This repo contains the PyTorch implementation of IHemoMIL in the following paper: "Towards Interpretable Hemodynamic Fluctuation Recognition of Photoplethysmography with Ranking-Based Multi-Instance Learning" (Under Review), which is a method that leverages weakly-supervised multiple instance learning and ranking-based aggregation to effectively recognize hemodynamic fluctuations within PPG waveforms.
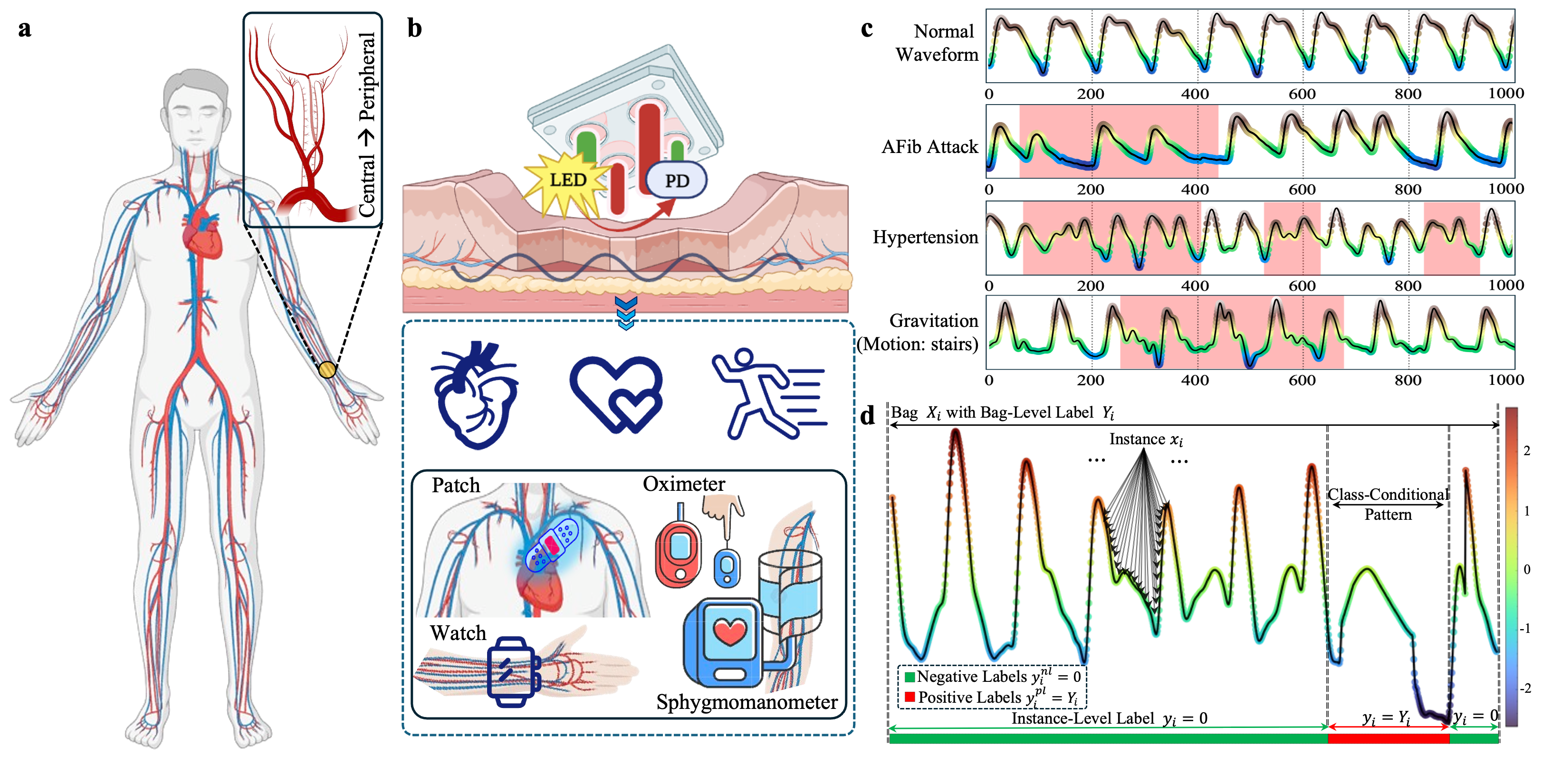
Following the problem formulation, as illustrated in Fig. 2, this section outlines our methodology for leveraging AI to make interpretable decisions in recognizing hemodynamic fluctuation patterns. This study addresses the challenges of current automatic PPG-based diagnostics, including interpretability for hemodynamic anomalies and collaboration between computer-assisted healthcare and human clinical workflows.
