-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 198
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Tree-shaking? #296
Comments
|
Try doing |
|
Yes, it would interest everyone. Why isn't this being done automatically. Most functions on this library really don't have many dependencies and yet they're all being bundled. |
|
Probably because of all the |
|
Indeed, that is the reason, I just tried. What can I do to make it so this is better? It is not really possible to import from |
|
I commented out all exports except for keys ( |
|
Honestly, I think the bundlers have to work on this, not the libraries. Or at least there should be some documentation somewhere about how the damn thing works. I can't find any. |
|
@fiatjaf I'll try with another bundler. Let me give this a shot |
|
@fr4nzap What bundler are you using?
This is why Deno letting you import directly by URL is good. Technically browsers can also do this. Some of them. |
|
Okay so tree shaking is a deep rabbit hole. Not a simple toggle but a nuanced subject; bundlers often times cannot detect which exports could trigger side-effects and therefore choose to act conservatively and keep them. For this reason the export const schnorr = /* @__PURE__ */ (() => ({
getPublicKey: schnorrGetPublicKey,
sign: schnorrSign,
verify: schnorrVerify,
utils: {
randomPrivateKey: secp256k1.utils.randomPrivateKey,
lift_x,
pointToBytes,
numberToBytesBE,
bytesToNumberBE,
taggedHash,
mod,
},
}))();However from what I read this is not great because, while this export is tree-shakeable, as soon as you use one of its functions you need to import the whole thing. The way it's done in I commented out all exports besides The I migrated I was using Vite (with Rollup) from to create the bundle from the client app using Quite difficult to understand exactly what to change. |
|
What tool are you using for the bundle analyzer in Vite? I need to do the same thing. |
|
@alexgleason |
|
Maybe we can improve tree-shaking in noble @paulmillr |
|
I tried to add |
|
@alexgleason @fr4nzap tree-shaking in noble works perfectly well. sha256 bundle only has code relevant to sha256. If it doesn't work for you, then you're doing something wrong. |
|
Just adding What do I do to ensure these subpackages are built separately and people can only import them if they do it explicitly, like |
I added In this new Solid project my initial bundle was 7.69 kb, when adding For comparison, my more complex Solid project https://github.com/fr4nzap/zapthreads uses This is proof that it is possible to use
|
No, but I did rebuild it with If I remember correctly by importing just |
|
if you can attach bundled nostr-tools with just generatePrivateKey I can help to investigate/decrease bundle size |
(() => {
var __defProp = Object.defineProperty;
var __export = (target, all) => {
for (var name in all)
__defProp(target, name, { get: all[name], enumerable: true });
};
// node_modules/@noble/curves/node_modules/@noble/hashes/esm/_assert.js
function number(n) {
if (!Number.isSafeInteger(n) || n < 0)
throw new Error(`Wrong positive integer: ${n}`);
}
function bytes(b, ...lengths) {
if (!(b instanceof Uint8Array))
throw new Error("Expected Uint8Array");
if (lengths.length > 0 && !lengths.includes(b.length))
throw new Error(`Expected Uint8Array of length ${lengths}, not of length=${b.length}`);
}
function hash(hash2) {
if (typeof hash2 !== "function" || typeof hash2.create !== "function")
throw new Error("Hash should be wrapped by utils.wrapConstructor");
number(hash2.outputLen);
number(hash2.blockLen);
}
function exists(instance, checkFinished = true) {
if (instance.destroyed)
throw new Error("Hash instance has been destroyed");
if (checkFinished && instance.finished)
throw new Error("Hash#digest() has already been called");
}
function output(out, instance) {
bytes(out);
const min = instance.outputLen;
if (out.length < min) {
throw new Error(`digestInto() expects output buffer of length at least ${min}`);
}
}
// node_modules/@noble/curves/node_modules/@noble/hashes/esm/crypto.js
var crypto = typeof globalThis === "object" && "crypto" in globalThis ? globalThis.crypto : void 0;
// node_modules/@noble/curves/node_modules/@noble/hashes/esm/utils.js
var u8a = (a) => a instanceof Uint8Array;
var createView = (arr) => new DataView(arr.buffer, arr.byteOffset, arr.byteLength);
var rotr = (word, shift) => word << 32 - shift | word >>> shift;
var isLE = new Uint8Array(new Uint32Array([287454020]).buffer)[0] === 68;
if (!isLE)
throw new Error("Non little-endian hardware is not supported");
function utf8ToBytes(str) {
if (typeof str !== "string")
throw new Error(`utf8ToBytes expected string, got ${typeof str}`);
return new Uint8Array(new TextEncoder().encode(str));
}
function toBytes(data) {
if (typeof data === "string")
data = utf8ToBytes(data);
if (!u8a(data))
throw new Error(`expected Uint8Array, got ${typeof data}`);
return data;
}
function concatBytes(...arrays) {
const r = new Uint8Array(arrays.reduce((sum, a) => sum + a.length, 0));
let pad = 0;
arrays.forEach((a) => {
if (!u8a(a))
throw new Error("Uint8Array expected");
r.set(a, pad);
pad += a.length;
});
return r;
}
var Hash = class {
// Safe version that clones internal state
clone() {
return this._cloneInto();
}
};
var toStr = {}.toString;
function wrapConstructor(hashCons) {
const hashC = (msg) => hashCons().update(toBytes(msg)).digest();
const tmp = hashCons();
hashC.outputLen = tmp.outputLen;
hashC.blockLen = tmp.blockLen;
hashC.create = () => hashCons();
return hashC;
}
function randomBytes(bytesLength = 32) {
if (crypto && typeof crypto.getRandomValues === "function") {
return crypto.getRandomValues(new Uint8Array(bytesLength));
}
throw new Error("crypto.getRandomValues must be defined");
}
// node_modules/@noble/curves/node_modules/@noble/hashes/esm/_sha2.js
function setBigUint64(view, byteOffset, value, isLE2) {
if (typeof view.setBigUint64 === "function")
return view.setBigUint64(byteOffset, value, isLE2);
const _32n = BigInt(32);
const _u32_max = BigInt(4294967295);
const wh = Number(value >> _32n & _u32_max);
const wl = Number(value & _u32_max);
const h = isLE2 ? 4 : 0;
const l = isLE2 ? 0 : 4;
view.setUint32(byteOffset + h, wh, isLE2);
view.setUint32(byteOffset + l, wl, isLE2);
}
var SHA2 = class extends Hash {
constructor(blockLen, outputLen, padOffset, isLE2) {
super();
this.blockLen = blockLen;
this.outputLen = outputLen;
this.padOffset = padOffset;
this.isLE = isLE2;
this.finished = false;
this.length = 0;
this.pos = 0;
this.destroyed = false;
this.buffer = new Uint8Array(blockLen);
this.view = createView(this.buffer);
}
update(data) {
exists(this);
const { view, buffer, blockLen } = this;
data = toBytes(data);
const len = data.length;
for (let pos = 0; pos < len; ) {
const take = Math.min(blockLen - this.pos, len - pos);
if (take === blockLen) {
const dataView = createView(data);
for (; blockLen <= len - pos; pos += blockLen)
this.process(dataView, pos);
continue;
}
buffer.set(data.subarray(pos, pos + take), this.pos);
this.pos += take;
pos += take;
if (this.pos === blockLen) {
this.process(view, 0);
this.pos = 0;
}
}
this.length += data.length;
this.roundClean();
return this;
}
digestInto(out) {
exists(this);
output(out, this);
this.finished = true;
const { buffer, view, blockLen, isLE: isLE2 } = this;
let { pos } = this;
buffer[pos++] = 128;
this.buffer.subarray(pos).fill(0);
if (this.padOffset > blockLen - pos) {
this.process(view, 0);
pos = 0;
}
for (let i = pos; i < blockLen; i++)
buffer[i] = 0;
setBigUint64(view, blockLen - 8, BigInt(this.length * 8), isLE2);
this.process(view, 0);
const oview = createView(out);
const len = this.outputLen;
if (len % 4)
throw new Error("_sha2: outputLen should be aligned to 32bit");
const outLen = len / 4;
const state = this.get();
if (outLen > state.length)
throw new Error("_sha2: outputLen bigger than state");
for (let i = 0; i < outLen; i++)
oview.setUint32(4 * i, state[i], isLE2);
}
digest() {
const { buffer, outputLen } = this;
this.digestInto(buffer);
const res = buffer.slice(0, outputLen);
this.destroy();
return res;
}
_cloneInto(to) {
to || (to = new this.constructor());
to.set(...this.get());
const { blockLen, buffer, length, finished, destroyed, pos } = this;
to.length = length;
to.pos = pos;
to.finished = finished;
to.destroyed = destroyed;
if (length % blockLen)
to.buffer.set(buffer);
return to;
}
};
