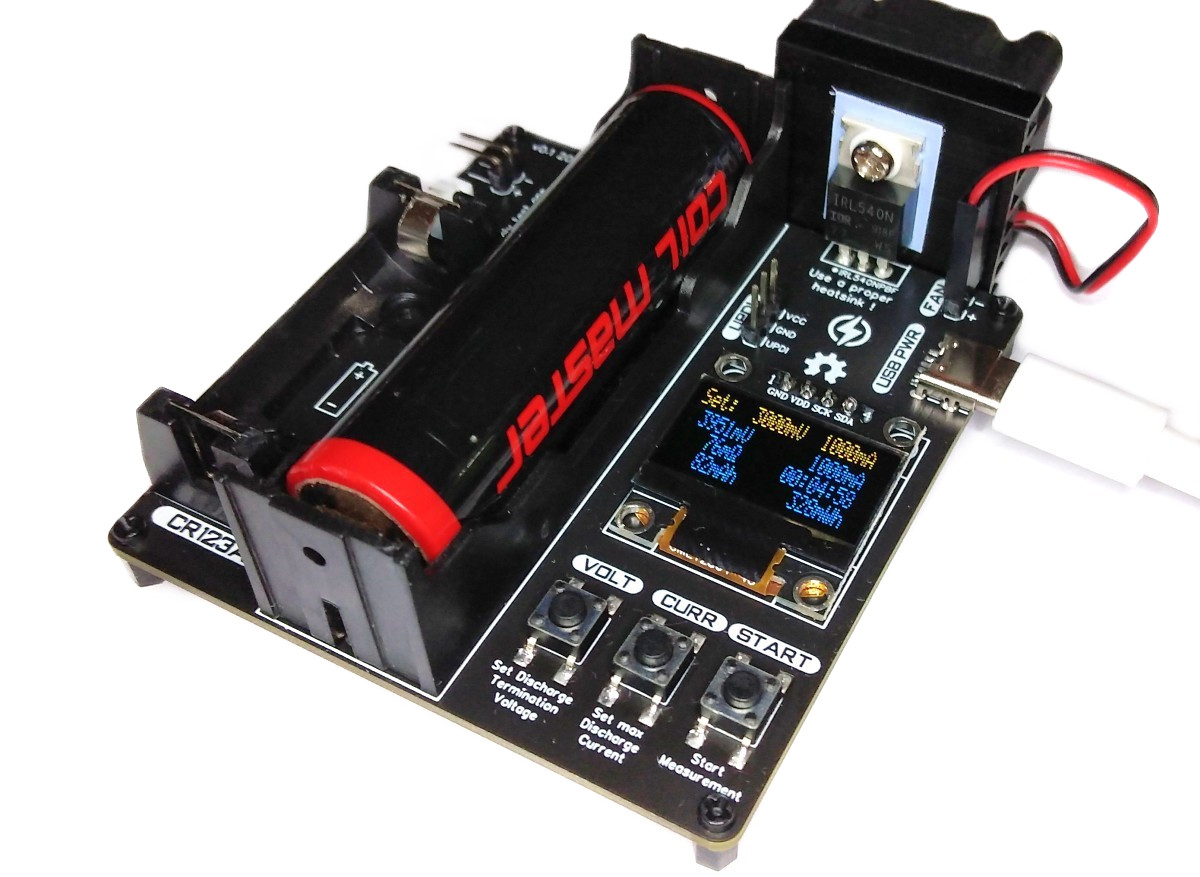
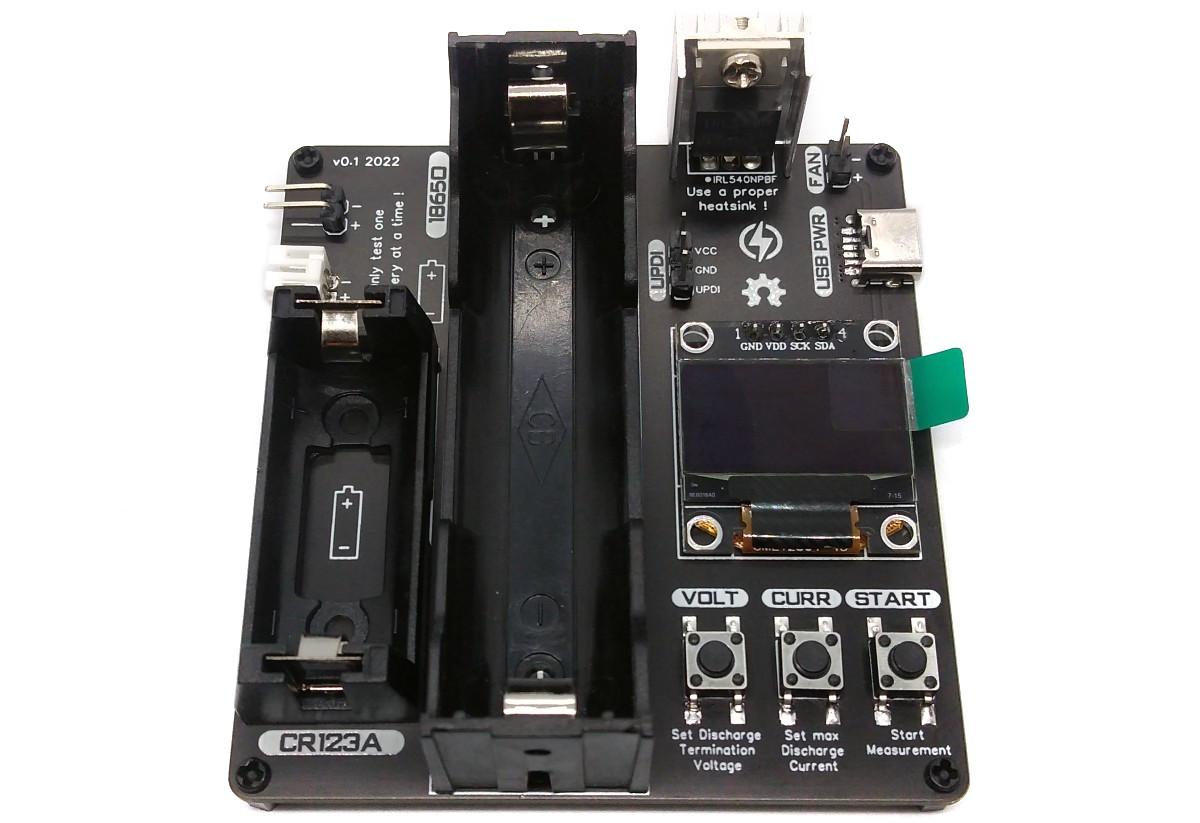
The ATtiny412 controlled battery capacity tester measures the capacity of single-cell Li-Ion, LiPo and LiFePO4 batteries using the built-in constant current load. Discharge termination (cutoff) voltage and discharge current can be selected by the user. During the discharging process, all relevant data is displayed on an OLED.
