TCP - Transmission Control Protocol UDP - User Diagram Protocol
HTTP = TCP 80 TFTP = UDP 69
Layer 2 it is known as a Frame Layer 3 Packet Layer 4 Segment
OSI Model TCP/IP Model
The majority of networking troubleshooting is done in the bottom 4 layers
Ethernet equipment. Standard
Illustrate the hierarchical network design model and architecture using the access, distribution, and core layers Compare and contrast the various hardware and software switching mechanisms and operation, while defining the Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM) and Content Addressable Memory (CAM), along with process switching, fast switching, and Cisco Express Forwarding concepts
Troubleshoot Layer 2 connectivity using VLANs and trunking Implementation of redundant switched networks using Spanning Tree Protocol Troubleshooting link aggregation using Etherchannel
Run ping to verify the network is live. Run a network stress test to connect the system
FTP 20/21 SSH 22 TELNET 23 SMTP 25 DNS 53 DHCP 67/68 TFTP 69
Layer 2 Address = MAC address Layer 3 address = IP address
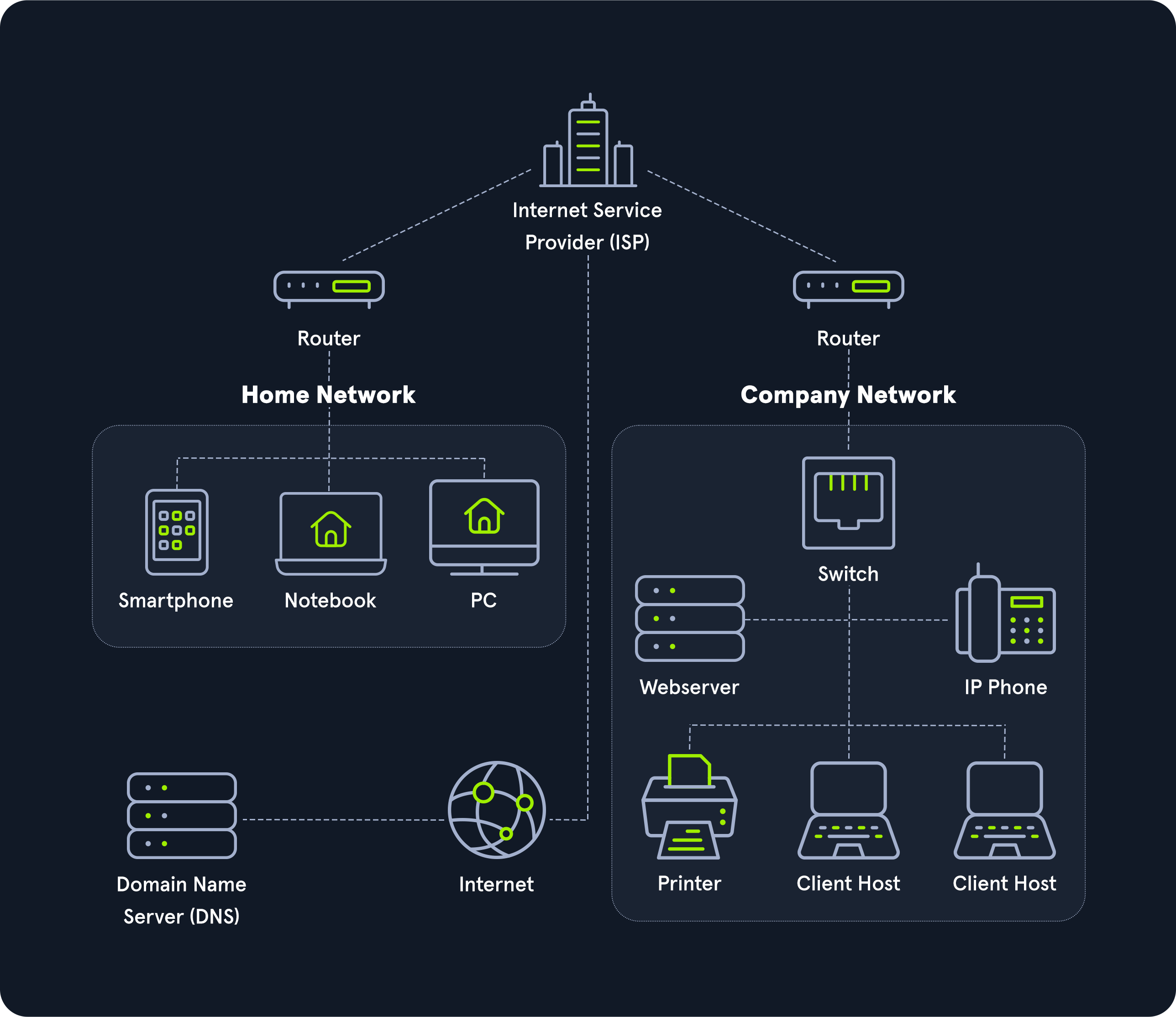
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is used to transfer webpages over the Internet. • File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is used to transfer files over a network. • Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is used to transfer files over a network. • Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is used to assign Internet Protocol (IP) addressing information to clients. • Domain Name System (DNS) is used to translate host names to IP addresses. • Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is used to send email messages. • Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3) is used to receive email messages. • Telnet is used to create a terminal connection to remote devices. • Secure Shell (SSH) is used to create a secure remote terminal connection to a networked device. Build out a home lab Devices/Equipment Media (cabling) Link Addresses or Names Sources & Destinations Internet Service Provider
OSI Model
TCP/IP
Telnet, FTP and TFTP
HDLC
IP Addressing and Subnetting
Cisco IOS
CDP
Router commands
Routing Protocols
EIGRP
OSPF
Routed protocol: Frame-Relay
Access-Lists
 This format will add your image
https://i0.wp.com/planetechusa.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/OSI-Model.png
<a href="http://website.example" rel="some text"></a>
Practice LAN Ethernet switching Lab Practice
ARP Requests
 <img src="https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/subnetting.111111.jpg"
<img src="https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/subnetting.111111.jpg"
Network Fundamentals: Routers, switches, cabling, TCP and UDP, IPv4 and IPv6 IP Connectivity: IP routing, OSPFv2 IP Services: NTP, DHCP, QoS, SNMP Security Fundamentals: VPNs, wireless security, port security Network Access: VLANs and trunking, EtherChannel Automation and Programmability: REST APIs, Puppet, Chef, JSON, SDN