// node_modules/@noble/curves/node_modules/@noble/hashes/esm/sha256.js
var Chi = (a, b, c) => a & b ^ ~a & c;
var Maj = (a, b, c) => a & b ^ a & c ^ b & c;
var SHA256_K = /* @__PURE__ */ new Uint32Array([
1116352408,
1899447441,
3049323471,
3921009573,
961987163,
1508970993,
2453635748,
2870763221,
3624381080,
310598401,
607225278,
1426881987,
1925078388,
2162078206,
2614888103,
3248222580,
3835390401,
4022224774,
264347078,
604807628,
770255983,
1249150122,
1555081692,
1996064986,
2554220882,
2821834349,
2952996808,
3210313671,
3336571891,
3584528711,
113926993,
338241895,
666307205,
773529912,
1294757372,
1396182291,
1695183700,
1986661051,
2177026350,
2456956037,
2730485921,
2820302411,
3259730800,
3345764771,
3516065817,
3600352804,
4094571909,
275423344,
430227734,
506948616,
659060556,
883997877,
958139571,
1322822218,
1537002063,
1747873779,
1955562222,
2024104815,
2227730452,
2361852424,
2428436474,
2756734187,
3204031479,
3329325298
]);
var IV = /* @__PURE__ */ new Uint32Array([
1779033703,
3144134277,
1013904242,
2773480762,
1359893119,
2600822924,
528734635,
1541459225
]);
var SHA256_W = /* @__PURE__ */ new Uint32Array(64);
var SHA256 = class extends SHA2 {
constructor() {
super(64, 32, 8, false);
this.A = IV[0] | 0;
this.B = IV[1] | 0;
this.C = IV[2] | 0;
this.D = IV[3] | 0;
this.E = IV[4] | 0;
this.F = IV[5] | 0;
this.G = IV[6] | 0;
this.H = IV[7] | 0;
}
get() {
const { A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H } = this;
return [A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H];
}
// prettier-ignore
set(A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H) {
this.A = A | 0;
this.B = B | 0;
this.C = C | 0;
this.D = D | 0;
this.E = E | 0;
this.F = F | 0;
this.G = G | 0;
this.H = H | 0;
}
process(view, offset) {
for (let i = 0; i < 16; i++, offset += 4)
SHA256_W[i] = view.getUint32(offset, false);
for (let i = 16; i < 64; i++) {
const W15 = SHA256_W[i - 15];
const W2 = SHA256_W[i - 2];
const s0 = rotr(W15, 7) ^ rotr(W15, 18) ^ W15 >>> 3;
const s1 = rotr(W2, 17) ^ rotr(W2, 19) ^ W2 >>> 10;
SHA256_W[i] = s1 + SHA256_W[i - 7] + s0 + SHA256_W[i - 16] | 0;
}
let { A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H } = this;
for (let i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
const sigma1 = rotr(E, 6) ^ rotr(E, 11) ^ rotr(E, 25);
const T1 = H + sigma1 + Chi(E, F, G) + SHA256_K[i] + SHA256_W[i] | 0;
const sigma0 = rotr(A, 2) ^ rotr(A, 13) ^ rotr(A, 22);
const T2 = sigma0 + Maj(A, B, C) | 0;
H = G;
G = F;
F = E;
E = D + T1 | 0;
D = C;
C = B;
B = A;
A = T1 + T2 | 0;
}
A = A + this.A | 0;
B = B + this.B | 0;
C = C + this.C | 0;
D = D + this.D | 0;
E = E + this.E | 0;
F = F + this.F | 0;
G = G + this.G | 0;
H = H + this.H | 0;
this.set(A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H);
}
roundClean() {
SHA256_W.fill(0);
}
destroy() {
this.set(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
this.buffer.fill(0);
}
};
var sha256 = /* @__PURE__ */ wrapConstructor(() => new SHA256());
// node_modules/@noble/curves/esm/abstract/utils.js
var utils_exports = {};
__export(utils_exports, {
bitGet: () => bitGet,
bitLen: () => bitLen,
bitMask: () => bitMask,
bitSet: () => bitSet,
bytesToHex: () => bytesToHex,
bytesToNumberBE: () => bytesToNumberBE,
bytesToNumberLE: () => bytesToNumberLE,
concatBytes: () => concatBytes2,
createHmacDrbg: () => createHmacDrbg,
ensureBytes: () => ensureBytes,
equalBytes: () => equalBytes,
hexToBytes: () => hexToBytes,
hexToNumber: () => hexToNumber,
numberToBytesBE: () => numberToBytesBE,
numberToBytesLE: () => numberToBytesLE,
numberToHexUnpadded: () => numberToHexUnpadded,
numberToVarBytesBE: () => numberToVarBytesBE,
utf8ToBytes: () => utf8ToBytes2,
validateObject: () => validateObject
});
var _0n = BigInt(0);
var _1n = BigInt(1);
var _2n = BigInt(2);
var u8a2 = (a) => a instanceof Uint8Array;
var hexes = /* @__PURE__ */ Array.from({ length: 256 }, (_, i) => i.toString(16).padStart(2, "0"));
function bytesToHex(bytes2) {
if (!u8a2(bytes2))
throw new Error("Uint8Array expected");
let hex = "";
for (let i = 0; i < bytes2.length; i++) {
hex += hexes[bytes2[i]];
}
return hex;
}
function numberToHexUnpadded(num) {
const hex = num.toString(16);
return hex.length & 1 ? `0${hex}` : hex;
}
function hexToNumber(hex) {
if (typeof hex !== "string")
throw new Error("hex string expected, got " + typeof hex);
return BigInt(hex === "" ? "0" : `0x${hex}`);
}
function hexToBytes(hex) {
if (typeof hex !== "string")
throw new Error("hex string expected, got " + typeof hex);
const len = hex.length;
if (len % 2)
throw new Error("padded hex string expected, got unpadded hex of length " + len);
const array = new Uint8Array(len / 2);
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
const j = i * 2;
const hexByte = hex.slice(j, j + 2);
const byte = Number.parseInt(hexByte, 16);
if (Number.isNaN(byte) || byte < 0)
throw new Error("Invalid byte sequence");
array[i] = byte;
}
return array;
}
function bytesToNumberBE(bytes2) {
return hexToNumber(bytesToHex(bytes2));
}
function bytesToNumberLE(bytes2) {
if (!u8a2(bytes2))
throw new Error("Uint8Array expected");
return hexToNumber(bytesToHex(Uint8Array.from(bytes2).reverse()));
}
function numberToBytesBE(n, len) {
return hexToBytes(n.toString(16).padStart(len * 2, "0"));
}
function numberToBytesLE(n, len) {
return numberToBytesBE(n, len).reverse();
}
function numberToVarBytesBE(n) {
return hexToBytes(numberToHexUnpadded(n));
}
function ensureBytes(title, hex, expectedLength) {
let res;
if (typeof hex === "string") {
try {
res = hexToBytes(hex);
} catch (e) {
throw new Error(`${title} must be valid hex string, got "${hex}". Cause: ${e}`);
}
} else if (u8a2(hex)) {
res = Uint8Array.from(hex);
} else {
throw new Error(`${title} must be hex string or Uint8Array`);
}
const len = res.length;
if (typeof expectedLength === "number" && len !== expectedLength)
throw new Error(`${title} expected ${expectedLength} bytes, got ${len}`);
return res;
}
function concatBytes2(...arrays) {
const r = new Uint8Array(arrays.reduce((sum, a) => sum + a.length, 0));
let pad = 0;
arrays.forEach((a) => {
if (!u8a2(a))
throw new Error("Uint8Array expected");
r.set(a, pad);
pad += a.length;
});
return r;
}
function equalBytes(b1, b2) {
if (b1.length !== b2.length)
return false;
for (let i = 0; i < b1.length; i++)
if (b1[i] !== b2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
function utf8ToBytes2(str) {
if (typeof str !== "string")
throw new Error(`utf8ToBytes expected string, got ${typeof str}`);
return new Uint8Array(new TextEncoder().encode(str));
}
function bitLen(n) {
let len;
for (len = 0; n > _0n; n >>= _1n, len += 1)
;
return len;
}
function bitGet(n, pos) {
return n >> BigInt(pos) & _1n;
}
var bitSet = (n, pos, value) => {
return n | (value ? _1n : _0n) << BigInt(pos);
};
var bitMask = (n) => (_2n << BigInt(n - 1)) - _1n;
var u8n = (data) => new Uint8Array(data);
var u8fr = (arr) => Uint8Array.from(arr);
function createHmacDrbg(hashLen, qByteLen, hmacFn) {
if (typeof hashLen !== "number" || hashLen < 2)
throw new Error("hashLen must be a number");
if (typeof qByteLen !== "number" || qByteLen < 2)
throw new Error("qByteLen must be a number");
if (typeof hmacFn !== "function")
throw new Error("hmacFn must be a function");
let v = u8n(hashLen);
let k = u8n(hashLen);
let i = 0;
const reset = () => {
v.fill(1);
k.fill(0);
i = 0;
};
const h = (...b) => hmacFn(k, v, ...b);
const reseed = (seed = u8n()) => {
k = h(u8fr([0]), seed);
v = h();
if (seed.length === 0)
return;
k = h(u8fr([1]), seed);
v = h();
};
const gen = () => {
if (i++ >= 1e3)
throw new Error("drbg: tried 1000 values");
let len = 0;
const out = [];
while (len < qByteLen) {
v = h();
const sl = v.slice();
out.push(sl);
len += v.length;
}
return concatBytes2(...out);
};
const genUntil = (seed, pred) => {
reset();
reseed(seed);
let res = void 0;
while (!(res = pred(gen())))
reseed();
reset();
return res;
};
return genUntil;
}
var validatorFns = {
bigint: (val) => typeof val === "bigint",
function: (val) => typeof val === "function",
boolean: (val) => typeof val === "boolean",
string: (val) => typeof val === "string",
stringOrUint8Array: (val) => typeof val === "string" || val instanceof Uint8Array,
isSafeInteger: (val) => Number.isSafeInteger(val),
array: (val) => Array.isArray(val),
field: (val, object) => object.Fp.isValid(val),
hash: (val) => typeof val === "function" && Number.isSafeInteger(val.outputLen)
};
