Easy to use and ready-to-go ASP.NET Core services for Azure
Startup.cs
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddDenevCloudAzure()
.UseVirtualMachines()
.UseKeyVaults()
.UseAzureDNS();
}appsettings.json
"DenevCloud": {
"tenant_id": "tenant_id",
"subscription_id": "subscriptionId",
"VM_client_id": "VMclient_id",
"VM_client_sercet": "VMclient_sercet",
"VM_resource": "https://management.core.windows.net/",
"VM_resource_group": "VMResourceGroup",
"keyVault_client_id": "KeyVault_clientId",
"keyVault_client_secret": "KeyVault_clientSecret",
"keyVault_endpoint": "KeyVault_endpoint",
"DNS_client_id": "DNS_clientId",
"DNS_secret": "DNS_secret",
"DNS_resource_group": "DNS_resourceGroupName",
"DNS_zone_location": "DNS_ZoneLocation",
"DNS_zone_name": "DNS_zoneName"
}Note: In KeyVault_endpoint you should enter only the endpoint name not the whole link (https://my-endpoint.vault.azure.net/ => KeyVault_endpoint : my-endpoint) Note: It's recommended to use different App Registration for each resource
Index.cshtml
@using DenevCloud.AspNetCore.Services.Azure.VirtualMachines
@using DenevCloud.AspNetCore.Services.Azure.VirtualMachines.NetworkInterfaces
@inject IVMManager vmManager
@inject INetworkInterfaceManager netManager
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Home Page";