- Design Files (EasyEDA): https://easyeda.com/wagiminator/attiny412-batterycapacitytester
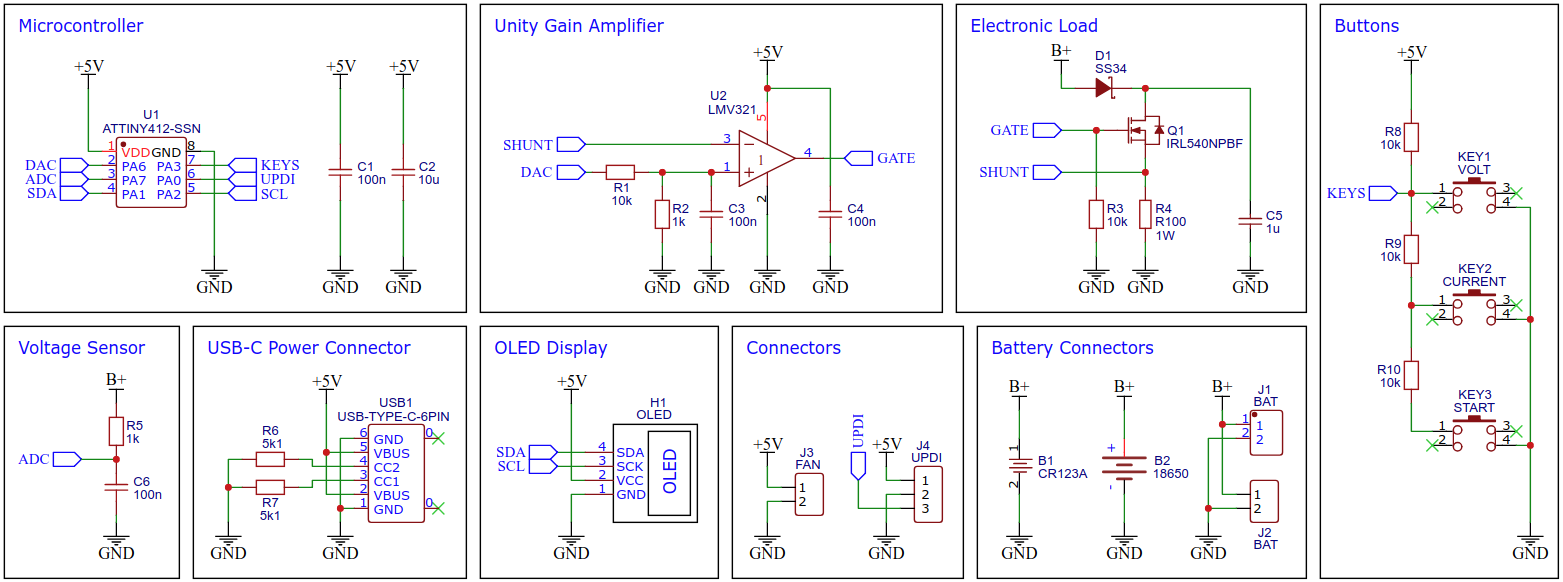
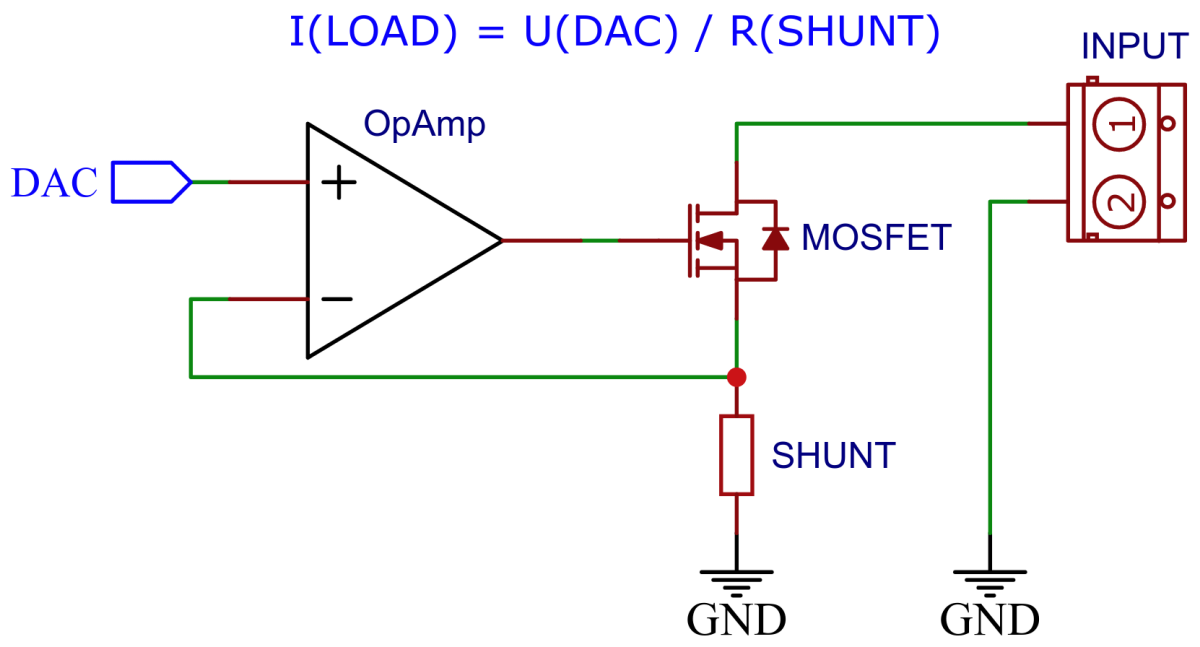
The electronic load control circuit, which essentially consists of an operational amplifier, a MOSFET and a shunt resistor, ensures that the same current flows regardless of the voltage applied.