function validateObject(object, validators, optValidators = {}) {
const checkField = (fieldName, type, isOptional) => {
const checkVal = validatorFns[type];
if (typeof checkVal !== "function")
throw new Error(`Invalid validator "${type}", expected function`);
const val = object[fieldName];
if (isOptional && val === void 0)
return;
if (!checkVal(val, object)) {
throw new Error(`Invalid param ${String(fieldName)}=${val} (${typeof val}), expected ${type}`);
}
};
for (const [fieldName, type] of Object.entries(validators))
checkField(fieldName, type, false);
for (const [fieldName, type] of Object.entries(optValidators))
checkField(fieldName, type, true);
return object;
}
// node_modules/@noble/curves/esm/abstract/modular.js
var _0n2 = BigInt(0);
var _1n2 = BigInt(1);
var _2n2 = BigInt(2);
var _3n = BigInt(3);
var _4n = BigInt(4);
var _5n = BigInt(5);
var _8n = BigInt(8);
var _9n = BigInt(9);
var _16n = BigInt(16);
function mod(a, b) {
const result = a % b;
return result >= _0n2 ? result : b + result;
}
function pow(num, power, modulo) {
if (modulo <= _0n2 || power < _0n2)
throw new Error("Expected power/modulo > 0");
if (modulo === _1n2)
return _0n2;
let res = _1n2;
while (power > _0n2) {
if (power & _1n2)
res = res * num % modulo;
num = num * num % modulo;
power >>= _1n2;
}
return res;
}
function pow2(x, power, modulo) {
let res = x;
while (power-- > _0n2) {
res *= res;
res %= modulo;
}
return res;
}
function invert(number2, modulo) {
if (number2 === _0n2 || modulo <= _0n2) {
throw new Error(`invert: expected positive integers, got n=${number2} mod=${modulo}`);
}
let a = mod(number2, modulo);
let b = modulo;
let x = _0n2, y = _1n2, u = _1n2, v = _0n2;
while (a !== _0n2) {
const q = b / a;
const r = b % a;
const m = x - u * q;
const n = y - v * q;
b = a, a = r, x = u, y = v, u = m, v = n;
}
const gcd = b;
if (gcd !== _1n2)
throw new Error("invert: does not exist");
return mod(x, modulo);
}
function tonelliShanks(P) {
const legendreC = (P - _1n2) / _2n2;
let Q, S, Z;
for (Q = P - _1n2, S = 0; Q % _2n2 === _0n2; Q /= _2n2, S++)
;
for (Z = _2n2; Z < P && pow(Z, legendreC, P) !== P - _1n2; Z++)
;
if (S === 1) {
const p1div4 = (P + _1n2) / _4n;
return function tonelliFast(Fp2, n) {
const root = Fp2.pow(n, p1div4);
if (!Fp2.eql(Fp2.sqr(root), n))
throw new Error("Cannot find square root");
return root;
};
}
const Q1div2 = (Q + _1n2) / _2n2;
return function tonelliSlow(Fp2, n) {
if (Fp2.pow(n, legendreC) === Fp2.neg(Fp2.ONE))
throw new Error("Cannot find square root");
let r = S;
let g = Fp2.pow(Fp2.mul(Fp2.ONE, Z), Q);
let x = Fp2.pow(n, Q1div2);
let b = Fp2.pow(n, Q);
while (!Fp2.eql(b, Fp2.ONE)) {
if (Fp2.eql(b, Fp2.ZERO))
return Fp2.ZERO;
let m = 1;
for (let t2 = Fp2.sqr(b); m < r; m++) {
if (Fp2.eql(t2, Fp2.ONE))
break;
t2 = Fp2.sqr(t2);
}
const ge2 = Fp2.pow(g, _1n2 << BigInt(r - m - 1));
g = Fp2.sqr(ge2);
x = Fp2.mul(x, ge2);
b = Fp2.mul(b, g);
r = m;
}
return x;
};
}
function FpSqrt(P) {
if (P % _4n === _3n) {
const p1div4 = (P + _1n2) / _4n;
return function sqrt3mod4(Fp2, n) {
const root = Fp2.pow(n, p1div4);
if (!Fp2.eql(Fp2.sqr(root), n))
throw new Error("Cannot find square root");
return root;
};
}
if (P % _8n === _5n) {
const c1 = (P - _5n) / _8n;
return function sqrt5mod8(Fp2, n) {
const n2 = Fp2.mul(n, _2n2);
const v = Fp2.pow(n2, c1);
const nv = Fp2.mul(n, v);
const i = Fp2.mul(Fp2.mul(nv, _2n2), v);
const root = Fp2.mul(nv, Fp2.sub(i, Fp2.ONE));
if (!Fp2.eql(Fp2.sqr(root), n))
throw new Error("Cannot find square root");
return root;
};
}
if (P % _16n === _9n) {
}
return tonelliShanks(P);
}
var FIELD_FIELDS = [
"create",
"isValid",
"is0",
"neg",
"inv",
"sqrt",
"sqr",
"eql",
"add",
"sub",
"mul",
"pow",
"div",
"addN",
"subN",
"mulN",
"sqrN"
];
function validateField(field) {
const initial = {
ORDER: "bigint",
MASK: "bigint",
BYTES: "isSafeInteger",
BITS: "isSafeInteger"
};
const opts = FIELD_FIELDS.reduce((map, val) => {
map[val] = "function";
return map;
}, initial);
return validateObject(field, opts);
}
function FpPow(f, num, power) {
if (power < _0n2)
throw new Error("Expected power > 0");
if (power === _0n2)
return f.ONE;
if (power === _1n2)
return num;
let p = f.ONE;
let d = num;
while (power > _0n2) {
if (power & _1n2)
p = f.mul(p, d);
d = f.sqr(d);
power >>= _1n2;
}
return p;
}
function FpInvertBatch(f, nums) {
const tmp = new Array(nums.length);
const lastMultiplied = nums.reduce((acc, num, i) => {
if (f.is0(num))
return acc;
tmp[i] = acc;
return f.mul(acc, num);
}, f.ONE);
const inverted = f.inv(lastMultiplied);
nums.reduceRight((acc, num, i) => {
if (f.is0(num))
return acc;
tmp[i] = f.mul(acc, tmp[i]);
return f.mul(acc, num);
}, inverted);
return tmp;
}
function nLength(n, nBitLength) {
const _nBitLength = nBitLength !== void 0 ? nBitLength : n.toString(2).length;
const nByteLength = Math.ceil(_nBitLength / 8);
return { nBitLength: _nBitLength, nByteLength };
}
function Field(ORDER, bitLen2, isLE2 = false, redef = {}) {
if (ORDER <= _0n2)
throw new Error(`Expected Field ORDER > 0, got ${ORDER}`);
const { nBitLength: BITS, nByteLength: BYTES } = nLength(ORDER, bitLen2);
if (BYTES > 2048)
throw new Error("Field lengths over 2048 bytes are not supported");
const sqrtP = FpSqrt(ORDER);
const f = Object.freeze({
ORDER,
BITS,
BYTES,
MASK: bitMask(BITS),
ZERO: _0n2,
ONE: _1n2,
create: (num) => mod(num, ORDER),
isValid: (num) => {
if (typeof num !== "bigint")
throw new Error(`Invalid field element: expected bigint, got ${typeof num}`);
return _0n2 <= num && num < ORDER;
},
is0: (num) => num === _0n2,
isOdd: (num) => (num & _1n2) === _1n2,
neg: (num) => mod(-num, ORDER),
eql: (lhs, rhs) => lhs === rhs,
sqr: (num) => mod(num * num, ORDER),
add: (lhs, rhs) => mod(lhs + rhs, ORDER),
sub: (lhs, rhs) => mod(lhs - rhs, ORDER),
mul: (lhs, rhs) => mod(lhs * rhs, ORDER),
pow: (num, power) => FpPow(f, num, power),
div: (lhs, rhs) => mod(lhs * invert(rhs, ORDER), ORDER),
// Same as above, but doesn't normalize
sqrN: (num) => num * num,
addN: (lhs, rhs) => lhs + rhs,
subN: (lhs, rhs) => lhs - rhs,
mulN: (lhs, rhs) => lhs * rhs,
inv: (num) => invert(num, ORDER),
sqrt: redef.sqrt || ((n) => sqrtP(f, n)),
invertBatch: (lst) => FpInvertBatch(f, lst),
// TODO: do we really need constant cmov?
// We don't have const-time bigints anyway, so probably will be not very useful
cmov: (a, b, c) => c ? b : a,
toBytes: (num) => isLE2 ? numberToBytesLE(num, BYTES) : numberToBytesBE(num, BYTES),
fromBytes: (bytes2) => {
if (bytes2.length !== BYTES)
throw new Error(`Fp.fromBytes: expected ${BYTES}, got ${bytes2.length}`);
return isLE2 ? bytesToNumberLE(bytes2) : bytesToNumberBE(bytes2);
}
});
return Object.freeze(f);
}
function getFieldBytesLength(fieldOrder) {
if (typeof fieldOrder !== "bigint")
throw new Error("field order must be bigint");
const bitLength = fieldOrder.toString(2).length;
return Math.ceil(bitLength / 8);
}
function getMinHashLength(fieldOrder) {
const length = getFieldBytesLength(fieldOrder);
return length + Math.ceil(length / 2);
}
function mapHashToField(key, fieldOrder, isLE2 = false) {
const len = key.length;
const fieldLen = getFieldBytesLength(fieldOrder);
const minLen = getMinHashLength(fieldOrder);
if (len < 16 || len < minLen || len > 1024)
throw new Error(`expected ${minLen}-1024 bytes of input, got ${len}`);
const num = isLE2 ? bytesToNumberBE(key) : bytesToNumberLE(key);
const reduced = mod(num, fieldOrder - _1n2) + _1n2;
return isLE2 ? numberToBytesLE(reduced, fieldLen) : numberToBytesBE(reduced, fieldLen);
}
// node_modules/@noble/curves/esm/abstract/curve.js
var _0n3 = BigInt(0);
var _1n3 = BigInt(1);
function wNAF(c, bits) {
const constTimeNegate = (condition, item) => {
const neg = item.negate();
return condition ? neg : item;
};
const opts = (W) => {
const windows = Math.ceil(bits / W) + 1;
const windowSize = 2 ** (W - 1);
return { windows, windowSize };
};
return {
constTimeNegate,
// non-const time multiplication ladder
unsafeLadder(elm, n) {
let p = c.ZERO;
let d = elm;
while (n > _0n3) {
if (n & _1n3)
p = p.add(d);
d = d.double();
n >>= _1n3;
}
return p;
},
/**
* Creates a wNAF precomputation window. Used for caching.
* Default window size is set by `utils.precompute()` and is equal to 8.
* Number of precomputed points depends on the curve size:
* 2^(𝑊−1) * (Math.ceil(𝑛 / 𝑊) + 1), where:
* - 𝑊 is the window size
* - 𝑛 is the bitlength of the curve order.
* For a 256-bit curve and window size 8, the number of precomputed points is 128 * 33 = 4224.