Describe characteristics of REST-based APIs (CRUD, HTTP verbs, and data encoding). Recognize the capabilities of configuration management mechanisms Puppet, Chef, and Ansible. Interpret JSON encoded data
firewall layer 7 wireless access point layer 2 wireless LAN controller layer 2 switch layer 2 router layer 3 bridge layer 2
Reformat. Stage. Commit. Push.
New piece added. Autosaved.
Study event logger.
ip dhcp pool <name>: Configures a DHCP address pool with the specified name.
network <network-address> <subnet-mask>: Specifies the network address and subnet mask for the DHCP pool.
default-router <gateway-address>: Specifies the default gateway (router) for DHCP clients.
dns-server <dns-address>: Specifies the DNS server address for DHCP clients.
lease <duration>: Sets the lease duration for IP addresses assigned by DHCP.
ip dhcp excluded-address <start-address> <end-address>: Excludes specific IP addresses or ranges from being assigned by DHCP.
interface <interface-type> <interface-number>: Enters interface configuration mode for the specified interface.
ip address <ip-address> <subnet-mask>: Assigns an IP address and subnet mask to an interface.
shutdown: Disables an interface.
no shutdown: Enables an interface.
vlan <vlan-id>: Enters VLAN configuration mode to configure VLANs on a switch.
name <vlan-name>: Assigns a name to a VLAN.
switchport mode access: Configures a switch port as an access port, allowing only untagged frames in a single VLAN.
switchport access vlan <vlan-id>: Assigns an access VLAN to a switch port.
switchport trunk encapsulation <encapsulation-type>: Configures the encapsulation method for a trunk port.
switchport trunk allowed vlan <vlan-list>: Specifies the list of VLANs allowed on a trunk port.
show ip interface brief: Displays a brief summary of the router's IP interface configuration and status.
show vlan: Displays information about VLANs configured on a switch.
show running-config: Displays the current running configuration of the device.
show startup-config: Displays the contents of the startup configuration, which is the configuration that will be loaded when the device boots up.
ping <ip-address>: Sends ICMP echo requests to a specified IP address to test connectivity.
traceroute <ip-address>: Traces the route that packets take to reach a destination IP address.
telnet <ip-address>: Initiates a telnet connection to a remote device with the specified IP address.
ssh <ip-address>: Initiates an SSH (Secure Shell) connection to a remote device with the specified IP address.
clear arp: Clears the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) cache on the device.
clear ip dhcp binding: Clears the DHCP binding database, removing all DHCP lease information.
reload: Reloads the device, restarting it and loading the startup configuration.
end: Exits from configuration mode and returns to privileged EXEC mode.
copy running-config startup-config: Saves the running configuration to the startup configuration, ensuring changes persist across reboots.
write memory: Alternative command to save the running configuration to the startup configuration.
Copy running-config startup-config [is another way to save]