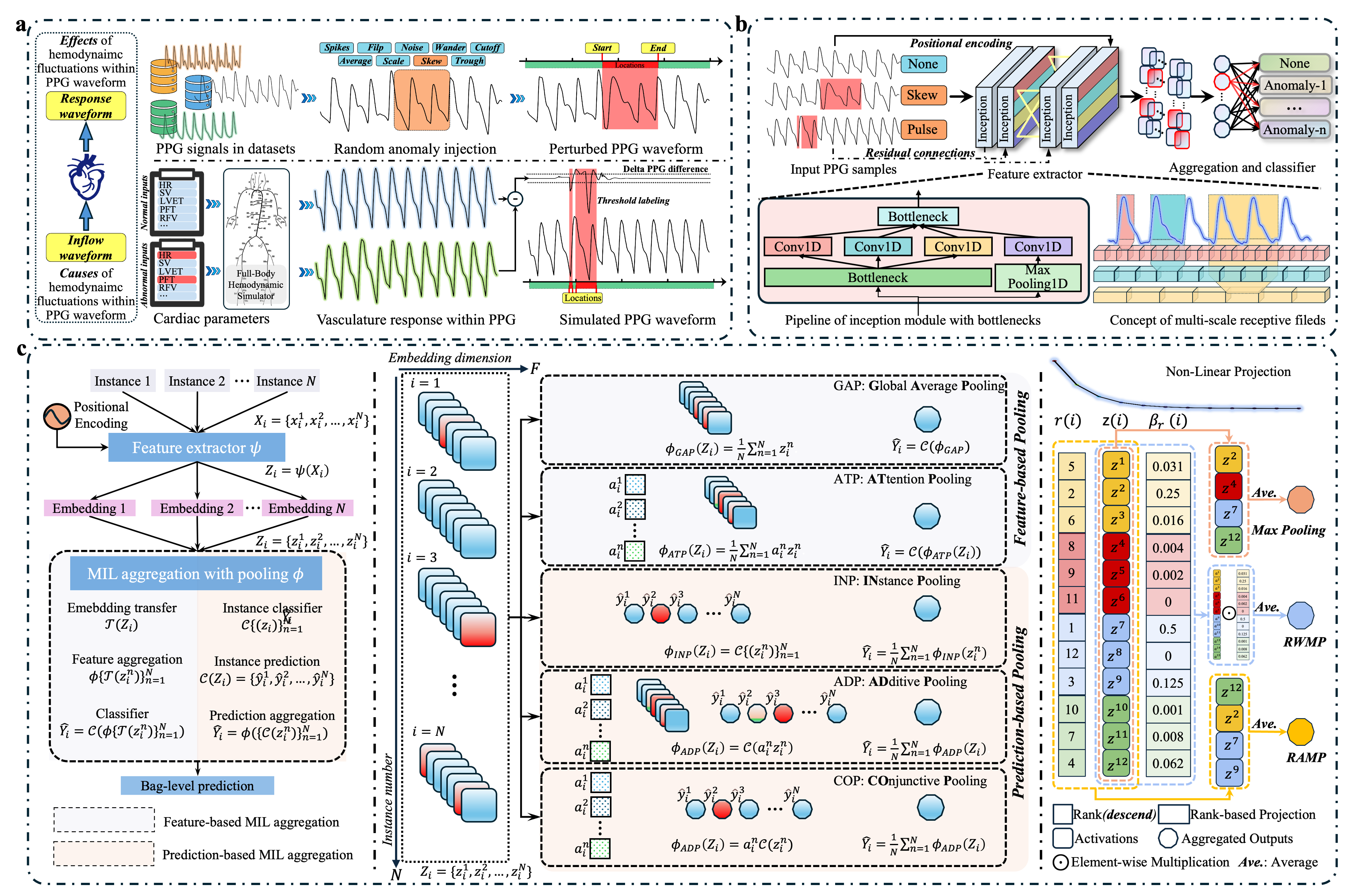
We utilize causality-informed synthetic PPG datasets (Fig.2a), incorporating morphological perturbation-based anomaly injection and vasculature response-based waveform simulation, to thoroughly examine cause-and-effect relationships in peripheral pulse waves. We propose IHemoMIL, a general framework for widespread adaptability and preceptive explainability via pinpoint discriminatory motifs under a weakly supervised multiple instance learning paradigm. IHemoMIL incorporates InceptionTime for multi-scale receptive fields (Fig.2b) and salience-induced MIL aggregation via ranking-based poolings (Fig.2c) to enhance both predictive and interpretable performance.