* @returns precomputed point tables flattened to a single array
*/
precomputeWindow(elm, W) {
const { windows, windowSize } = opts(W);
const points = [];
let p = elm;
let base = p;
for (let window = 0; window < windows; window++) {
base = p;
points.push(base);
for (let i = 1; i < windowSize; i++) {
base = base.add(p);
points.push(base);
}
p = base.double();
}
return points;
},
/**
* Implements ec multiplication using precomputed tables and w-ary non-adjacent form.
* @param W window size
* @param precomputes precomputed tables
* @param n scalar (we don't check here, but should be less than curve order)
* @returns real and fake (for const-time) points
*/
wNAF(W, precomputes, n) {
const { windows, windowSize } = opts(W);
let p = c.ZERO;
let f = c.BASE;
const mask = BigInt(2 ** W - 1);
const maxNumber = 2 ** W;
const shiftBy = BigInt(W);
for (let window = 0; window < windows; window++) {
const offset = window * windowSize;
let wbits = Number(n & mask);
n >>= shiftBy;
if (wbits > windowSize) {
wbits -= maxNumber;
n += _1n3;
}
const offset1 = offset;
const offset2 = offset + Math.abs(wbits) - 1;
const cond1 = window % 2 !== 0;
const cond2 = wbits < 0;
if (wbits === 0) {
f = f.add(constTimeNegate(cond1, precomputes[offset1]));
} else {
p = p.add(constTimeNegate(cond2, precomputes[offset2]));
}
}
return { p, f };
},
wNAFCached(P, precomputesMap, n, transform) {
const W = P._WINDOW_SIZE || 1;
let comp = precomputesMap.get(P);
if (!comp) {
comp = this.precomputeWindow(P, W);
if (W !== 1) {
precomputesMap.set(P, transform(comp));
}
}
return this.wNAF(W, comp, n);
}
};
}
function validateBasic(curve) {
validateField(curve.Fp);
validateObject(curve, {
n: "bigint",
h: "bigint",
Gx: "field",
Gy: "field"
}, {
nBitLength: "isSafeInteger",
nByteLength: "isSafeInteger"
});
return Object.freeze({
...nLength(curve.n, curve.nBitLength),
...curve,
...{ p: curve.Fp.ORDER }
});
}
// node_modules/@noble/curves/esm/abstract/weierstrass.js
function validatePointOpts(curve) {
const opts = validateBasic(curve);
validateObject(opts, {
a: "field",
b: "field"
}, {
allowedPrivateKeyLengths: "array",
wrapPrivateKey: "boolean",
isTorsionFree: "function",
clearCofactor: "function",
allowInfinityPoint: "boolean",
fromBytes: "function",
toBytes: "function"
});
const { endo, Fp: Fp2, a } = opts;
if (endo) {
if (!Fp2.eql(a, Fp2.ZERO)) {
throw new Error("Endomorphism can only be defined for Koblitz curves that have a=0");
}
if (typeof endo !== "object" || typeof endo.beta !== "bigint" || typeof endo.splitScalar !== "function") {
throw new Error("Expected endomorphism with beta: bigint and splitScalar: function");
}
}
return Object.freeze({ ...opts });
}
var { bytesToNumberBE: b2n, hexToBytes: h2b } = utils_exports;
var DER = {
// asn.1 DER encoding utils
Err: class DERErr extends Error {
constructor(m = "") {
super(m);
}
},
_parseInt(data) {
const { Err: E } = DER;
if (data.length < 2 || data[0] !== 2)
throw new E("Invalid signature integer tag");
const len = data[1];
const res = data.subarray(2, len + 2);
if (!len || res.length !== len)
throw new E("Invalid signature integer: wrong length");
if (res[0] & 128)
throw new E("Invalid signature integer: negative");
if (res[0] === 0 && !(res[1] & 128))
throw new E("Invalid signature integer: unnecessary leading zero");
return { d: b2n(res), l: data.subarray(len + 2) };
},
toSig(hex) {
const { Err: E } = DER;
const data = typeof hex === "string" ? h2b(hex) : hex;
if (!(data instanceof Uint8Array))
throw new Error("ui8a expected");
let l = data.length;
if (l < 2 || data[0] != 48)
throw new E("Invalid signature tag");
if (data[1] !== l - 2)
throw new E("Invalid signature: incorrect length");
const { d: r, l: sBytes } = DER._parseInt(data.subarray(2));
const { d: s, l: rBytesLeft } = DER._parseInt(sBytes);
if (rBytesLeft.length)
throw new E("Invalid signature: left bytes after parsing");
return { r, s };
},
hexFromSig(sig) {
const slice = (s2) => Number.parseInt(s2[0], 16) & 8 ? "00" + s2 : s2;
const h = (num) => {
const hex = num.toString(16);
return hex.length & 1 ? `0${hex}` : hex;
};
const s = slice(h(sig.s));
const r = slice(h(sig.r));
const shl = s.length / 2;
const rhl = r.length / 2;
const sl = h(shl);
const rl = h(rhl);
return `30${h(rhl + shl + 4)}02${rl}${r}02${sl}${s}`;
}
};
var _0n4 = BigInt(0);
var _1n4 = BigInt(1);
var _2n3 = BigInt(2);
var _3n2 = BigInt(3);
var _4n2 = BigInt(4);
function weierstrassPoints(opts) {
const CURVE = validatePointOpts(opts);
const { Fp: Fp2 } = CURVE;
const toBytes2 = CURVE.toBytes || ((_c, point, _isCompressed) => {
const a = point.toAffine();
return concatBytes2(Uint8Array.from([4]), Fp2.toBytes(a.x), Fp2.toBytes(a.y));
});
const fromBytes = CURVE.fromBytes || ((bytes2) => {
const tail = bytes2.subarray(1);
const x = Fp2.fromBytes(tail.subarray(0, Fp2.BYTES));
const y = Fp2.fromBytes(tail.subarray(Fp2.BYTES, 2 * Fp2.BYTES));
return { x, y };
});
function weierstrassEquation(x) {
const { a, b } = CURVE;
const x2 = Fp2.sqr(x);
const x3 = Fp2.mul(x2, x);
return Fp2.add(Fp2.add(x3, Fp2.mul(x, a)), b);
}
if (!Fp2.eql(Fp2.sqr(CURVE.Gy), weierstrassEquation(CURVE.Gx)))
throw new Error("bad generator point: equation left != right");
function isWithinCurveOrder(num) {
return typeof num === "bigint" && _0n4 < num && num < CURVE.n;
}
function assertGE(num) {
if (!isWithinCurveOrder(num))
throw new Error("Expected valid bigint: 0 < bigint < curve.n");
}
function normPrivateKeyToScalar(key) {
const { allowedPrivateKeyLengths: lengths, nByteLength, wrapPrivateKey, n } = CURVE;
if (lengths && typeof key !== "bigint") {
if (key instanceof Uint8Array)
key = bytesToHex(key);
if (typeof key !== "string" || !lengths.includes(key.length))
throw new Error("Invalid key");
key = key.padStart(nByteLength * 2, "0");
}
let num;
try {
num = typeof key === "bigint" ? key : bytesToNumberBE(ensureBytes("private key", key, nByteLength));
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`private key must be ${nByteLength} bytes, hex or bigint, not ${typeof key}`);
}
if (wrapPrivateKey)
num = mod(num, n);
assertGE(num);
return num;
}
const pointPrecomputes = /* @__PURE__ */ new Map();
function assertPrjPoint(other) {
if (!(other instanceof Point2))
throw new Error("ProjectivePoint expected");
}
class Point2 {
constructor(px, py, pz) {
this.px = px;
this.py = py;
this.pz = pz;
if (px == null || !Fp2.isValid(px))
throw new Error("x required");
if (py == null || !Fp2.isValid(py))
throw new Error("y required");
if (pz == null || !Fp2.isValid(pz))
throw new Error("z required");
}
// Does not validate if the point is on-curve.
// Use fromHex instead, or call assertValidity() later.
static fromAffine(p) {
const { x, y } = p || {};
if (!p || !Fp2.isValid(x) || !Fp2.isValid(y))
throw new Error("invalid affine point");
if (p instanceof Point2)
throw new Error("projective point not allowed");
const is0 = (i) => Fp2.eql(i, Fp2.ZERO);
if (is0(x) && is0(y))
return Point2.ZERO;
return new Point2(x, y, Fp2.ONE);
}
get x() {
return this.toAffine().x;
}
get y() {
return this.toAffine().y;
}
/**
* Takes a bunch of Projective Points but executes only one
* inversion on all of them. Inversion is very slow operation,
* so this improves performance massively.
* Optimization: converts a list of projective points to a list of identical points with Z=1.
*/
static normalizeZ(points) {
const toInv = Fp2.invertBatch(points.map((p) => p.pz));
return points.map((p, i) => p.toAffine(toInv[i])).map(Point2.fromAffine);
}
/**
* Converts hash string or Uint8Array to Point.
* @param hex short/long ECDSA hex
*/
static fromHex(hex) {
const P = Point2.fromAffine(fromBytes(ensureBytes("pointHex", hex)));
P.assertValidity();
return P;
}
// Multiplies generator point by privateKey.
static fromPrivateKey(privateKey) {
return Point2.BASE.multiply(normPrivateKeyToScalar(privateKey));
}
// "Private method", don't use it directly
_setWindowSize(windowSize) {
this._WINDOW_SIZE = windowSize;
pointPrecomputes.delete(this);
}
// A point on curve is valid if it conforms to equation.
assertValidity() {
if (this.is0()) {
if (CURVE.allowInfinityPoint && !Fp2.is0(this.py))
return;
throw new Error("bad point: ZERO");
}
const { x, y } = this.toAffine();
if (!Fp2.isValid(x) || !Fp2.isValid(y))
throw new Error("bad point: x or y not FE");
const left = Fp2.sqr(y);
const right = weierstrassEquation(x);
if (!Fp2.eql(left, right))
throw new Error("bad point: equation left != right");
if (!this.isTorsionFree())
throw new Error("bad point: not in prime-order subgroup");
}
hasEvenY() {
const { y } = this.toAffine();
if (Fp2.isOdd)
return !Fp2.isOdd(y);
throw new Error("Field doesn't support isOdd");
}
/**
* Compare one point to another.
