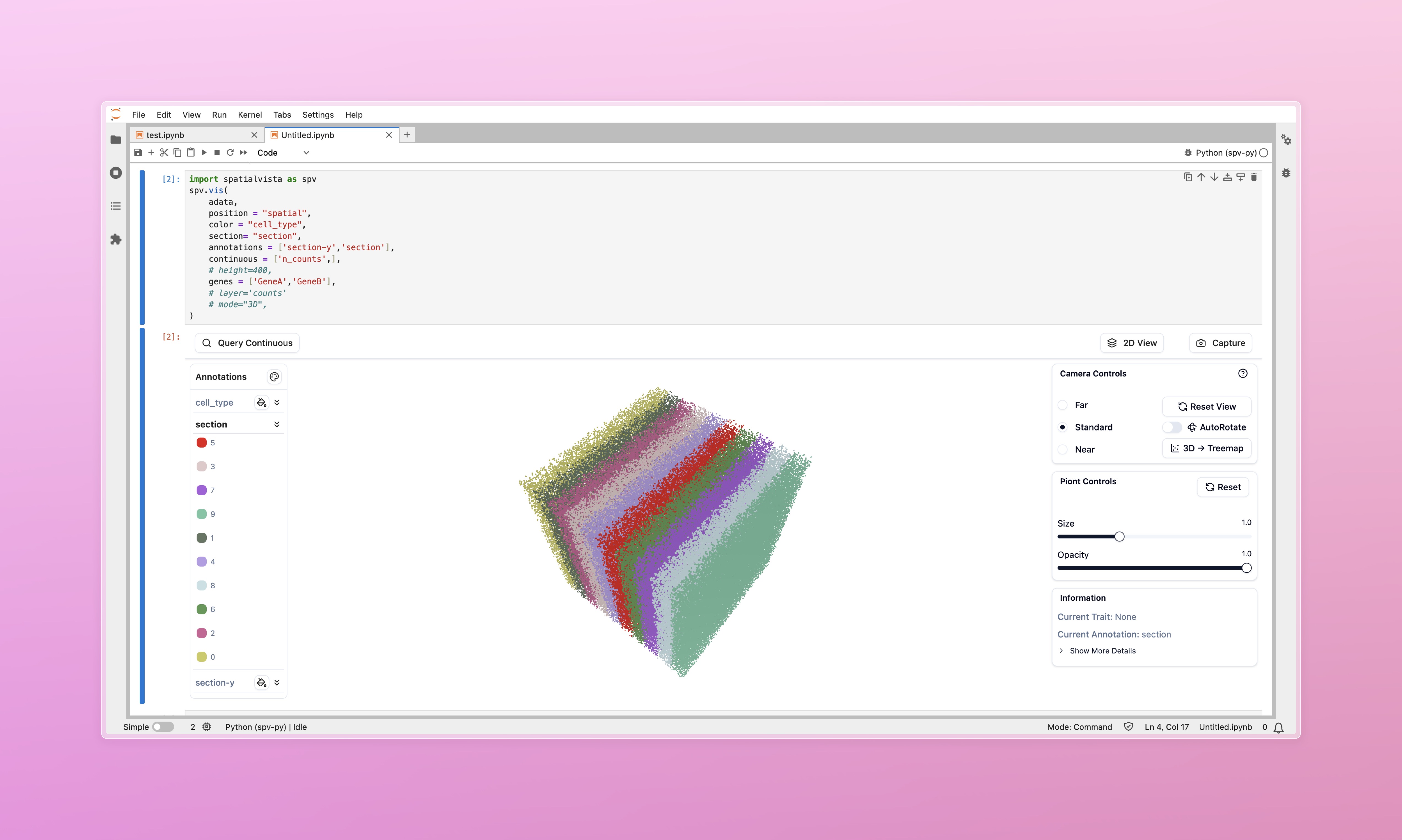
SpatialVista is an interactive 3D spatial transcriptomics visualization tool designed specifically for Jupyter Notebook/Lab. It seamlessly integrates into your data analysis workflow, providing efficient and intuitive exploration of spatial omics data.
- 🚀 High-Performance Rendering - WebGL-based 3D rendering supporting millions of cells
- 📊 Multi-Dimensional Data Display - Support for categorical annotations, continuous values, gene expression, and more
- 🎨 Interactive Controls - Real-time adjustment of colors, transparency, point size, and other parameters
- 🔬 2D/3D View Switching - Flexible switching between 3D point cloud and 2D slice views
- 🧬 Gene Expression Query - Quick visualization of spatial expression patterns for any gene
- 📐 Multiple Layout Modes - Support for original coordinates, 2D Treemap, histogram, and more
- 🎯 Precise Filtering - Filter data points by category, numerical range, and other conditions
- 💾 One-Click Screenshots - Easily save current views for publications and reports
SpatialVista is particularly suitable for:
- Spatial Transcriptomics Data Exploration - Visium, MERFISH, seqFISH, STARmap, and other technologies
- Single-Cell Spatial Data Analysis - Visualize spatial distribution of cell types
- Tissue Architecture Studies - Explore molecular features of tissue regions
- Gene Expression Pattern Analysis - View spatial expression of specific genes
- Data Quality Control - Quickly check data integrity and outliers
pip install spatialvistaLaunch your jupyter notebook or jupyter lab. And play with SpatialVista!
import spatialvista as spv
import numpy as np
# Create minimal test data
class FakeAnnData:
def __init__(self, n: int):
self.obsm = {"spatial": np.random.rand(n, 3)}
self.obs = {"celltype": np.random.choice(["A", "B", "C"], n)}
self.var_names = []
self.X = None
self.n_obs = n
adata = FakeAnnData(n=10_000)
# Create visualization
spv.vis(adata, position="spatial", color="celltype")
import scanpy as sc
# Load yout real data
adata = sc.read_h5ad("spatial_data.h5ad")
# Create interactive visualization
spv.vis(
adata,
position="spatial", # obsm key containing spatial coordinates
color="celltype", # Default annotation for coloring
height=600 # Widget height in pixels
)That's it! 🎉
# Color by cell type
widget = spv.vis(
adata,
position="spatial",
color="celltype",
annotations=["leiden", "tissue_region"] # Additional annotations to load
)# Visualize continuous values (e.g., QC metrics)
widget = spv.vis(
adata,
position="spatial",
color="celltype",
continuous=["total_counts", "n_genes"] # Continuous value fields
)# View expression patterns of specific genes
widget = spv.vis(
adata,
position="spatial",
color="celltype",
genes=["Pecam1", "Cd3e", "Epcam"], # Gene list
layer="normalized" # Optional: use specific layer if available
)# If data has section information, switch to 2D view in UI
widget = spv.vis(
adata,
position="spatial",
color="celltype",
section="slice_id", # Section identifier field for section browser
)Once displayed, the widget provides rich interactive controls for exploring your data:
- Navigate in 3D space (rotate, pan, zoom)
- Switch between annotations and customize colors
- Query continuous values and gene expression
- Filter by thresholds and hide specific categories
- Adjust visualization parameters (size, opacity, layout)
- Export screenshots
Issues and Pull Requests are welcome!
- GitHub: https://github.com/JianYang-Lab/spatial-vista-py
- Documentation: https://spatial-vista-py.readthedocs.io
SpatialVista is open-sourced under the MIT License.
Built with ❤️ by WenjieWei@YangLab