Microeconomics/macroeconomics graphs made with ggplot2
This package allows creating microeconomics or macroeconomics charts in R with simple functions. This package inspiration is reconPlots by Andrew Heiss.
THE PACKAGE IS UNDER HEAVY DEVELOPMENT. WORK IN PROGRESS. You can suggest ideas by submitting an Issue
- Finish documentation
- Price control (in
sdcurvefunction) - Allow drawing custom functions
- Add graph for budget constraints
- Fix
linecolargument - Tax graph
- Shade producer and consumer surplus
- Add Edgeworth box
- General equilibrium (suggested by Ilya)
- Prospect theory value function (suggested by @brshallo)
- Neoclassical labor supply (suggested by @hilton1)
- Installation
- Supply curve
- Demand curve
- Supply and demand
- Neoclassical labor supply
- Indifference curves
- Production–possibility frontier
- Tax graph
- Prospect Theory value function
- Laffer curve
- Calculating the intersections
- Citation
# Install the development version from GitHub:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("R-CoderDotCom/econocharts")The package will be on CRAN as soon as possible
supply() # Default plotsupply(ncurves = 1, # Number of supply curves to be plotted
type = "line", # Type of the curve
x = c(2, 4, 5), # Y-axis values where to create intersections
linecol = 2, # Color of the curves
geom = "label", # Label type of the intersection points
geomfill = "pink", # If geom = "label", is the background color of the label
main = "Supply curve") # Title of the plotsupply(ncurves = 3, # Three supply curves
xlab = "X", # X-axis label
ylab = "Y", # Y-axis label
bg.col = "lightblue") # Background colordemand(x = 3:6, # Intersections
generic = FALSE) # Axis values with the actual numbersdemand(main = "Demand", # Title
sub = "curve", # Subtitle
xlab = "X", # X-axis label
ylab = "Y", # Y-axis label
names = "D[1]", # Custom name for the curve
geomcol = 2) # Color of the custom name of the curvesdcurve() # Default supply and demand plot# Custom data
supply1 <- data.frame(x = c(1, 9), y = c(1, 9))
supply1
demand1 <- data.frame(x = c(7, 2), y = c(2, 7))
demand1
supply2 <- data.frame(x = c(2, 10), y = c(1, 9))
supply2
demand2 <- data.frame(x = c(8, 2), y = c(2, 8))
demand2
p <- sdcurve(supply1, # Custom data
demand1,
supply2,
demand2,
equilibrium = TRUE, # Calculate the equilibrium
bg.col = "#fff3cd") # Background color
p + annotate("segment", x = 2.5, xend = 3, y = 6.5, yend = 7, # Add more layers
arrow = arrow(length = unit(0.3, "lines")), colour = "grey50")neolabsup(x = c(2, 3, 5, 7), xlab = "Quantity of\n labor supplied", ylab = "Wage rate")indifference() # Default indifference curveindifference(ncurves = 2, # Two curves
x = c(2, 4), # Intersections
main = "Indifference curves",
xlab = "Good X",
ylab = "Good Y",
linecol = 2, # Color of the curves
pointcol = 2) # Color of the intersection pointsp <- indifference(ncurves = 2, x = c(2, 4), main = "Indifference curves", xlab = "Good X", ylab = "Good Y")
int <- bind_rows(curve_intersect(data.frame(x = 1:1000, y = rep(3, nrow(p$curve))), p$curve + 1))
p$p + geom_segment(data = int, aes(x = 0, y = y, xend = x, yend = y), lty = "dotted") +
geom_segment(data = int, aes(x = x, y = 0, xend = x, yend = y), lty = "dotted") +
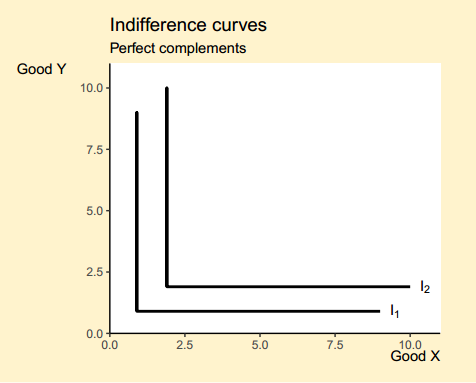
geom_point(data = int, size = 3)indifference(ncurves = 2, # Two curves
type = "pcom", # Perfect complements
main = "Indifference curves",
sub = "Perfect complements",
xlab = "Good X",
ylab = "Good Y",
bg.col = "#fff3cd", # Background color
linecol = 1) # Color of the curveindifference(ncurves = 5, # Five curves
type = "psubs", # Perfect substitutes
main = "Indifference curves",
sub = "Perfect substitutes",
xlab = "Good X",
ylab = "Good Y",
bg.col = "#fff3cd", # Background color
linecol = 1) # Color of the curveppf(x = 1:6, # Intersections
main = "PPF",
geom = "text",
generic = TRUE, # Generic axis labels
xlab = "X",
ylab = "Y",
labels = 1:6,
acol = 3)$pp <- ppf(x = 4:6, # Intersections
main = "PPF",
geom = "text",
generic = TRUE, # Generic labels
labels = c("A", "B", "C"), # Custom labels
xlab = "BIKES",
ylab = "CARS",
acol = 3) # Color of the area
p$p + geom_point(data = data.frame(x = 5, y = 5), size = 3) +
geom_point(data = data.frame(x = 2, y = 2), size = 3) +
annotate("segment", x = 3.1, xend = 4.25, y = 5, yend = 5,
arrow = arrow(length = unit(0.5, "lines")), colour = 3, lwd = 1) +
annotate("segment", x = 4.25, xend = 4.25, y = 5, yend = 4,
arrow = arrow(length = unit(0.5, "lines")), colour = 3, lwd = 1)Original function by Andrew Heiss.