For this purpose, a 100mΩ/1W shunt resistor is located in the load circuit, via which the current is measured. The LMV321 rail-to-rail OpAmp compares this with the target value, which is specified by the ATtiny's internal digital to analog converter (DAC) via a voltage divider and accordingly controls the gate of an IRL540N logic level n-channel power MOSFET, which in turn adjusts the current through its internal resistance set in this way.
The ATtiny412 controls the electronic dummy load with its internal digital to analog converter (DAC). All of its 5 internal reference voltages are being used in order to get the maximum accuracy and resolution of the DAC. The DAC is connected to an OpAmp which acts as a unity gain amplifier controlling the resistance of the MOSFET.
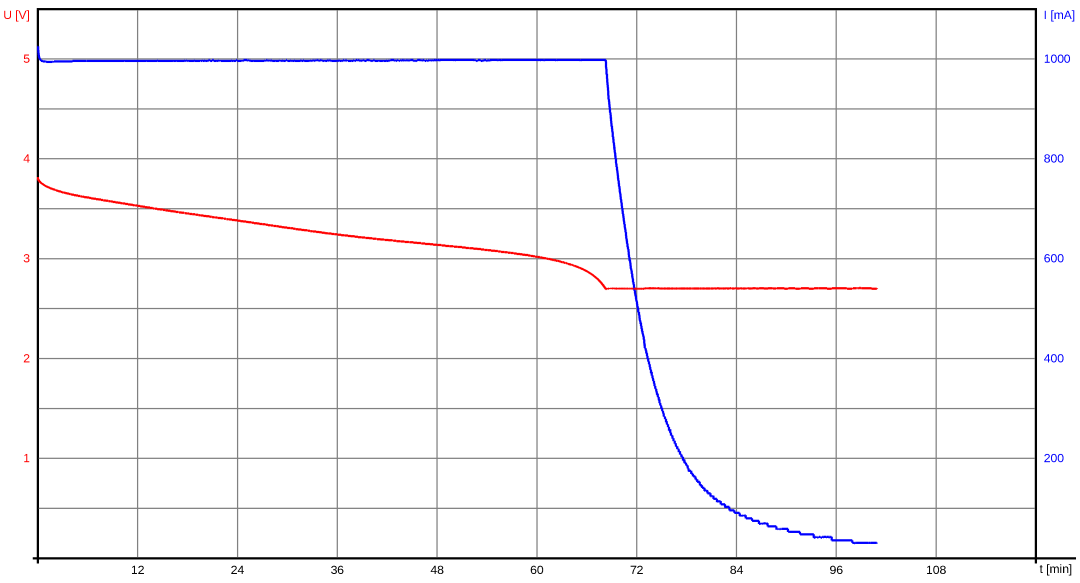
After pressing the START button the device measures the battery voltage without load via the ATtiny's analog to digital converter (ADC). Then it sets a constant current load with the selected maximum discharge current and measures the battery voltage again. The internal resistance of the battery is calculated from the voltage drop and the discharge current. During the discharging process, the battery voltage is measured regularly and the time is measured via the timer (TCB). In conjunction with the known discharge current, the charge drawn and ultimately the capacity of the battery can be determined. If the voltage drops below the selected discharge termination voltage the device constantly decreases the load to maintain this voltage. It stops automatically if the load current drops to 0mA. The voltage and current curve of a discharge cycle is illustrated in the graph below (discharge termination voltage: 2700mV, max discharge current: 1000mA):
If a continuous reduction in the discharge current at the end of the discharge process is not desired, this can be set in the firmware parameters.