*/
equals(other) {
assertPrjPoint(other);
const { px: X1, py: Y1, pz: Z1 } = this;
const { px: X2, py: Y2, pz: Z2 } = other;
const U1 = Fp2.eql(Fp2.mul(X1, Z2), Fp2.mul(X2, Z1));
const U2 = Fp2.eql(Fp2.mul(Y1, Z2), Fp2.mul(Y2, Z1));
return U1 && U2;
}
/**
* Flips point to one corresponding to (x, -y) in Affine coordinates.
*/
negate() {
return new Point2(this.px, Fp2.neg(this.py), this.pz);
}
// Renes-Costello-Batina exception-free doubling formula.
// There is 30% faster Jacobian formula, but it is not complete.
// https://eprint.iacr.org/2015/1060, algorithm 3
// Cost: 8M + 3S + 3*a + 2*b3 + 15add.
double() {
const { a, b } = CURVE;
const b3 = Fp2.mul(b, _3n2);
const { px: X1, py: Y1, pz: Z1 } = this;
let X3 = Fp2.ZERO, Y3 = Fp2.ZERO, Z3 = Fp2.ZERO;
let t0 = Fp2.mul(X1, X1);
let t1 = Fp2.mul(Y1, Y1);
let t2 = Fp2.mul(Z1, Z1);
let t3 = Fp2.mul(X1, Y1);
t3 = Fp2.add(t3, t3);
Z3 = Fp2.mul(X1, Z1);
Z3 = Fp2.add(Z3, Z3);
X3 = Fp2.mul(a, Z3);
Y3 = Fp2.mul(b3, t2);
Y3 = Fp2.add(X3, Y3);
X3 = Fp2.sub(t1, Y3);
Y3 = Fp2.add(t1, Y3);
Y3 = Fp2.mul(X3, Y3);
X3 = Fp2.mul(t3, X3);
Z3 = Fp2.mul(b3, Z3);
t2 = Fp2.mul(a, t2);
t3 = Fp2.sub(t0, t2);
t3 = Fp2.mul(a, t3);
t3 = Fp2.add(t3, Z3);
Z3 = Fp2.add(t0, t0);
t0 = Fp2.add(Z3, t0);
t0 = Fp2.add(t0, t2);
t0 = Fp2.mul(t0, t3);
Y3 = Fp2.add(Y3, t0);
t2 = Fp2.mul(Y1, Z1);
t2 = Fp2.add(t2, t2);
t0 = Fp2.mul(t2, t3);
X3 = Fp2.sub(X3, t0);
Z3 = Fp2.mul(t2, t1);
Z3 = Fp2.add(Z3, Z3);
Z3 = Fp2.add(Z3, Z3);
return new Point2(X3, Y3, Z3);
}
// Renes-Costello-Batina exception-free addition formula.
// There is 30% faster Jacobian formula, but it is not complete.
// https://eprint.iacr.org/2015/1060, algorithm 1
// Cost: 12M + 0S + 3*a + 3*b3 + 23add.
add(other) {
assertPrjPoint(other);
const { px: X1, py: Y1, pz: Z1 } = this;
const { px: X2, py: Y2, pz: Z2 } = other;
let X3 = Fp2.ZERO, Y3 = Fp2.ZERO, Z3 = Fp2.ZERO;
const a = CURVE.a;
const b3 = Fp2.mul(CURVE.b, _3n2);
let t0 = Fp2.mul(X1, X2);
let t1 = Fp2.mul(Y1, Y2);
let t2 = Fp2.mul(Z1, Z2);
let t3 = Fp2.add(X1, Y1);
let t4 = Fp2.add(X2, Y2);
t3 = Fp2.mul(t3, t4);
t4 = Fp2.add(t0, t1);
t3 = Fp2.sub(t3, t4);
t4 = Fp2.add(X1, Z1);
let t5 = Fp2.add(X2, Z2);
t4 = Fp2.mul(t4, t5);
t5 = Fp2.add(t0, t2);
t4 = Fp2.sub(t4, t5);
t5 = Fp2.add(Y1, Z1);
X3 = Fp2.add(Y2, Z2);
t5 = Fp2.mul(t5, X3);
X3 = Fp2.add(t1, t2);
t5 = Fp2.sub(t5, X3);
Z3 = Fp2.mul(a, t4);
X3 = Fp2.mul(b3, t2);
Z3 = Fp2.add(X3, Z3);
X3 = Fp2.sub(t1, Z3);
Z3 = Fp2.add(t1, Z3);
Y3 = Fp2.mul(X3, Z3);
t1 = Fp2.add(t0, t0);
t1 = Fp2.add(t1, t0);
t2 = Fp2.mul(a, t2);
t4 = Fp2.mul(b3, t4);
t1 = Fp2.add(t1, t2);
t2 = Fp2.sub(t0, t2);
t2 = Fp2.mul(a, t2);
t4 = Fp2.add(t4, t2);
t0 = Fp2.mul(t1, t4);
Y3 = Fp2.add(Y3, t0);
t0 = Fp2.mul(t5, t4);
X3 = Fp2.mul(t3, X3);
X3 = Fp2.sub(X3, t0);
t0 = Fp2.mul(t3, t1);
Z3 = Fp2.mul(t5, Z3);
Z3 = Fp2.add(Z3, t0);
return new Point2(X3, Y3, Z3);
}
subtract(other) {
return this.add(other.negate());
}
is0() {
return this.equals(Point2.ZERO);
}
wNAF(n) {
return wnaf.wNAFCached(this, pointPrecomputes, n, (comp) => {
const toInv = Fp2.invertBatch(comp.map((p) => p.pz));
return comp.map((p, i) => p.toAffine(toInv[i])).map(Point2.fromAffine);
});
}
/**
* Non-constant-time multiplication. Uses double-and-add algorithm.
* It's faster, but should only be used when you don't care about
* an exposed private key e.g. sig verification, which works over *public* keys.
*/
multiplyUnsafe(n) {
const I = Point2.ZERO;
if (n === _0n4)
return I;
assertGE(n);
if (n === _1n4)
return this;
const { endo } = CURVE;
if (!endo)
return wnaf.unsafeLadder(this, n);
let { k1neg, k1, k2neg, k2 } = endo.splitScalar(n);
let k1p = I;
let k2p = I;
let d = this;
while (k1 > _0n4 || k2 > _0n4) {
if (k1 & _1n4)
k1p = k1p.add(d);
if (k2 & _1n4)
k2p = k2p.add(d);
d = d.double();
k1 >>= _1n4;
k2 >>= _1n4;
}
if (k1neg)
k1p = k1p.negate();
if (k2neg)
k2p = k2p.negate();
k2p = new Point2(Fp2.mul(k2p.px, endo.beta), k2p.py, k2p.pz);
return k1p.add(k2p);
}
/**
* Constant time multiplication.
* Uses wNAF method. Windowed method may be 10% faster,
* but takes 2x longer to generate and consumes 2x memory.
* Uses precomputes when available.
* Uses endomorphism for Koblitz curves.
* @param scalar by which the point would be multiplied
* @returns New point
*/
multiply(scalar) {
assertGE(scalar);
let n = scalar;
let point, fake;
const { endo } = CURVE;
if (endo) {
const { k1neg, k1, k2neg, k2 } = endo.splitScalar(n);
let { p: k1p, f: f1p } = this.wNAF(k1);
let { p: k2p, f: f2p } = this.wNAF(k2);
k1p = wnaf.constTimeNegate(k1neg, k1p);
k2p = wnaf.constTimeNegate(k2neg, k2p);
k2p = new Point2(Fp2.mul(k2p.px, endo.beta), k2p.py, k2p.pz);
point = k1p.add(k2p);
fake = f1p.add(f2p);
} else {
const { p, f } = this.wNAF(n);
point = p;
fake = f;
}
return Point2.normalizeZ([point, fake])[0];
}
/**
* Efficiently calculate `aP + bQ`. Unsafe, can expose private key, if used incorrectly.
* Not using Strauss-Shamir trick: precomputation tables are faster.
* The trick could be useful if both P and Q are not G (not in our case).
* @returns non-zero affine point
*/
multiplyAndAddUnsafe(Q, a, b) {
const G = Point2.BASE;
const mul = (P, a2) => a2 === _0n4 || a2 === _1n4 || !P.equals(G) ? P.multiplyUnsafe(a2) : P.multiply(a2);
const sum = mul(this, a).add(mul(Q, b));
return sum.is0() ? void 0 : sum;
}
// Converts Projective point to affine (x, y) coordinates.
// Can accept precomputed Z^-1 - for example, from invertBatch.
