- AEM Training
- AEM basic technical knowledge study
- 1. 什么是AEM
- 2. AEM 技术架构
- 3. AEM 开发和使用
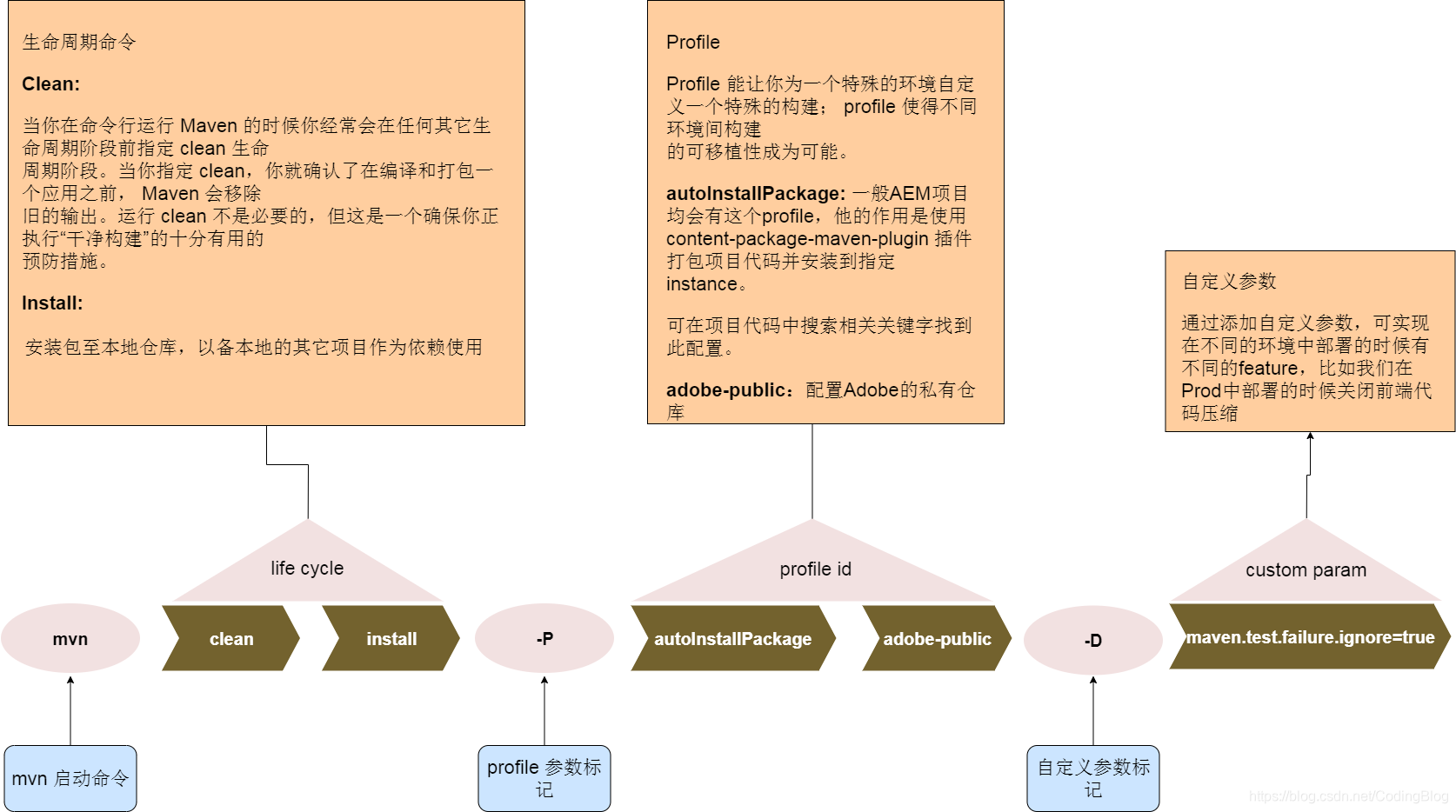
- 4. AEM Build命令详解
- 5. AEM 相关学习资料
- 6. AEM分步学习
- 7. 常用技术点
- 7.1 在线查看AEM的log
- 7.2 Create AEM component by using Sling Model
- 7.3 Create AEM component by using WCMUsePojo
- 7.4 Scheduling with a cron expression
- 7.5 Query Builder API
- 7.6 SSO in AEM
- 7.7 Content Services
- 7.8 Developing AEM Mobile Content Services
- 7.9 Getting Started with AEM Content Services
- 7.10 Developing Sling Model Exporters in AEM
- 7.11 Enabling JSON Export for a Component
- 7.12 Scripting variables in JSP
- 7.13 How to Build AEM Projects using Apache Maven
- 7.14 动态下拉菜单
- 7.15 Using Translator to Manage Dictionaries
- 7.16 Configuring the Rich Text Editor
- 7.17 Components for Page Authoring
- 7.18 Understanding AEM Content Fragments
- 7.19 使用Multifield
- 7.20 使用SlingModel
- 7.21 Creating an Adobe Experience Manager HTML Template Language component that uses the WCMUsePojo API
- 7.22 SlingModel
- 7.23 创建custom sling servlet
- 7.24 创建render component
- 7.25 创建一个Servlet service