Before compiling the firmware, some parameters can be adjusted to suit user behavior.
// Firmware parameters
#define VOLT_MIN 2500 // minimum selectable termination voltage
#define VOLT_MAX 3200 // maximum selectable termination voltage
#define VOLT_STEP 100 // voltage selection steps
#define VOLT_START 3000 // voltage start value
#define CURR_MIN 200 // minimum selectable load current
#define CURR_MAX 2000 // maximum selectable load current
#define CURR_STEP 200 // current selection steps
#define CURR_START 200 // current start value
#define CYCLE_END 1 // 0-stop immediately, 1-decrease load- Open your Arduino IDE.
- Make sure you have installed megaTinyCore.
- Go to Tools -> Board -> megaTinyCore and select ATtiny412/402/212/202.
- Go to Tools and choose the following board options:
- Chip: ATtiny412
- Clock: 5 MHz internal
- Leave the rest at the default settings.
- Connect your programmer to your PC and to the UPDI header on the board.
- Go to Tools -> Programmer and select your UPDI programmer.
- Go to Tools -> Burn Bootloader to burn the fuses.
- Open the sketch and click Upload.
- Make sure you have installed the latest avr-gcc toolchain.
- Open a terminal.
- Navigate to the folder with the makefile and the sketch.
- Run
PROGRMR=serialupdi PORT=/dev/ttyUSB0 make installto compile, burn the fuses and upload the firmware (change PROGRMR and PORT accordingly).
- Connect the device to a 5V power supply via the USB Type-C port.
- Use the buttons to select the discharge termination voltage and the maximum discharge current.
- Connect the previously fully charged battery to be tested to the device.
- Press the START button.
- Wait for the discharging process to finish. The capacity can now be read.
- Remove the battery afterwards and press any key.
The discharge termination voltage should not be selected below 2700mA for Li-Ion or LiPo batteries, or below 2000mA for LiFePO4 batteries, in order to avoid deep discharge and damage to the battery. The recommended discharge termination voltage is 3200mA for Li-Ion and LiPo batteries and 2500mA for LiFePO4 batteries, since around 95% of the capacity is already used here and this also protects the battery. Keep in mind that batteries with a built-in protection circuit can interrupt the discharge process beforehand. The battery voltage may rise again after the discharge process is finished.
Check the battery's data sheet for its maximum discharge current. If this is not known, then discharge the battery with a maximum of 1C (e.g. a 400mAh battery with a maximum of 400mA). Since the battery voltage drops as the load increases, it can make sense to choose the discharge current according to the intended application for the battery.
- The device is designed for a maximum discharge current of 3000mA. This should never be exceeded!
- The higher the selected discharge current, the better the cooling for the MOSFET should be. If necessary, the cooling should be actively supported by a 5V fan. Check the temperature of the MOSFET when you use it for the first time.
- Only use the device under supervision!
- Only use single-cell Li-Ion, LiPo or LiFePO4 batteries!
- Only connect one battery to the device at a time!
- Do not use damaged batteries!
- Pay attention to the correct polarity when connecting the battery to the device!
- Remove the battery immediately after discharging, as small currents may continue to flow.
- ATtiny814 Power Analyzer
- ATtiny412 Datasheet
- LMV321 Datasheet
- IRL540N Datasheet
- SSD1306 Datasheet
- 128x64 OLED on Aliexpress
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)