Simple Implementation of Dynamo: amazon's highly available key-value store https://www.researchgate.net/publication/220910159_Dynamo_Amazon%27s_highly_available_key-value_store
- Incremental scalability: Dynamo should be able to scale out one storage host (henceforth, referred to as “node”) at a time, with minimal impact on both operators of the system and the system itself.
- Symmetry: Every node in Dynamo should have the same set of responsibilities as its peers; there should be no distinguished node or nodes that take special roles or extra set of responsibilities. In our experience, symmetry simplifies the process of system provisioning and maintenance.
- Decentralization: An extension of symmetry, the design should favor decentralized peer-to-peer techniques over centralized control. In the past, centralized control has resulted in outages and the goal is to avoid it as much as possible. This leads to a simpler, more scalable, and more available system.
- Heterogeneity: The system needs to be able to exploit heterogeneity in the infrastructure it runs on. e.g. the work distribution must be proportional to the capabilities of the individual servers. This is essential in adding new nodes with higher capacity without having to upgrade all hosts at once.
Solution: Consistency Hashing Advantage: Incremental Scalability
기존의 retational DB(SQL)는 strong consistency 때문에 partition 이 불가능함 (partition 을 하면 strong consistency 가 어려움). 따라서 dynamo는 nosql 기반 (key-value 기반.)
Traditional replicated relational database systems focus on the problem of guaranteeing strong consistency to replicated data. Although strong consistency provides the application writer a convenient programming model, these systems are limited in scalability and availability [7]. These systems are not capable of handling network partitions because they typically provide strong consistency guarantees.
만일 키 요청이 특정 area 에만 몰리면, 그 키값 범위의 노드만 데이터가 많아짐. (non-uniform, not equal load distribution) 노드간의 performance 가 다를 수 있음을 고려하지안음.
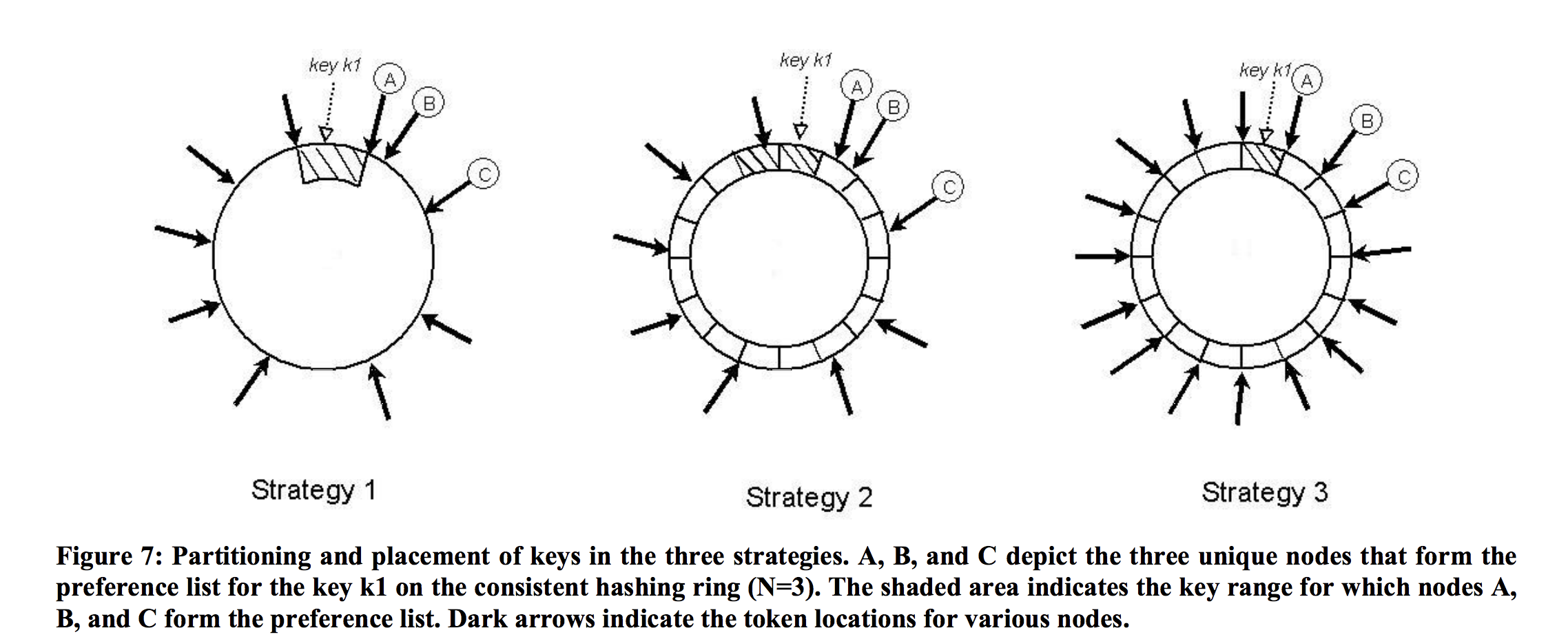
The basic consistent hashing algorithm presents some challenges. First, the random position assignment of each node on the ring leads to non-uniform data and load distribution. Second, the basic algorithm is oblivious to the heterogeneity in the performance of nodes.