var vm = vmManager.GetVirtualMachine("Your_VM_Name");
}
<div class="text-center">
<h1 class="display-4">Welcome</h1>
<p>Name: @vm.Name</p>
<p>Location: @vm.Location</p>
<p>Public Ipv4: @netManager.GetListPublicIpv4(vm).First()</p>
<p>Public Ipv6: @netManager.GetListPublicIpv6(vm).First()</p>
<p>Private Ipv4: @netManager.GetListPrivateIpv4(vm).First()</p>
<p>Private Ipv6: @netManager.GetListPrivateIpv6(vm).First()</p>
<div>
<form class="form-inline" asp-action="SaveSecret" asp-controller="Home" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label class="mr-2">Secret Name</label>
<input class="form-control" name="SecretName" value="" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="mr-2">Secret Value</label>
<input class="form-control" name="SecretValue" type="password" value="" />
</div>
<button class="btn btn-secondary" type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
@if (ViewBag.SecretSaved == true)
{
<p class="text-success">Saved</p>
}
</div>HomeController.cs
private readonly IKeyVaultManager keyVaultManager;
public HomeController(IKeyVaultManager keyVaultManager)
{
this.keyVaultManager = keyVaultManager;
}
[HttpPost("SaveSecret")]
public IActionResult SaveSecret(string SecretName, string SecretValue)
{
keyVaultManager.SetNewSecret(SecretName, SecretValue);
