Complementary code to reproduce the work of "Assessing the Robustness in Predictive Process Monitoring through Adversarial Attacks"
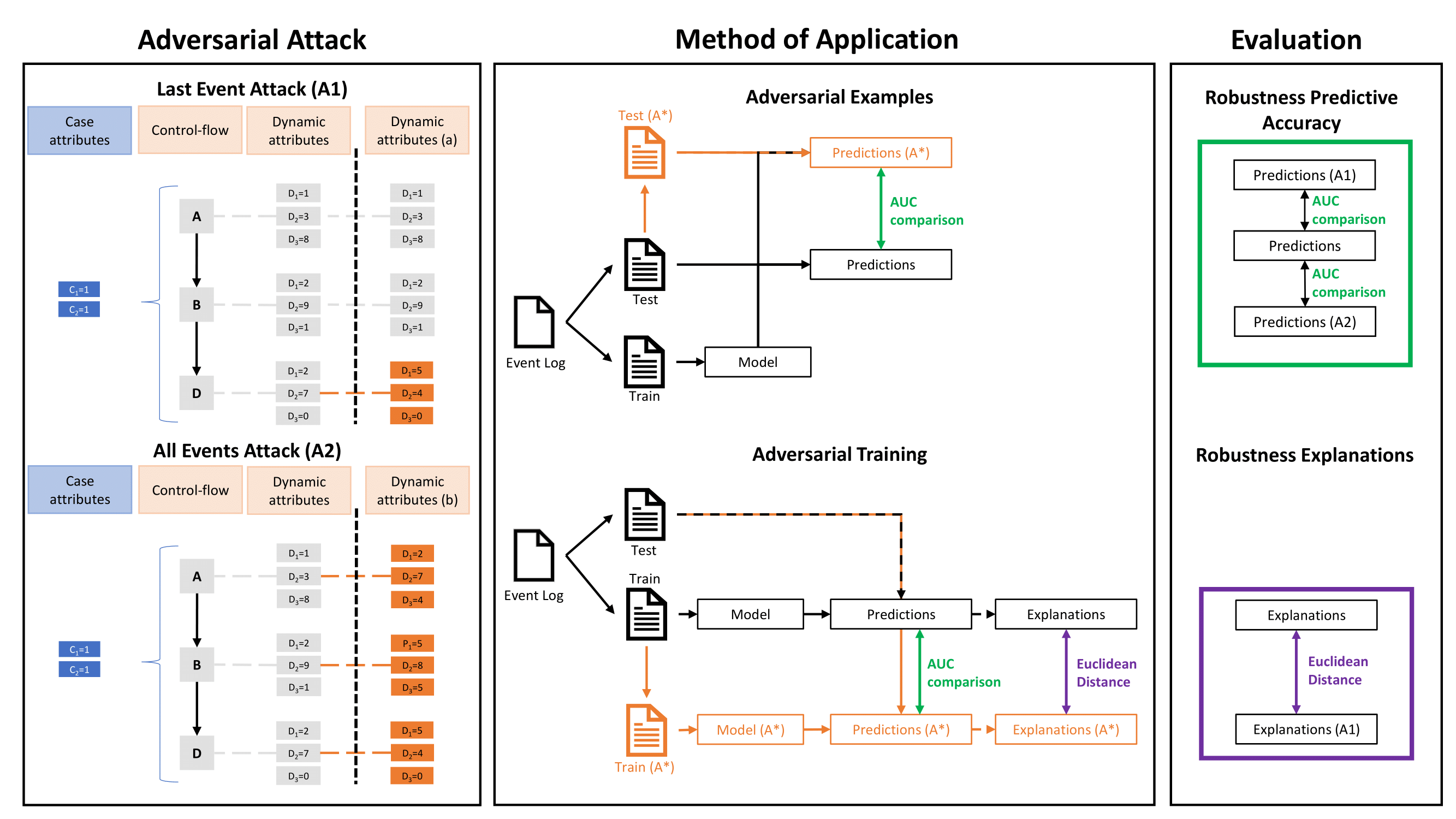 This figure contains the robustness assessment framework as introduced in the paper. The framework describes the different adversarial attacks, the method of application and how the evaluation is performed.
This figure contains the robustness assessment framework as introduced in the paper. The framework describes the different adversarial attacks, the method of application and how the evaluation is performed.
An overview of the folders and files is given below.
The preprocessing and hyperoptimalisation are derivative work based on the code provided by Outcome-Oriented Predictive Process Monitoring: Review and Benchmark. We would like to thank the authors for the high quality code that allowed to fastly reproduce the provided work.
- dataset_confs.py
- DatasetManager.py
- EncoderFactory.py
- Hyperoptimalisation_ML_Attack
- Hyperoptimalisation_DL_Attack (GC).ipynb
Logistic Regression (LR) and Random Forest (RF)
- Experiment_ML_Attack.py Long short-term memory neural networks (LSTM)
- Experiment_DL_Attack (GC).py
Logistic Regression (LR) and Random Forest (RF)
- Experiment_ML_Attack_Test.py
Long short-term memory neural networks (LSTM)
- Experiment_ML_Attack_Test (GC).py
This jupyter notebook file contains the code to obtain the plots as displayed in the paper (+ an additional plot to show the differences in label flips, which was omitted from the paper).
This folder contains cleaned and preprocessed event logs that are made available by this GitHub repository: Benchmark for outcome-oriented predictive process monitoring. They provide 22 event logs, and we have selected 13 of them. The authors' GitHub repository provide a Google drive link to download these event logs
The folder PDF contains the high-resolution figures (PDF format) that have been used in the paper
First, we would like to thank the authors of Outcome-Oriented Predictive Process Monitoring: Review and Benchmark for their interesting work and open source access to their preprocessed event logs and code.
Next, we acknowledge the work provided by Building Interpretable Models for Business Process Prediction using Shared and Specialised Attention Mechanisms for their attention-based bidirectional LSTM architecture to create the long short-term neural networks with attention layers visualisations. In this paper, they use the attributes resource, activity and time and the two former categorical attributes are one-hot encoded (OHE). We have extended this work by allowing different case and event attributes. Here, the categorical attributes are OHE and the dynamic attributes are inserted into an LSTM (to learn the dynamic behaviour).
Secondly, the hyperoptimalisation and experiments for the deep learning models are performed with the use of Google Colab. The authors are thankful for this easy-to-use jupyter notebook that provides computing on a GPU.