single point 에 저장하는대신 한 노드가 여러 partition 을 담당함.
한 노드 장애 발생시 → 다른 이용가능한 노드가 data 를 핸들 새 노드 추가시 → 다른 노드만큼의 equivalent amount of load 를 가짐 한 노드가 담당하는 virtual node 의 갯수는 그 노드의 성능에 따라 다르게 설정할수있음 (인프라의 heterogeneity 대응 가능)
- Coordinator node: node in charge of data items (first node in preference list).
- Preference list: The list of nodes that is responsible for storing a particular key
- failure 에 대비해 N 노드 보다 많이 들어있다. (N 이란 한노드당 replica 개수)
- ring 에서 pref list 를 만들때 최소 N개의 다른 physical 노드가 들어있도록 같은 노드가 나오면 skip 한다.
- coordinator 는 이 pref list 중 첫번쨰 노드
- any request 는 이 pref list 노드중 아무 노드나 선택하는데 만약 top N 노드말고 다른 노드가 선택되면 (failure 대비하기 위한 예비노드) 이 노드로 전파되는게 아니라 coordinator 로 간다.
- Adding/Removing Storage Nodes (chapter 4.9 in paper)
- 새로운 Node 가 추가되면, 기존의 노드가 갖고있던 key range 중 일부를 새로운 Node 의 key range 로 바꿔주면됨 (Laod Balancer 의 hashmap 을 수정해주면 됨). (데이터 이동에 대한 말은 논문에는 없음.)
Solution: Vector clocs with reconciliation during reads Advantage: Version size is decoupled from update rates.
version 컨트롤 백터클락 사용해서. 기록한다음 나중에 read 할때 모든 노드들 중 최신거 읽으면 됨 write 할때는 버전이 나뉠수있으니 ( 노드 y 에 write 할때 x 의 최신 데이터 읽고 쓰는데 바로뒤에 z에도 동시에 x에서 읽고 쓸때 일단 벡터 클락, 버전으로 저장한다음 나중에 x에서 읽을때 다 합침. 백터클락이기 때문에 합칠때 클락값 높아짐 x의)
Solution: Sloppy Quorum and hinted handoff Advantage: Provides high availability and durability guarantee when some of the replicas are not available
Quorum: minimum number of members which should agree to mark an action as successful. r 읽을때 합치는 노드수 + w 쓰는 노드수 > 노드 수 보다 커야 됨 Sloppy Quorum: Reads and writes still require r and w successful responses, but those may include nodes that are not in the “preference list” for the key. Hinted handoff: 노드 A,B,C 가 있을 때 B 가 장애 발생했는데 key k 쓰기 요청이 오면 일단 C 에 쓰고 B가 복구가 됬을때 B 에 다시 전달한다. 그러나 failure rate 이 low 하고 transient(일시적) 일때만 사용가능.
Solution: Anti-Entropy using Merkle trees Advantage: Synchronizes divergent replicas in the background
만일 hinted node 조차도 원래 노드로 data를 전달 하기 전에 offline 되어 버린다면?? → anti entrophy to maintain replica synchronization.
A Merkle tree is a hash tree where leaf nodes contain hashed values of each key. Parent nodes higher in the tree are hashes of their respective children. If the hash values of the root nodes of two trees are the same, then it means those two trees are equal.
merkle tree 를 사용한 replica synchronization
This projects supports
- Partitioning with Consistent Hash.
- gRPC