// (x, y, z) ∋ (x=x/z, y=y/z)
toAffine(iz) {
const { px: x, py: y, pz: z } = this;
const is0 = this.is0();
if (iz == null)
iz = is0 ? Fp2.ONE : Fp2.inv(z);
const ax = Fp2.mul(x, iz);
const ay = Fp2.mul(y, iz);
const zz = Fp2.mul(z, iz);
if (is0)
return { x: Fp2.ZERO, y: Fp2.ZERO };
if (!Fp2.eql(zz, Fp2.ONE))
throw new Error("invZ was invalid");
return { x: ax, y: ay };
}
isTorsionFree() {
const { h: cofactor, isTorsionFree } = CURVE;
if (cofactor === _1n4)
return true;
if (isTorsionFree)
return isTorsionFree(Point2, this);
throw new Error("isTorsionFree() has not been declared for the elliptic curve");
}
clearCofactor() {
const { h: cofactor, clearCofactor } = CURVE;
if (cofactor === _1n4)
return this;
if (clearCofactor)
return clearCofactor(Point2, this);
return this.multiplyUnsafe(CURVE.h);
}
toRawBytes(isCompressed = true) {
this.assertValidity();
return toBytes2(Point2, this, isCompressed);
}
toHex(isCompressed = true) {
return bytesToHex(this.toRawBytes(isCompressed));
}
}
Point2.BASE = new Point2(CURVE.Gx, CURVE.Gy, Fp2.ONE);
Point2.ZERO = new Point2(Fp2.ZERO, Fp2.ONE, Fp2.ZERO);
const _bits = CURVE.nBitLength;
const wnaf = wNAF(Point2, CURVE.endo ? Math.ceil(_bits / 2) : _bits);
return {
CURVE,
ProjectivePoint: Point2,
normPrivateKeyToScalar,
weierstrassEquation,
isWithinCurveOrder
};
}
function validateOpts(curve) {
const opts = validateBasic(curve);
validateObject(opts, {
hash: "hash",
hmac: "function",
randomBytes: "function"
}, {
bits2int: "function",
bits2int_modN: "function",
lowS: "boolean"
});
return Object.freeze({ lowS: true, ...opts });
}
function weierstrass(curveDef) {
const CURVE = validateOpts(curveDef);
const { Fp: Fp2, n: CURVE_ORDER } = CURVE;
const compressedLen = Fp2.BYTES + 1;
const uncompressedLen = 2 * Fp2.BYTES + 1;
function isValidFieldElement(num) {
return _0n4 < num && num < Fp2.ORDER;
}
function modN2(a) {
return mod(a, CURVE_ORDER);
}
function invN(a) {
return invert(a, CURVE_ORDER);
}
const { ProjectivePoint: Point2, normPrivateKeyToScalar, weierstrassEquation, isWithinCurveOrder } = weierstrassPoints({
...CURVE,
toBytes(_c, point, isCompressed) {
const a = point.toAffine();
const x = Fp2.toBytes(a.x);
const cat = concatBytes2;
if (isCompressed) {
return cat(Uint8Array.from([point.hasEvenY() ? 2 : 3]), x);
} else {
return cat(Uint8Array.from([4]), x, Fp2.toBytes(a.y));
}
},
fromBytes(bytes2) {
const len = bytes2.length;
const head = bytes2[0];
const tail = bytes2.subarray(1);
if (len === compressedLen && (head === 2 || head === 3)) {
const x = bytesToNumberBE(tail);
if (!isValidFieldElement(x))
throw new Error("Point is not on curve");
const y2 = weierstrassEquation(x);
let y = Fp2.sqrt(y2);
const isYOdd = (y & _1n4) === _1n4;
const isHeadOdd = (head & 1) === 1;
if (isHeadOdd !== isYOdd)
y = Fp2.neg(y);
return { x, y };
} else if (len === uncompressedLen && head === 4) {
const x = Fp2.fromBytes(tail.subarray(0, Fp2.BYTES));
const y = Fp2.fromBytes(tail.subarray(Fp2.BYTES, 2 * Fp2.BYTES));
return { x, y };
} else {
throw new Error(`Point of length ${len} was invalid. Expected ${compressedLen} compressed bytes or ${uncompressedLen} uncompressed bytes`);
}
}
});
const numToNByteStr = (num) => bytesToHex(numberToBytesBE(num, CURVE.nByteLength));
function isBiggerThanHalfOrder(number2) {
const HALF = CURVE_ORDER >> _1n4;
return number2 > HALF;
}
function normalizeS(s) {
return isBiggerThanHalfOrder(s) ? modN2(-s) : s;
}
const slcNum = (b, from, to) => bytesToNumberBE(b.slice(from, to));
class Signature {
constructor(r, s, recovery) {
this.r = r;
this.s = s;
this.recovery = recovery;
this.assertValidity();
}
// pair (bytes of r, bytes of s)
static fromCompact(hex) {
const l = CURVE.nByteLength;
hex = ensureBytes("compactSignature", hex, l * 2);
return new Signature(slcNum(hex, 0, l), slcNum(hex, l, 2 * l));
}
// DER encoded ECDSA signature
// https://bitcoin.stackexchange.com/questions/57644/what-are-the-parts-of-a-bitcoin-transaction-input-script
static fromDER(hex) {
const { r, s } = DER.toSig(ensureBytes("DER", hex));
return new Signature(r, s);
}
assertValidity() {
if (!isWithinCurveOrder(this.r))
throw new Error("r must be 0 < r < CURVE.n");
if (!isWithinCurveOrder(this.s))
throw new Error("s must be 0 < s < CURVE.n");
}
addRecoveryBit(recovery) {
return new Signature(this.r, this.s, recovery);
}
recoverPublicKey(msgHash) {
const { r, s, recovery: rec } = this;
const h = bits2int_modN(ensureBytes("msgHash", msgHash));
if (rec == null || ![0, 1, 2, 3].includes(rec))
throw new Error("recovery id invalid");
const radj = rec === 2 || rec === 3 ? r + CURVE.n : r;
if (radj >= Fp2.ORDER)
throw new Error("recovery id 2 or 3 invalid");
const prefix = (rec & 1) === 0 ? "02" : "03";
const R = Point2.fromHex(prefix + numToNByteStr(radj));
const ir = invN(radj);
const u1 = modN2(-h * ir);
const u2 = modN2(s * ir);
const Q = Point2.BASE.multiplyAndAddUnsafe(R, u1, u2);
if (!Q)
throw new Error("point at infinify");
Q.assertValidity();
return Q;
}
// Signatures should be low-s, to prevent malleability.
hasHighS() {
return isBiggerThanHalfOrder(this.s);
}
normalizeS() {
return this.hasHighS() ? new Signature(this.r, modN2(-this.s), this.recovery) : this;
}
// DER-encoded
toDERRawBytes() {
return hexToBytes(this.toDERHex());
}
toDERHex() {
return DER.hexFromSig({ r: this.r, s: this.s });
}
// padded bytes of r, then padded bytes of s
toCompactRawBytes() {
return hexToBytes(this.toCompactHex());
}
toCompactHex() {
return numToNByteStr(this.r) + numToNByteStr(this.s);
}
}
const utils = {
isValidPrivateKey(privateKey) {
try {
normPrivateKeyToScalar(privateKey);
return true;
} catch (error) {
return false;
}
},
normPrivateKeyToScalar,
/**
* Produces cryptographically secure private key from random of size
* (groupLen + ceil(groupLen / 2)) with modulo bias being negligible.
*/
randomPrivateKey: () => {
const length = getMinHashLength(CURVE.n);
return mapHashToField(CURVE.randomBytes(length), CURVE.n);
},
/**
* Creates precompute table for an arbitrary EC point. Makes point "cached".
* Allows to massively speed-up `point.multiply(scalar)`.
* @returns cached point
* @example
* const fast = utils.precompute(8, ProjectivePoint.fromHex(someonesPubKey));
* fast.multiply(privKey); // much faster ECDH now
*/
precompute(windowSize = 8, point = Point2.BASE) {
point._setWindowSize(windowSize);
point.multiply(BigInt(3));
return point;
}
};
function getPublicKey(privateKey, isCompressed = true) {
return Point2.fromPrivateKey(privateKey).toRawBytes(isCompressed);
}
function isProbPub(item) {
const arr = item instanceof Uint8Array;
const str = typeof item === "string";
const len = (arr || str) && item.length;
if (arr)
return len === compressedLen || len === uncompressedLen;
if (str)
return len === 2 * compressedLen || len === 2 * uncompressedLen;
if (item instanceof Point2)
return true;
return false;
}
function getSharedSecret(privateA, publicB, isCompressed = true) {
if (isProbPub(privateA))
throw new Error("first arg must be private key");
if (!isProbPub(publicB))
throw new Error("second arg must be public key");
const b = Point2.fromHex(publicB);
return b.multiply(normPrivateKeyToScalar(privateA)).toRawBytes(isCompressed);
}
const bits2int = CURVE.bits2int || function(bytes2) {
const num = bytesToNumberBE(bytes2);
const delta = bytes2.length * 8 - CURVE.nBitLength;
return delta > 0 ? num >> BigInt(delta) : num;
};
const bits2int_modN = CURVE.bits2int_modN || function(bytes2) {
return modN2(bits2int(bytes2));
};
const ORDER_MASK = bitMask(CURVE.nBitLength);
function int2octets(num) {
if (typeof num !== "bigint")
throw new Error("bigint expected");
if (!(_0n4 <= num && num < ORDER_MASK))