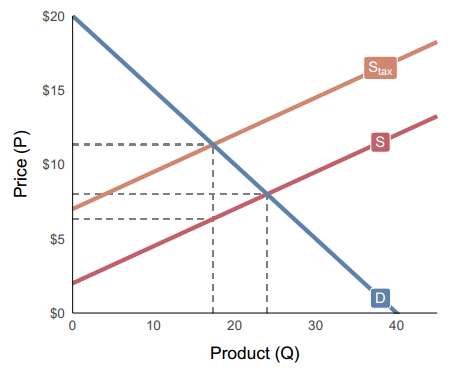
# Data
demand <- function(Q) 20 - 0.5 * Q
supply <- function(Q) 2 + 0.25 * Q
supply_tax <- function(Q) supply(Q) + 5
# Chart
tax_graph(demand, supply, supply_tax, NULL)# Chart with shaded areas
tax_graph(demand, supply, supply_tax, shaded = TRUE)ptvalue(sigma = 0.88, # From Tversky & Kahneman, 1992
lambda = -2.25, # From Tversky & Kahneman, 1992
col = 2, # Color of the curve
xint = seq(0, 75, 25), # Intersections
xintcol = 4, # Color of the intersection segments
ticks = TRUE, # Display ticks on the axes
xlabels = TRUE, # Display the X-axis tick labels
ylabels = TRUE, # Display the Y-axis tick labels
by_x = 25, by_y = 50, # Axis steps
main = "Prospect Theory Value Function")laffer(ylab = "T", xlab = "t",
acol = "lightblue", # Color of the area
pointcol = 4) # Color of the maximum pointlaffer(xmax = 20, # Modify the curve
t = c(3, 6, 9), # Intersections
generic = FALSE,
ylab = "T",
xlab = "t",
acol = "lightblue", # Color of the area
alpha = 0.6, # Transparency of the area
pointcol = 4) # Color of the maximum point
The functions above can have a limited functionality if you want a fully customized plot. The curve_intersection function allows you to calculate the intersection points between two curves. You can use this function to create your custom charts.
Credits to Andrew Heiss for this function and examples.
# Curves
curve1 <- data.frame(Hmisc::bezier(c(1, 8, 9), c(1, 5, 9)))
curve2 <- data.frame(Hmisc::bezier(c(1, 3, 9), c(9, 3, 1)))
# Calculate the intersections
curve_intersection <- curve_intersect(curve1, curve2)
# Create the chart
ggplot(mapping = aes(x = x, y = y)) +
geom_line(data = curve1, color = "red", size = 1) +
geom_line(data = curve2, color = "blue", size = 1) +
geom_vline(xintercept = curve_intersection$x, linetype = "dotted") +
geom_hline(yintercept = curve_intersection$y, linetype = "dotted") +
theme_classic()Specify a X-axis range and set empirical = FALSE.
# Define curves with functions
curve1 <- function(q) (q - 10)^2
curve2 <- function(q) q^2 + 2*q + 8
# X-axis range
x_range <- 0:5
# Calculate the intersections between the two curves
curve_intersection <- curve_intersect(curve1, curve2, empirical = FALSE,
domain = c(min(x_range), max(x_range)))
# Create your custom plot
ggplot(data.frame(x = x_range)) +
stat_function(aes(x = x), color = "blue", size = 1, fun = curve1) +
stat_function(aes(x = x), color = "red", size = 1, fun = curve2) +
geom_vline(xintercept = curve_intersection$x, linetype = "dotted") +
geom_hline(yintercept = curve_intersection$y, linetype = "dotted") +
theme_classic()To cite package ‘econocharts’ in publications use:
José Carlos Soage González and Andrew Heiss (2020). econocharts: Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Charts Made with 'ggplot2'. R package version 1.0.
https://r-coder.com/, https://r-coder.com/economics-charts-r/.
A BibTeX entry for LaTeX users is
@Manual{,
title = {econocharts: Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Charts Made with 'ggplot2'},
author = {José Carlos {Soage González} and Andrew Heiss},
year = {2020},
note = {R package version 1.0},
url = {https://r-coder.com/, https://r-coder.com/economics-charts-r/},
}
- Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/RCODERweb
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/RCoderWeb