Our causality-informed synthetic dataset generation pipeline, as illustrated in Fig. 2a, focuses on modeling physiological changes (Causes) and their effects on PPG waveforms (Effects) due to hemodynamic fluctuations.
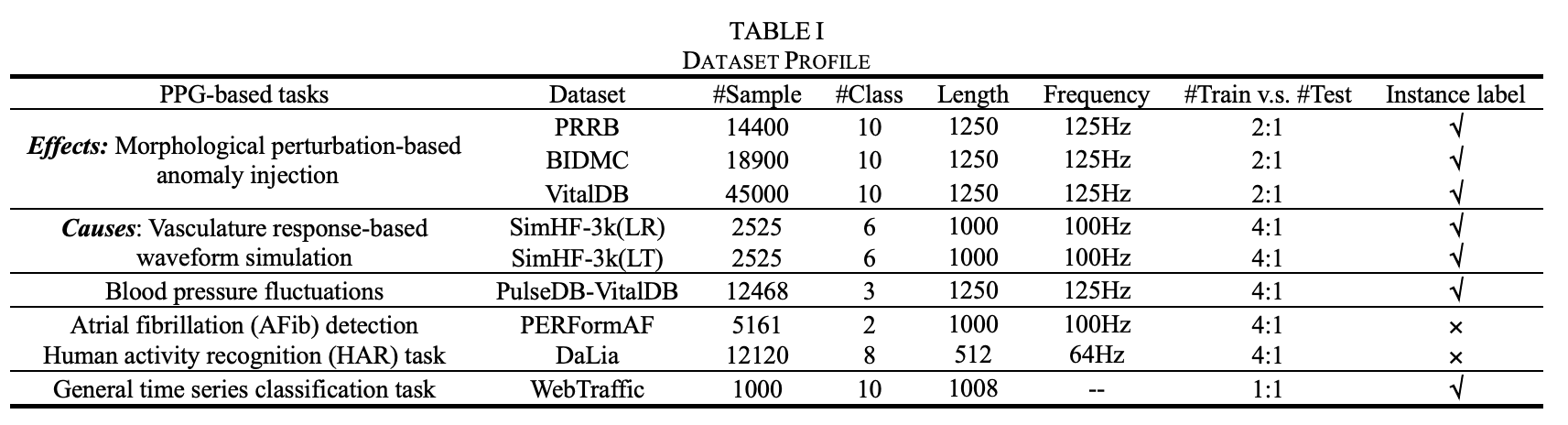
As presented in Table I, we utilized nine datasets, including five synthetic PPG datasets generated using morphological perturbation and vasculature response-based simulation as discussed in Section 2.2, three realistic PPG datasets for hypertension/hypotension identification, AFib detection, and HAR, and the WebTraffic dataset for general time series benchmarking.The tailored datasets can be downloaded here:
- Microsoft OneDrive, password: dEHghdNxue83hmR
- Baidu NetDisk, password: vcwt
To use the models and algorithms in this project, refer to the example notebooks in the notebooks directory. These notebooks provide step-by-step instructions on how to load data, train models, and evaluate results.
