocation}/gold/aggs')
.queryName(f'{gold_path}/aggs')
.start()
)
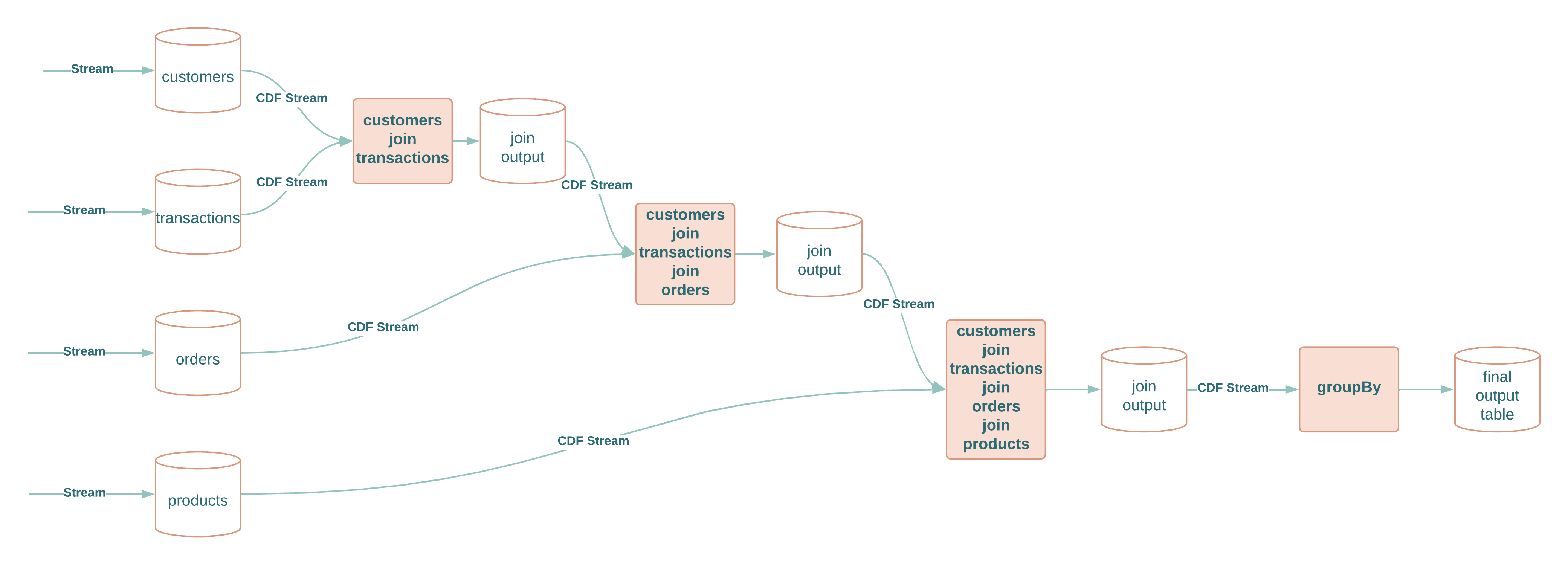 Each 2 way join and aggregation outputs an intermediate Delta table of that join or aggregation and CDF stream from that table is used as input into the following join or aggregation, except for the last one which writes out the resulting Delta table.
The joins and aggregations are done incrementally for each streaming microbatch. The microbatch readStream is configured with maxBytesPerTrigger option of 1GB to ensure each microbatch can be broadcast for the join thereby avoiding shuffle where possible and ensuring file and partition pruning taking effect for joins.
Each 2 way join and aggregation outputs an intermediate Delta table of that join or aggregation and CDF stream from that table is used as input into the following join or aggregation, except for the last one which writes out the resulting Delta table.
The joins and aggregations are done incrementally for each streaming microbatch. The microbatch readStream is configured with maxBytesPerTrigger option of 1GB to ensure each microbatch can be broadcast for the join thereby avoiding shuffle where possible and ensuring file and partition pruning taking effect for joins.
You can run tests by running RunTests Notebook. Each new run uses functions in GenerateData Notebook to generate new customer, transaction, orders, and products tables first.