throw new Error(`bigint expected < 2^${CURVE.nBitLength}`);
return numberToBytesBE(num, CURVE.nByteLength);
}
function prepSig(msgHash, privateKey, opts = defaultSigOpts) {
if (["recovered", "canonical"].some((k) => k in opts))
throw new Error("sign() legacy options not supported");
const { hash: hash2, randomBytes: randomBytes2 } = CURVE;
let { lowS, prehash, extraEntropy: ent } = opts;
if (lowS == null)
lowS = true;
msgHash = ensureBytes("msgHash", msgHash);
if (prehash)
msgHash = ensureBytes("prehashed msgHash", hash2(msgHash));
const h1int = bits2int_modN(msgHash);
const d = normPrivateKeyToScalar(privateKey);
const seedArgs = [int2octets(d), int2octets(h1int)];
if (ent != null) {
const e = ent === true ? randomBytes2(Fp2.BYTES) : ent;
seedArgs.push(ensureBytes("extraEntropy", e));
}
const seed = concatBytes2(...seedArgs);
const m = h1int;
function k2sig(kBytes) {
const k = bits2int(kBytes);
if (!isWithinCurveOrder(k))
return;
const ik = invN(k);
const q = Point2.BASE.multiply(k).toAffine();
const r = modN2(q.x);
if (r === _0n4)
return;
const s = modN2(ik * modN2(m + r * d));
if (s === _0n4)
return;
let recovery = (q.x === r ? 0 : 2) | Number(q.y & _1n4);
let normS = s;
if (lowS && isBiggerThanHalfOrder(s)) {
normS = normalizeS(s);
recovery ^= 1;
}
return new Signature(r, normS, recovery);
}
return { seed, k2sig };
}
const defaultSigOpts = { lowS: CURVE.lowS, prehash: false };
const defaultVerOpts = { lowS: CURVE.lowS, prehash: false };
function sign(msgHash, privKey, opts = defaultSigOpts) {
const { seed, k2sig } = prepSig(msgHash, privKey, opts);
const C = CURVE;
const drbg = createHmacDrbg(C.hash.outputLen, C.nByteLength, C.hmac);
return drbg(seed, k2sig);
}
Point2.BASE._setWindowSize(8);
function verify(signature, msgHash, publicKey, opts = defaultVerOpts) {
const sg = signature;
msgHash = ensureBytes("msgHash", msgHash);
publicKey = ensureBytes("publicKey", publicKey);
if ("strict" in opts)
throw new Error("options.strict was renamed to lowS");
const { lowS, prehash } = opts;
let _sig = void 0;
let P;
try {
if (typeof sg === "string" || sg instanceof Uint8Array) {
try {
_sig = Signature.fromDER(sg);
} catch (derError) {
if (!(derError instanceof DER.Err))
throw derError;
_sig = Signature.fromCompact(sg);
}
} else if (typeof sg === "object" && typeof sg.r === "bigint" && typeof sg.s === "bigint") {
const { r: r2, s: s2 } = sg;
_sig = new Signature(r2, s2);
} else {
throw new Error("PARSE");
}
P = Point2.fromHex(publicKey);
} catch (error) {
if (error.message === "PARSE")
throw new Error(`signature must be Signature instance, Uint8Array or hex string`);
return false;
}
if (lowS && _sig.hasHighS())
return false;
if (prehash)
msgHash = CURVE.hash(msgHash);
const { r, s } = _sig;
const h = bits2int_modN(msgHash);
const is = invN(s);
const u1 = modN2(h * is);
const u2 = modN2(r * is);
const R = Point2.BASE.multiplyAndAddUnsafe(P, u1, u2)?.toAffine();
if (!R)
return false;
const v = modN2(R.x);
return v === r;
}
return {
CURVE,
getPublicKey,
getSharedSecret,
sign,
verify,
ProjectivePoint: Point2,
Signature,
utils
};
}
// node_modules/@noble/curves/node_modules/@noble/hashes/esm/hmac.js
var HMAC = class extends Hash {
constructor(hash2, _key) {
super();
this.finished = false;
this.destroyed = false;
hash(hash2);
const key = toBytes(_key);
this.iHash = hash2.create();
if (typeof this.iHash.update !== "function")
throw new Error("Expected instance of class which extends utils.Hash");
this.blockLen = this.iHash.blockLen;
this.outputLen = this.iHash.outputLen;
const blockLen = this.blockLen;
const pad = new Uint8Array(blockLen);
pad.set(key.length > blockLen ? hash2.create().update(key).digest() : key);
for (let i = 0; i < pad.length; i++)
pad[i] ^= 54;
this.iHash.update(pad);
this.oHash = hash2.create();
for (let i = 0; i < pad.length; i++)
pad[i] ^= 54 ^ 92;
this.oHash.update(pad);
pad.fill(0);
}
update(buf) {
exists(this);
this.iHash.update(buf);
return this;
}
digestInto(out) {
exists(this);
bytes(out, this.outputLen);
this.finished = true;
this.iHash.digestInto(out);
this.oHash.update(out);
this.oHash.digestInto(out);
this.destroy();
}
digest() {
const out = new Uint8Array(this.oHash.outputLen);
this.digestInto(out);
return out;
}
_cloneInto(to) {
to || (to = Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(this), {}));
const { oHash, iHash, finished, destroyed, blockLen, outputLen } = this;
to = to;
to.finished = finished;
to.destroyed = destroyed;
to.blockLen = blockLen;
to.outputLen = outputLen;
to.oHash = oHash._cloneInto(to.oHash);
to.iHash = iHash._cloneInto(to.iHash);
return to;
}
destroy() {
this.destroyed = true;
this.oHash.destroy();
this.iHash.destroy();
}
};
var hmac = (hash2, key, message) => new HMAC(hash2, key).update(message).digest();
hmac.create = (hash2, key) => new HMAC(hash2, key);
// node_modules/@noble/curves/esm/_shortw_utils.js
function getHash(hash2) {
return {
hash: hash2,
hmac: (key, ...msgs) => hmac(hash2, key, concatBytes(...msgs)),
randomBytes
};
}
function createCurve(curveDef, defHash) {
const create = (hash2) => weierstrass({ ...curveDef, ...getHash(hash2) });
return Object.freeze({ ...create(defHash), create });
}
// node_modules/@noble/curves/esm/secp256k1.js
var secp256k1P = BigInt("0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffefffffc2f");
var secp256k1N = BigInt("0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffebaaedce6af48a03bbfd25e8cd0364141");
var _1n5 = BigInt(1);
var _2n4 = BigInt(2);
var divNearest = (a, b) => (a + b / _2n4) / b;
function sqrtMod(y) {
const P = secp256k1P;
const _3n3 = BigInt(3), _6n = BigInt(6), _11n = BigInt(11), _22n = BigInt(22);
const _23n = BigInt(23), _44n = BigInt(44), _88n = BigInt(88);
const b2 = y * y * y % P;
const b3 = b2 * b2 * y % P;
const b6 = pow2(b3, _3n3, P) * b3 % P;
const b9 = pow2(b6, _3n3, P) * b3 % P;
const b11 = pow2(b9, _2n4, P) * b2 % P;
const b22 = pow2(b11, _11n, P) * b11 % P;
const b44 = pow2(b22, _22n, P) * b22 % P;
const b88 = pow2(b44, _44n, P) * b44 % P;
const b176 = pow2(b88, _88n, P) * b88 % P;
const b220 = pow2(b176, _44n, P) * b44 % P;
const b223 = pow2(b220, _3n3, P) * b3 % P;
const t1 = pow2(b223, _23n, P) * b22 % P;
const t2 = pow2(t1, _6n, P) * b2 % P;
const root = pow2(t2, _2n4, P);
if (!Fp.eql(Fp.sqr(root), y))
throw new Error("Cannot find square root");
return root;
}
var Fp = Field(secp256k1P, void 0, void 0, { sqrt: sqrtMod });
var secp256k1 = createCurve({
a: BigInt(0),
b: BigInt(7),
Fp,
n: secp256k1N,
// Base point (x, y) aka generator point
Gx: BigInt("55066263022277343669578718895168534326250603453777594175500187360389116729240"),
Gy: BigInt("32670510020758816978083085130507043184471273380659243275938904335757337482424"),
h: BigInt(1),
lowS: true,
/**
* secp256k1 belongs to Koblitz curves: it has efficiently computable endomorphism.
* Endomorphism uses 2x less RAM, speeds up precomputation by 2x and ECDH / key recovery by 20%.
* For precomputed wNAF it trades off 1/2 init time & 1/3 ram for 20% perf hit.
* Explanation: https://gist.github.com/paulmillr/eb670806793e84df628a7c434a873066
*/
endo: {
beta: BigInt("0x7ae96a2b657c07106e64479eac3434e99cf0497512f58995c1396c28719501ee"),
splitScalar: (k) => {
const n = secp256k1N;
const a1 = BigInt("0x3086d221a7d46bcde86c90e49284eb15");
const b1 = -_1n5 * BigInt("0xe4437ed6010e88286f547fa90abfe4c3");
const a2 = BigInt("0x114ca50f7a8e2f3f657c1108d9d44cfd8");
const b2 = a1;
const POW_2_128 = BigInt("0x100000000000000000000000000000000");
const c1 = divNearest(b2 * k, n);
const c2 = divNearest(-b1 * k, n);
let k1 = mod(k - c1 * a1 - c2 * a2, n);
let k2 = mod(-c1 * b1 - c2 * b2, n);
const k1neg = k1 > POW_2_128;
const k2neg = k2 > POW_2_128;
if (k1neg)
k1 = n - k1;