ViewBag.SecretSaved = true;
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}IVMManager=> A set of Virtual Machine functionsINetworkInterfaceManager=> A set of Network Interface functions including getting public and private IPv4 / IPv6IKeyVaultManager=> A set of Key Vault functions
Note: All of the above include Async functionality too
- Instead of appsettings.json , an option to use Azure Key Vault will be supported
- Azure Key Vault Manager (further improvement and set of functions)
- Azure Virtual Machines (further improvement and set of functions)
- Network Interfaces (further improvement and set of functions)
- Azure Analytics Workspace Manager (with special futures for IIS and Azure CDN Logs)
- Azure DNS Manager
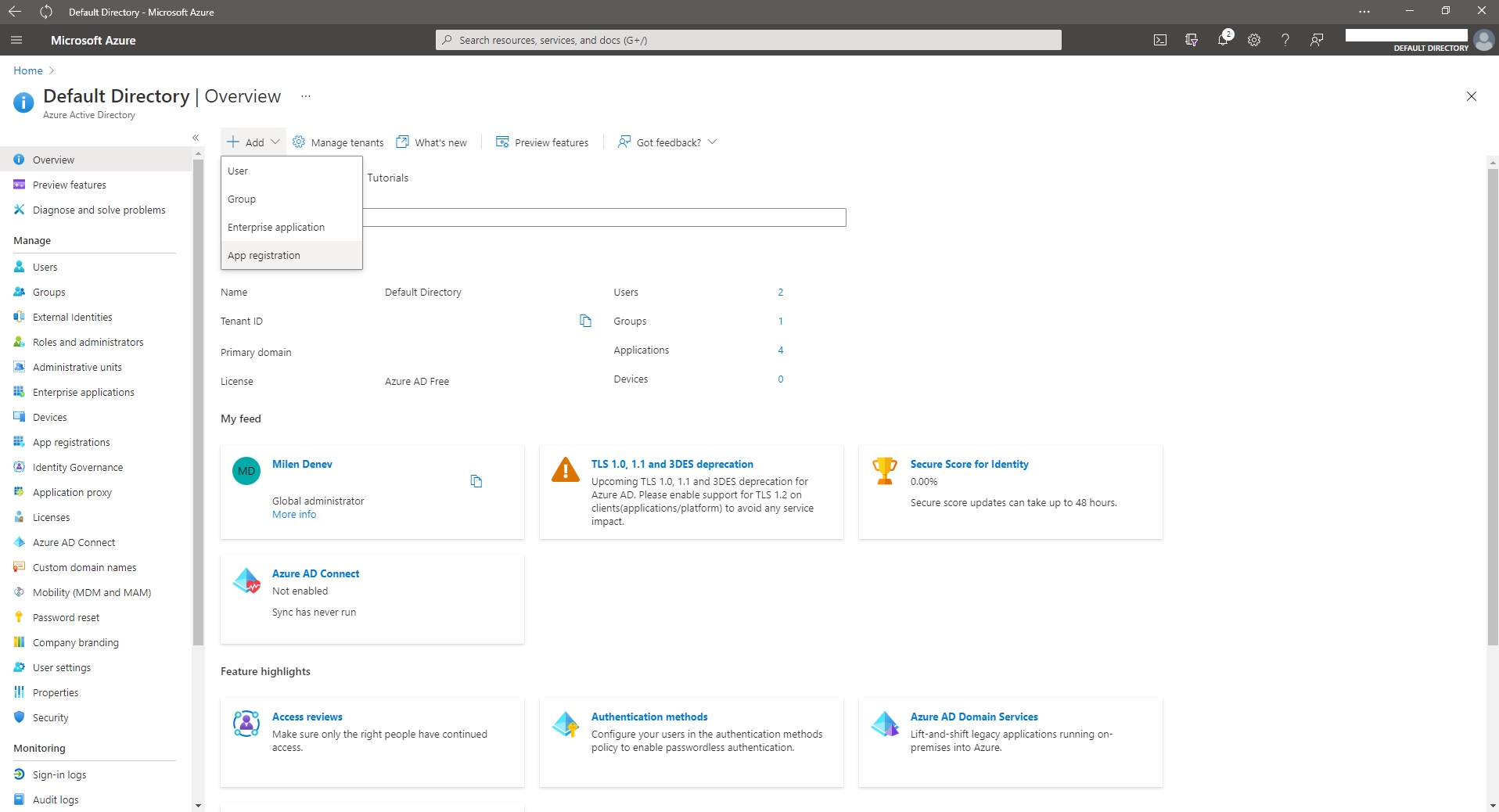
- Step 1: Create new App Registration in Azure Active Directory
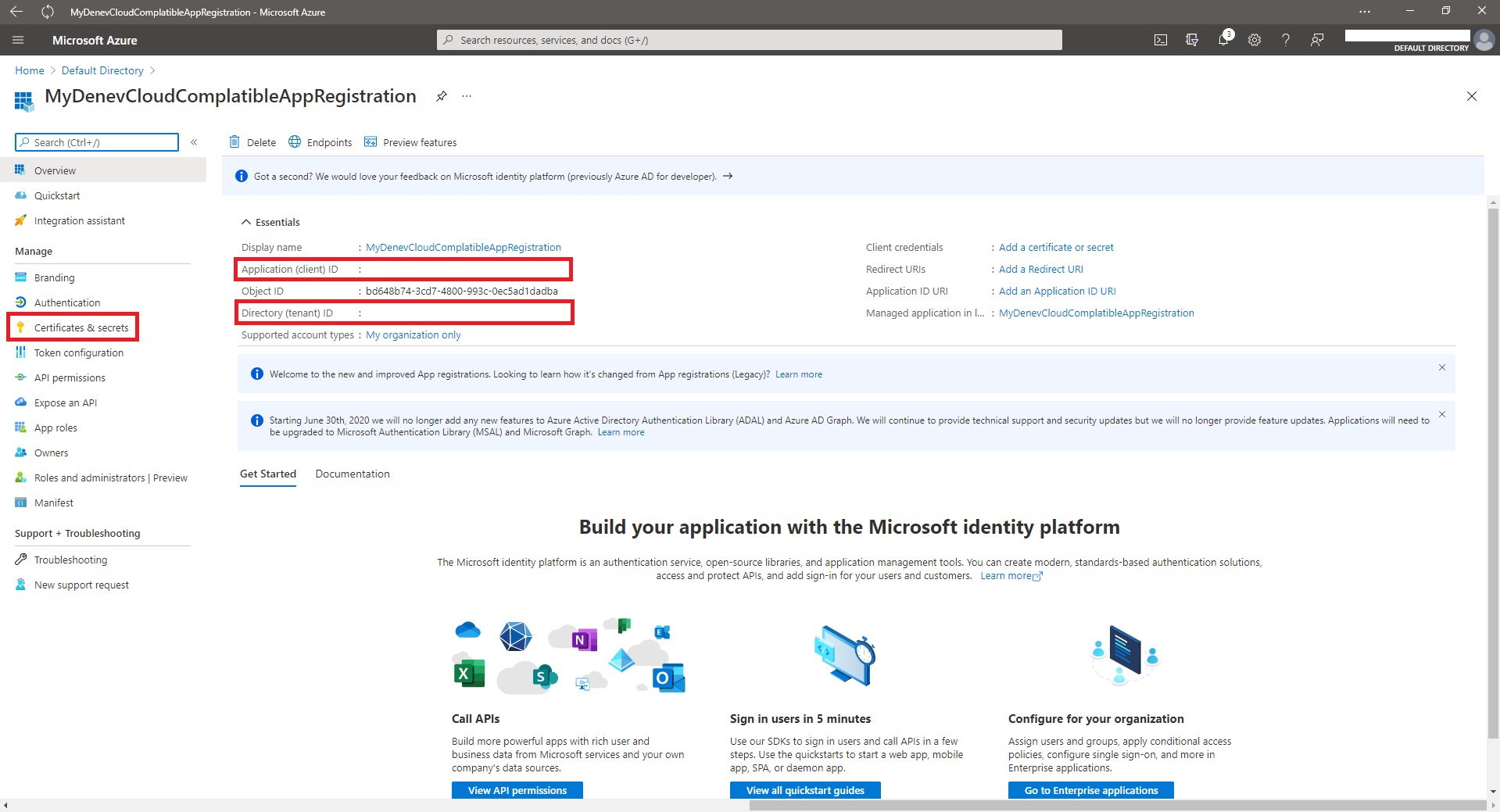
- Step 2: Create a new secret for the new App Registration
Note: Remember to save Secret and Ids
- Step 3: Assign the App with a role to the appropriete resource that will be accessed using the Access Control (IAM)
Note: Please consult with your team if this follows your company's security guideness. Also for the exact Role that has to be assigned or any other details about Azure contact their support