- 7.26 Sling Servlet service 文档
- 7.27 AEM配置系统用户
- 7.28 SegmentNotFound Issue or AuthenticationSupport service missing issue
- 7.29 Mvn build 时出现类似不能下载Adobe相关依赖的依赖性错误
- 8. Self-Assessment Preparation and Learning worksheet
- AEM advanced technical knowledge study
- AEM basic technical knowledge study
- Adobe Experience Manager is a web-based client-server system for building, managing, and deploying commercial websites and related services.
- A number of infrastructure-level and application-level functions are combined into a single integrated package.
AEM本质为 Adobe 出品的一个CMS管理系统,相比于市面上其他著名的CMS系统,比如Wordpress,织梦等。
所见即所得: 一般的CMS系统都会提供很多预开发好的功能和页面,比如首页,文章详情页,文章列表页等页面,然后用户可以在CMS提供的管理后台管理和维护站点的相关信息,或者创建新的文章,而这些管理后台都只是表单型的提交数据到数据库,用户再次进入站点前台页面时,前台页面会读取新的数据配置的页面信息再次渲染出来。一般管理后台长这样:
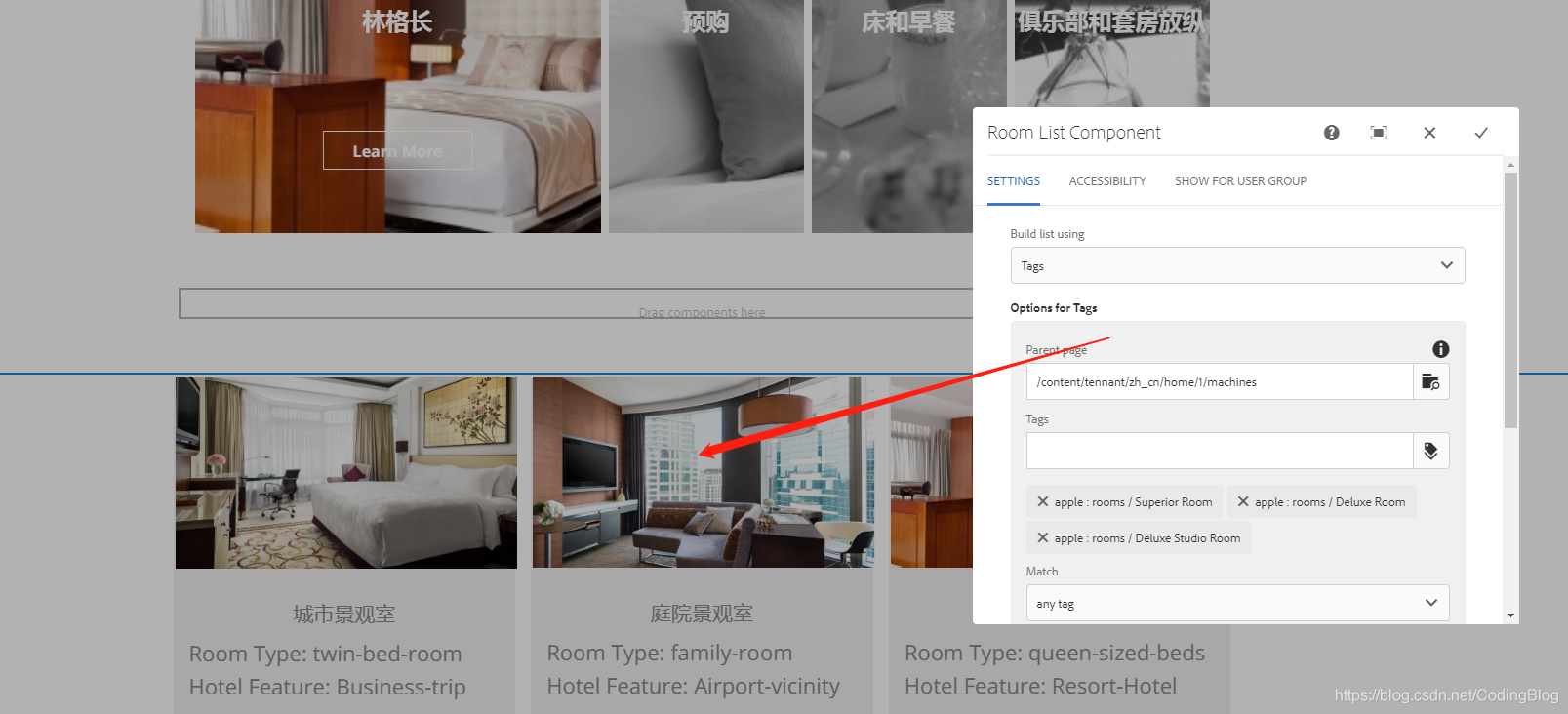
AEM 作为一个企业级的CMS管理系统,主要用户维护,创建和部署大型商业网站及其服务
Apache Sling :: Servlet Resolution https://sling.apache.org/old-stuff/servlet-resolution.html Apache Sling :: URL decomposition http://sling.apache.org/documentation/the-sling-engine/url-decomposition.html Apache Sling :: HTL Scripting https://sling.apache.org/documentation/bundles/scripting/scripting-htl.html Apache Sling :: Sling Models https://sling.apache.org/documentation/bundles/models.html#specifying-an-alternate-adapter-class- since-110 拓展书目: Continuous Delivery of Apache Sling Applications Server-side OSGi with Apache Sling
Java JSR-170(JCR) JCR规范下载 http://download.oracle.com/otndocs/jcp/content_repository-1.0.1-mr-oth-JSpec/index.html Jackrabbit 依据JCR规范的一个JCR实现类库 http://jackrabbit.apache.org/jcr/jackrabbit-architecture.html
一个OSGI实现 官网 http://felix.apache.org/ 拓展书目: OSGi and Apache Felix 3.0 Beginner's Guide
HTML Template Language (HTL)是AEM所推荐使用的服务器端动态HTML模板语言 HTL 语法详解 https://github.com/Adobe-Marketing-Cloud/htl-spec/blob/master/SPECIFICATION.md#221-use HTL Adobe 官方教程 https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/htl/using/getting-started.html
-
Author instance Typically, for security, governance, and other reasons, a production site will divide instances of AEM into Author and Publish instances. For more information on deployment architecture (including Author/Publish instances), see documentation about AEM Instances.
-
Publish instance For security, governance, and other reasons, a production site will typically divide instances of AEM into Author and Publish instances. For more information on deployment architecture (including Author/Publish instances), see documentation about AEM Instances.
-
Component In AEM, a Component is an object type, instances of which can generally be created by dragging and dropping them from, say, the Sidekick. So for example, out-of-the-box components that ship with AEM include the Text, Title, Tag Cloud, Carousel, Image, and List components, all available from the Sidekick at runtime.
-
Digital assets In AEM, Digital Assets are (typically) images and rich media files. For further information, see Working with Digital Assets in DAM.
-
Template In AEM, a Template specifies a particular type of page. It defines the structure of a page (while also typically specifying a thumbnail image, and various properties). For example, you may have separate templates for product pages, sitemaps, and contact information.
- Workflow The AEM Workflow system allows for creation of automated processes involving pages or assets.
-
Dispatcher The Dispatcher is both a caching and load-balancing tool, as well as providing certain security safeguards.
-
JCR, Java Content Repository The Java Content Repository specification (JSR-283) provides both an abstract data model and an Application Programming Interface for realizing a massively scalable NoSQL data repository that combines features of a file system and an object database. While you do not need to understand JSR-283 in exhaustive detail, you should take time to familiarize yourself with the basic capabilities of JCR and the data model underlying it, because JCR is what makes possible the "everything is content" philosophy of AEM.
In essence, JCR is a system of nodes and properties, in which nodes can inherit from other nodes and all content is stored as property values. Note that in addition to ordinary inheritance, JCR allows for a concept of "mixin" nodes, which enables modelling of multiple inheritance.
JCR has a number of predefined node types and property types, but in general the typing system is quite flexible, and (indeed) one of the strengths of JCR is that it allows structured as well as unstructured content to be stored/managed with equal ease. That is, JCR can accommodate highly structured data, but it can also accommodate arbitrary dynamic data structures without schema constraints.
The JavaDoc for JCR's Java API is here.
Before attempting to read the JavaDoc or the JCR spec itself, you might want to look at this high-level explanation of JCR as implemented by Adobe Experience Services.
-
OSGi OSGi is the services-based runtime technology that provides the basis for modularized Java development in AEM. It is a framework that provides not only a highly dynamic (and secure) classloading and execution environment for code resources (known as bundles), but also full control over the visibility and lifecycle of the various services exposed by bundles. A service registry provides a cooperation model for bundles that takes lifecycle dynamics (and version requirements) into account. OSGi solves many of the problems that application servers were intended to solve, but does so in a lightweight, highly dynamic way, making it possible, for example, to hot-deploy services (making the new code immediately available without restarting the server).
-
Quickstart Unlike many other programs, you install AEM by using a single "Quickstart" self-extracting JAR file. When you double-click the JAR file for the first time, everything you need is automatically installed. The quickstart JAR includes all files required for the CRX repository (including administrative facilities), virtual repository services, index and search services, workflow services, security, and a Web server, plus the CQ Servlet Engine (CQSE) and all AEM services. There are no other files to install: the Quickstart is self-contained.
The first time you start the Quickstart, it creates an entire JCR-compliant repository in the background, which can take several minutes. After this initial startup, subsequent startups are much quicker as the repository infrastructure has already been laid down.
Many startup options (such as the active port number and whether the AEM instance in question should be a Publish instance versus an Author instance; and much more) can be controlled by appropriately renaming the Quickstart file. To see a list of options in this regard, run the JAR with "-help" on the command line: java -jar .jar –help
-
Replication agents Replication agents are central to AEM as the mechanism used to Publish (activate) content from an author to a publish environment; flush content from the Dispatcher cache; return user generated content (for example, form input) from the Publish environment to the Author environment.
-
Tar Storage (TarMK) TarMK is the default persistence system in AEM. Although AEM can be configured to use a different persistence system (such as MongoDB), TarMK has certain advantages in that it is performance-optimized for typical JCR use-cases (thus is very fast), uses an industry-standard data format, and can be quickly and easily backed up. Read more here.