if (k2neg)
k2 = n - k2;
if (k1 > POW_2_128 || k2 > POW_2_128) {
throw new Error("splitScalar: Endomorphism failed, k=" + k);
}
return { k1neg, k1, k2neg, k2 };
}
}
}, sha256);
var _0n5 = BigInt(0);
var fe = (x) => typeof x === "bigint" && _0n5 < x && x < secp256k1P;
var ge = (x) => typeof x === "bigint" && _0n5 < x && x < secp256k1N;
var TAGGED_HASH_PREFIXES = {};
function taggedHash(tag, ...messages) {
let tagP = TAGGED_HASH_PREFIXES[tag];
if (tagP === void 0) {
const tagH = sha256(Uint8Array.from(tag, (c) => c.charCodeAt(0)));
tagP = concatBytes2(tagH, tagH);
TAGGED_HASH_PREFIXES[tag] = tagP;
}
return sha256(concatBytes2(tagP, ...messages));
}
var pointToBytes = (point) => point.toRawBytes(true).slice(1);
var numTo32b = (n) => numberToBytesBE(n, 32);
var modP = (x) => mod(x, secp256k1P);
var modN = (x) => mod(x, secp256k1N);
var Point = secp256k1.ProjectivePoint;
var GmulAdd = (Q, a, b) => Point.BASE.multiplyAndAddUnsafe(Q, a, b);
function schnorrGetExtPubKey(priv) {
let d_ = secp256k1.utils.normPrivateKeyToScalar(priv);
let p = Point.fromPrivateKey(d_);
const scalar = p.hasEvenY() ? d_ : modN(-d_);
return { scalar, bytes: pointToBytes(p) };
}
function lift_x(x) {
if (!fe(x))
throw new Error("bad x: need 0 < x < p");
const xx = modP(x * x);
const c = modP(xx * x + BigInt(7));
let y = sqrtMod(c);
if (y % _2n4 !== _0n5)
y = modP(-y);
const p = new Point(x, y, _1n5);
p.assertValidity();
return p;
}
function challenge(...args) {
return modN(bytesToNumberBE(taggedHash("BIP0340/challenge", ...args)));
}
function schnorrGetPublicKey(privateKey) {
return schnorrGetExtPubKey(privateKey).bytes;
}
function schnorrSign(message, privateKey, auxRand = randomBytes(32)) {
const m = ensureBytes("message", message);
const { bytes: px, scalar: d } = schnorrGetExtPubKey(privateKey);
const a = ensureBytes("auxRand", auxRand, 32);
const t = numTo32b(d ^ bytesToNumberBE(taggedHash("BIP0340/aux", a)));
const rand = taggedHash("BIP0340/nonce", t, px, m);
const k_ = modN(bytesToNumberBE(rand));
if (k_ === _0n5)
throw new Error("sign failed: k is zero");
const { bytes: rx, scalar: k } = schnorrGetExtPubKey(k_);
const e = challenge(rx, px, m);
const sig = new Uint8Array(64);
sig.set(rx, 0);
sig.set(numTo32b(modN(k + e * d)), 32);
if (!schnorrVerify(sig, m, px))
throw new Error("sign: Invalid signature produced");
return sig;
}
function schnorrVerify(signature, message, publicKey) {
const sig = ensureBytes("signature", signature, 64);
const m = ensureBytes("message", message);
const pub = ensureBytes("publicKey", publicKey, 32);
try {
const P = lift_x(bytesToNumberBE(pub));
const r = bytesToNumberBE(sig.subarray(0, 32));
if (!fe(r))
return false;
const s = bytesToNumberBE(sig.subarray(32, 64));
if (!ge(s))
return false;
const e = challenge(numTo32b(r), pointToBytes(P), m);
const R = GmulAdd(P, s, modN(-e));
if (!R || !R.hasEvenY() || R.toAffine().x !== r)
return false;
return true;
} catch (error) {
return false;
}
}
var schnorr = /* @__PURE__ */ (() => ({
getPublicKey: schnorrGetPublicKey,
sign: schnorrSign,
verify: schnorrVerify,
utils: {
randomPrivateKey: secp256k1.utils.randomPrivateKey,
lift_x,
pointToBytes,
numberToBytesBE,
bytesToNumberBE,
taggedHash,
mod
}
}))();
// main.js
var whatever = schnorr.utils.randomPrivateKey();
console.log("blargh", whatever);
})();
/*! Bundled license information:
@noble/hashes/esm/utils.js:
(*! noble-hashes - MIT License (c) 2022 Paul Miller (paulmillr.com) *)
@noble/curves/esm/abstract/utils.js:
(*! noble-curves - MIT License (c) 2022 Paul Miller (paulmillr.com) *)
@noble/curves/esm/abstract/modular.js:
(*! noble-curves - MIT License (c) 2022 Paul Miller (paulmillr.com) *)
@noble/curves/esm/abstract/curve.js:
(*! noble-curves - MIT License (c) 2022 Paul Miller (paulmillr.com) *)
@noble/curves/esm/abstract/weierstrass.js:
(*! noble-curves - MIT License (c) 2022 Paul Miller (paulmillr.com) *)
@noble/curves/esm/_shortw_utils.js:
(*! noble-curves - MIT License (c) 2022 Paul Miller (paulmillr.com) *)
@noble/curves/esm/secp256k1.js:
(*! noble-curves - MIT License (c) 2022 Paul Miller (paulmillr.com) *)
*/ |
|
This is not nostr-tools, it's just a dumb JS file importing from |
|
Yeah. It's all necessary because If you want your generatePrivateKey imports to be as minimal as possible, you can re-implement it by copy-pasting this code: https://github.com/paulmillr/noble-curves/blob/ce7a8fda552d052a7cc01796c4909af56a945734/src/abstract/weierstrass.ts#L853 Doing that would ensure ProjectivePoint is not pulled in. However, it is necessary if you need any signing or verification functionality. So, not a big deal. |
|
This was my suspicion when following the visualization I posted earlier. So, @paulmillr you don't see any meaningful way to reduce the bundle contribution from the curves, hashes and scure packages given what import { schnorr } from '@noble/curves/secp256k1'
import { sha256 } from '@noble/hashes/sha256'
import { bytesToHex, concatBytes, hexToBytes } from '@noble/hashes/utils'
import { randomBytes } from '@noble/hashes/utils'
import { secp256k1 } from '@noble/curves/secp256k1'
import { xchacha20 } from '@noble/ciphers/chacha'
import { base64 } from '@scure/base'
import { wordlist } from '@scure/bip39/wordlists/english'
import { generateMnemonic, mnemonicToSeedSync, validateMnemonic } from '@scure/bip39'
import { HDKey } from '@scure/bip32'
import { bech32 } from '@scure/base'Most of these imports are required by common functions in ( |
|
Not really. xchacha is only imported by nostr-tools/nip44 and that shouldn't even be used. bip32 and bip39 are only used by nostr-tools/nip06. bech32 is only used by nostr-tools/nip19. base64 is only used by nostr-tools/nip04, which also shouldn't be used. But again, I must find a way to remove these subpackages from the bigger nostr-tools bundle. I just don't know how because JavaScript is a mystery. |
|
@fr4nzap everything you import is tree-shakeable. So, all imports are needed and actually used.
I don't see an issue here. Almost everyone these days is using NPM or other package manager. They can write If you are looking for configuration setup, take a look at https://github.com/paulmillr/noble-curves/tree/main/build. It uses esbuild with |
|
Check out my experiment in #301 |
|
I tried with @paulmillr 's suggestions and I think I have something working:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"outDir": "lib/esm",
"target": "es2020",
"module": "es6",
"moduleResolution": "node16",
"baseUrl": ".",
"sourceMap": true,
"strict": true,
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": false,
"allowUnreachableCode": false,
"esModuleInterop": false,
"noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true,
"noImplicitReturns": true,
"noUncheckedIndexedAccess": false,
"noUnusedLocals": true,
"noUnusedParameters": true,
},
"include": ["."],
"exclude": ["node_modules", "lib"]
}
I'm now able to do This seems correct as I copied what Do you want me to continue with these exports and submit a PR? |
|
This sounds good to me. But ensure there is also |
|
Ended up modifying the esbuild script to allow for multiple entrypoints, e.g. I don't know if this is a definitive fix but definitely appears to help with bundle sizes from apps that use Also, I don't understand how this can be transparent/automatic in other languages (like Dart) and need a PhD to do the same in Typescript |
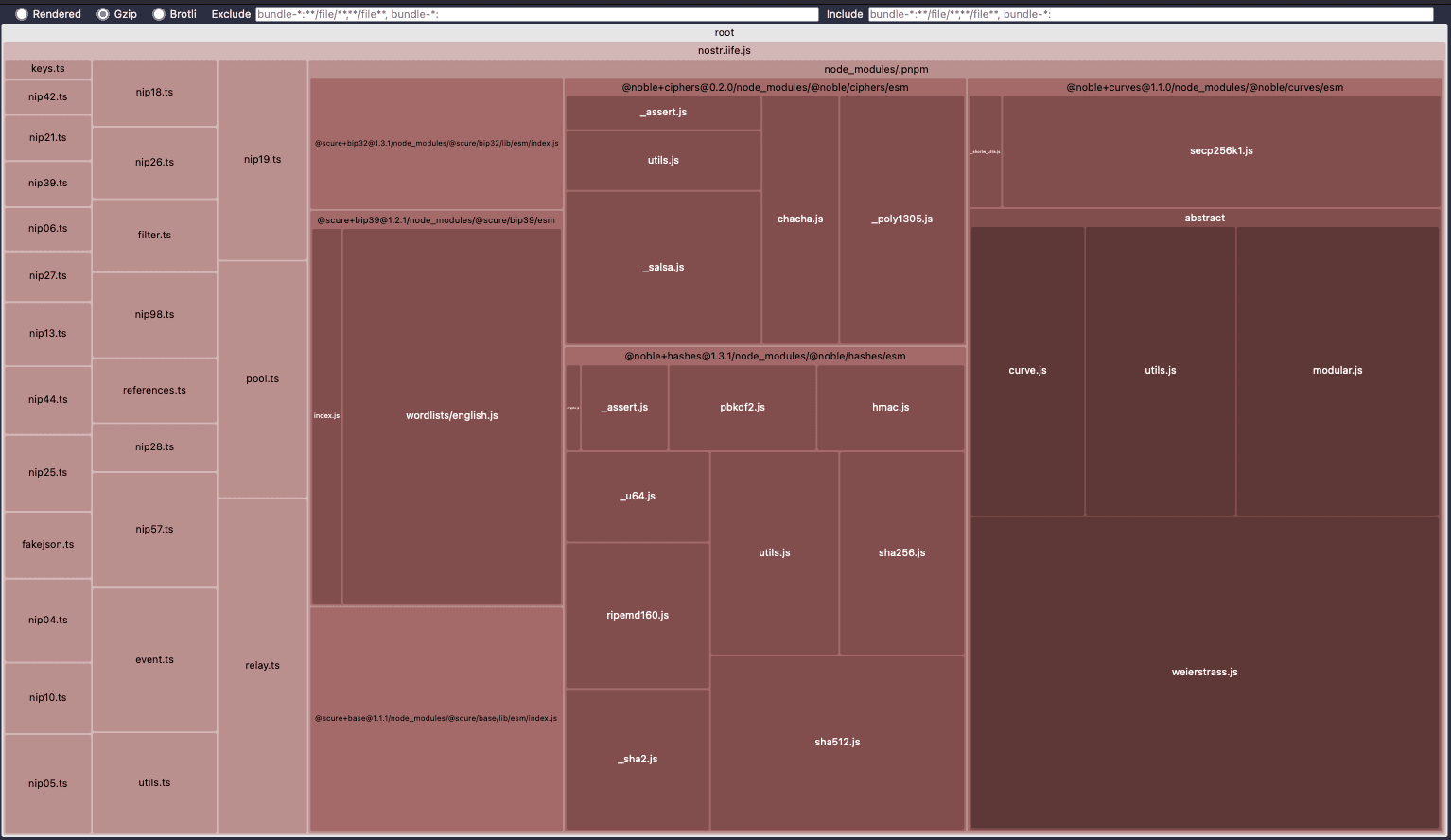
My bundle before:
Added
nostr-toolsto my project.My bundle after:
I'm building tiny widgets that I want to keep extremely small.
Is there an effort to improve tree-shaking? Would this interest anyone?
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: