We give the disjoint training and test sets used, which can be viewed by running Demo_show_training_testing.m. We also give the classification result maps of the proposed RC-3DSSA.
RC-3DSSA.zip contains the code for our method. The code uses disjoint IP as a data example, and you can run Demo_RC3DSSA.m directly to see the results.
For detailed classification accuracy, please see: H. Fu, G. Sun, L. Zhang, A. Zhang, J. Ren, X. Jia, et al., "Three-dimensional singular spectrum analysis for precise land cover classification from UAV-borne hyperspectral benchmark datasets," ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, vol. 203, pp. 115-134, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.07.013.
BaiduCloud: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1uWKr2bcetF53_OLd08rovg (extraction code: 1234)
Zenodo: https://zenodo.org/record/8223066
Qingdao UAV-borne HSI (QUH) dataset consists of three sub-datasets: QUH-Tangdaowan, QUH-Qingyun, and QUH-Pingan, which are freely available as benchmarks for precise land cover classification.
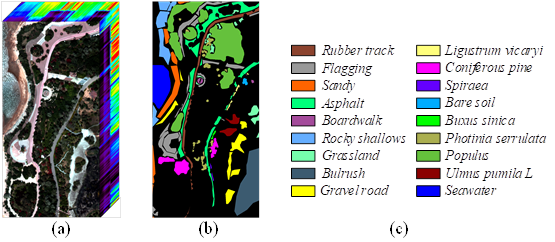
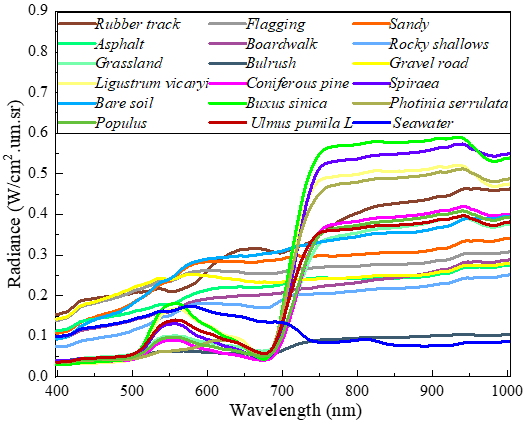
The QUH-Tangdaowan dataset: it contains a variety of irregular land covers with very similar spectral curves, such as four vegetation species: Coniferous pine, Buxus sinica, Populus, Ulmus pumila L, and three pavements: Flagging, Boardwalk, Gravel road, which undoubtedly poses a great challenge for precise classification.
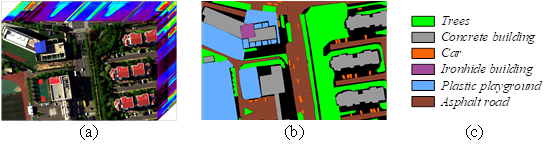
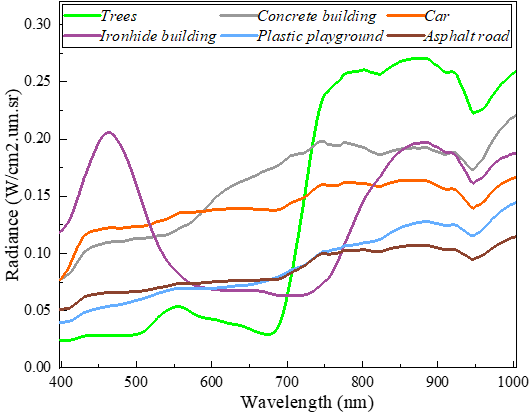
The QUH-Qingyun dataset: it has areas obscured by building shadows, including classes such as Trees, Car, and Asphalt road. The interference of shadows can significantly reduce the accuracy of identification and can be used to assess the robustness of the classification methods.
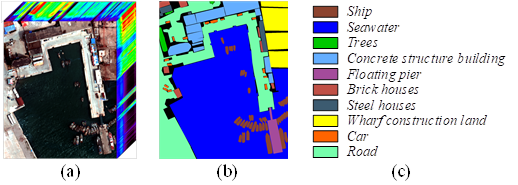
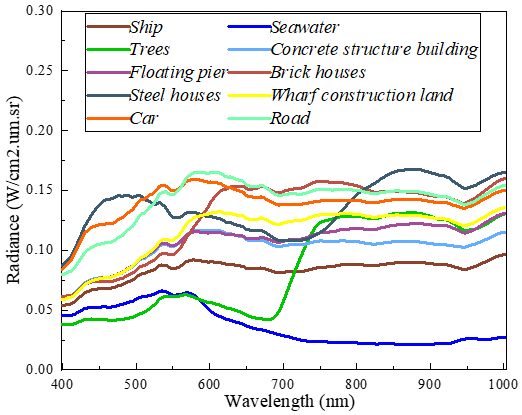
The QUH-Pingan dataset: it has a relatively regular distribution of land cover, but there are large differences in size: Seawater, Road at large scales, Trees, Floating pier, Brick houses, Steel houses at medium scales, and Ship, Car at small scales, which are the most difficult to identify. This dataset can be used to assess the ability of classification methods to portray targets at different scales.