参考书目:Maven权威指南中文版
https://helpx.adobe.com/support/experience-manager/6-3.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/kt/index/aem-6-3-videos.html
教你一步一步的开发AEM,很实用 附带官方实例源码 https://github.com/Adobe-Marketing-Cloud/aem-guides-wknd
mvn archetype:generate -DarchetypeGroupId=com.adobe.granite.archetypes -DarchetypeArtifactId=aem-project-archetype -DarchetypeVersion=10 -DarchetypeRepository=https://repo.adobe.com/nexus/content/groups/public/https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/topics/how-to.html
http://localhost:4502/system/console/slinglog
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/using/aem63_slingmodel.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/using/first_htl_WCMUsePojo.html
https://sling.apache.org/documentation/bundles/scheduler-service-commons-scheduler.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/6-3/sites/developing/using/querybuilder-api.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/6-3/sites/deploying/using/single-sign-on.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/6-4/mobile/using/content-services.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/6-4/mobile/using/spaces-and-entities.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/kt/sites/using/content-services-tutorial-use.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/6-3/release-notes/json-exporter-dev-fp.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/6-4/sites/developing/using/ht-projects-maven.html
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/granite-datasource-inside-touch-ui-select-object-aem-gonz%C3%A1lez-ramos https://mkbansal.wordpress.com/2016/01/04/aem-acs-generic-list-dialog-configuration-touch-ui/ https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/using/creating-touchui-validate11.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/6-3/sites/developing/using/i18n-translator.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/6-2/sites/authoring/using/editmode.html#Text
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/using/multifield_aem63.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/using/aem63_htl_repeat_slingmodel.html
7.21 Creating an Adobe Experience Manager HTML Template Language component that uses the WCMUsePojo API
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/using/first_htl_WCMUsePojo.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/using/aem64_coral_resourcetypes.html
https://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/using/resourcetypes.html
http://www.6dglobal.com/blog/servlets-sling-case-disappearing-servlet-path-2013-01-31
https://sling.apache.org/documentation/the-sling-engine/servlets.html
http://localhost:4502/crx/explorer/index.jsp
Maven settings http://helpx.adobe.com/experience-manager/kb/SetUpTheAdobeMavenRepository.html 运行时加上
-Padobe-public| Topics | Cost(hours) | Details | Reference | Start Date | End Date | Completed? | Questions | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic AEM knowledge study | ||||||||
| Installing and configuring an AEM developer environment | 1. Install AEM on supported operating systems. 2. Install AEM with different run modes (Author and Publish). 3. Start AEM in debug mode for remote debugging. 4. Setup and configure replication agents. 5. Setup and configure a Web server 5. Setup and manage OSGi configurations. 6. Manage users and groups 7. Manage Access Control Level (ACL) permissions. |
|||||||
| Building and deploying AEM projects | 1. Configure a source control system to manage files in AEM 2. Build and deploy AEM projects by using Maven |
|||||||
| Building AEM components | 1. Create custom components and dialogs 2. Create templates and page components 3. Create client libraries. 4. Extend out-of-the-box AEM components. |
|||||||
| Building OSGi services | 1. Create custom OSGi services. 2. Create and manage custom OSGi configurations. 3. Configure and manage OSGi services and bundles by using the Felix web console. 4. Manage Maven dependencies. |
|||||||
| Troubleshooting AEM projects | 1. Create custom log files by using the Web console. 2. Configure and manage AEM log levels for specific AEM environments. 3. Given an option for starting AEM, I can select the correct parameter(s) for starting AEM. 4. Troubleshoot caching issues related to the Dispatcher and browsers. 5. Troubleshoot AEM configurations. |
|||||||
| Topics | Cost(hours) | Details | Reference | Start Date | End Date | Completed? | Questions | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|