- checkpoint - Contains the weight files and trained models.
- data - Contains datasets.
- ihemomil - Includes the core algorithms with data processing, ihemomil backbone, and pooling method scripts.
- notebooks - Jupyter notebooks for experiments and interpretable analysis (Main Results can be cheack in notebooks/IHemoMIL_visualization.ipynb).
- training scripts - train.py
- Python 3.8
- matplotlib == 3.7.0
- numpy == 1.23.5
- pandas == 1.5.3
- scikit_learn == 1.2.2
- torch == 1.13.0
Dependencies can be installed using the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txtTo easily reproduce the results you can follow the next steps:
- Initialize: Create a python virtual environment, follow the required dependencies.
- Download the datasets and put at ./data/.
- Run script autotask_trainer.sh.
# IHemoMIL with backbone inceptiontime and pooling gap on PRRB
python train.py \
--is_train True \
--dataset "mp_ppg_PRRB" \
--data_path "data" \
--checkpoint "checkpoint" \
--channel 1 \
--backbone "inceptiontime"\
--pooling "gap" \
--d_model 128 \
--apply_positional_encoding True \
--batch_size 512 \
--epochs 1500 \
--learning_rate 0.001 \
--use_gpu True \
--gpu_id 1Extensive evaluations across nine diverse datasets demonstrate that IHemoMIL outperforms state-of-the-art methods, showcasing superior performance. Ablations validate the effectiveness of key components. Our method offers reliable and interpretable diagnostics for hemodynamic anomalies in PPG, which not only enhances the robustness of PPG-based monitoring but also paves the way for improved therapies and the seamless integration into healthcare systems, ultimately contributing to better patient outcomes and more efficient healthcare delivery.
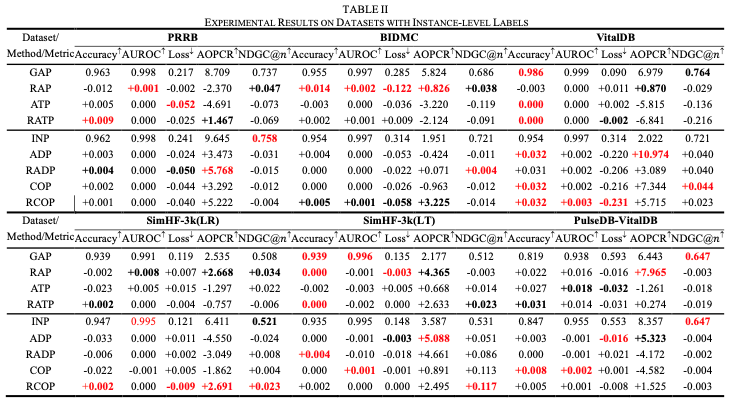
Table. II Cmparative analysis of performance metrics against baseline pooling methods, focusing on the numerical evaluation of FMIL and PMIL aggregation approaches, and highlighting the benefits of ranking-based pooling strategy. The optimal variants within each aggregation type are highlighted in bold, with the overall best-performing variants indicated in red.
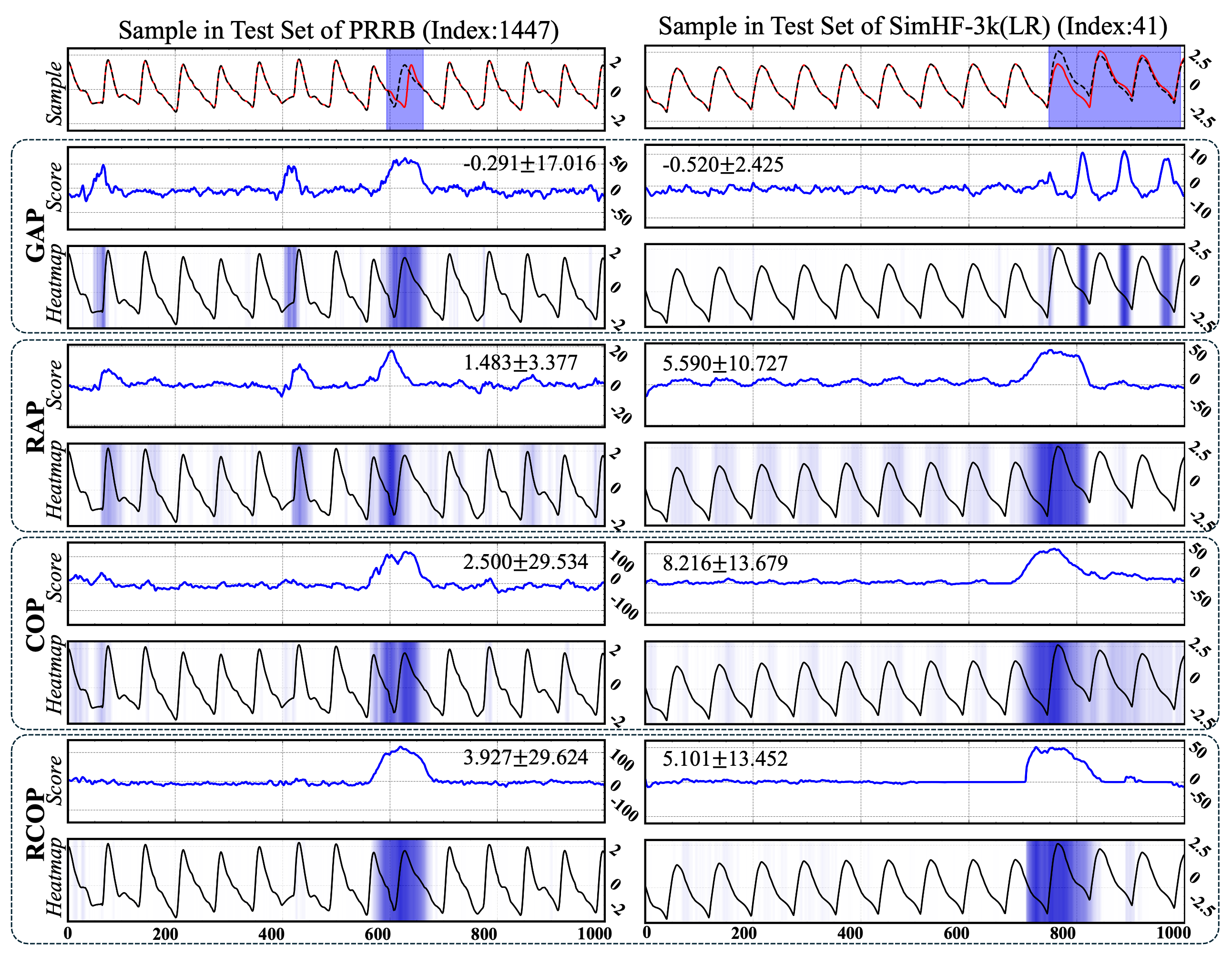
Fig. 3 Ranking-based pooling strategies, exemplified by RAP and RCOP, significantly enhanced model explainability, thereby facilitating informed decision-making in clinical diagnosis. These ranking-based variants effectively identified discriminative regions within PPG waveforms, correlating the strength of discriminative support with waveform morphological variation.
If you have any questions, feel free to contact Daomiao Wang through Email (daomiao.wang@live.com) or Github issues. Pull requests are highly welcomed!
This library follows the implementation of baseline models:
- InceptionTime: https://github.com/hfawaz/InceptionTime
- MILLET: https://github.com/JAEarly/MILTimeSeriesClassification
- Time Series Library (TSLib): https://github.com/thuml/Time-Series-Library
Thanks for the in-house cardiovascular simulation model Nektar1D for vasculature response-based waveform generation. At the same time, thank you all for your attention to this work!
This project is licensed under the Apache-2.0 License. See the LICENSE file for more details.