|
1 | 1 | genetic-programming |
2 | 2 | =================== |
3 | 3 |
|
4 | | -Symbolic regression solver, based on genetic programming methodology. |
5 | | -More info in this [article](http://habrahabr.ru/post/163195/) |
| 4 | +[Symbolic regression](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Symbolic_regression) solver, based on [genetic programming](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_programming) methodology. |
| 5 | + |
| 6 | +## Description ## |
| 7 | + |
| 8 | +Each mathematical expression can be represented in form of syntax tree: <br/> |
| 9 | +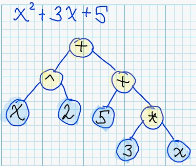 |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +Actually, it worth to keep in mind, that there exists infinite number of different syntax trees, which corresponds to semantically equivalent expressions. For example: <br/> |
| 12 | +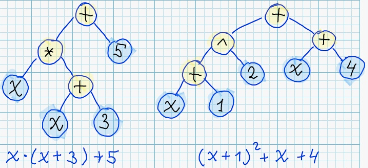 |
| 13 | + |
| 14 | +In practice, on of the most generic problems - is reconstruction of original function, having the information about its values in some specific points. |
| 15 | + |
| 16 | +It is possible to apply [genetic algorithm](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_algorithm) - for solving of given problem: |
| 17 | + |
| 18 | +1. In terms of Genetic Algorithm - each syntax tree can be treated as a "chromosome" (an entity, which can "mutate" and change by "crossover" with other "chromosome") |
| 19 | + |
| 20 | +2. It is needed to define [fitness function](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fitness_function): the function, which will calculate, how good each formula (which was encoded by syntax tree) - can represent existing data (e.g.: using [mean squared error](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mean_squared_error) value). |
| 21 | + |
| 22 | +### Crossover ### |
| 23 | +During "crossover" - syntax tree is modified by substituion of its subtree, with some subtree from other syntax tree. |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +Following image explains implementation of "crossover" operation over syntax trees: <br/> |
| 26 | +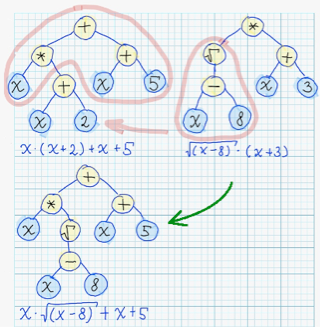 |
| 27 | + |
| 28 | +### Mutation ### |
| 29 | +Currently implemented following "mutation" operations: |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +1. Substituion of some node of syntax tree - with node, which corresponds to different arithmetical operation: <br/> |
| 32 | +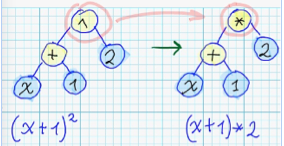 |
| 33 | + |
| 34 | +2. Substituion of some subtree with randomly generated subtree: <br/> |
| 35 | +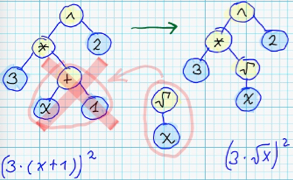 |
| 36 | + |
| 37 | +3. Removing of some intermediate node from syntax tree: <br/> |
| 38 | +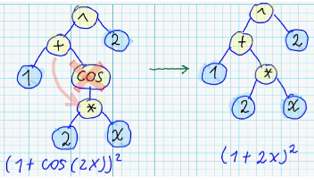 |
| 39 | + |
| 40 | +4. Expanding tree from root: <br/> |
| 41 | +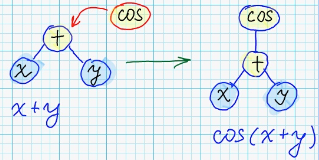 |
| 42 | + |
| 43 | +5. Swapping subtrees for non-commutative oparations: <br/> |
| 44 | +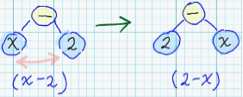 |
| 45 | + |
| 46 | +### Optimization of coefficients ### |
| 47 | +Actually, some syntax tree might represent correct structure of searchable function, but due to some non-optimal values of coefficients - given syntax tree can be considered as non-optimal by fitness function. |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +For example, following image displays target values of searchable function (red crosses) - and two functions-candidates (green and blue): <br/> |
| 50 | +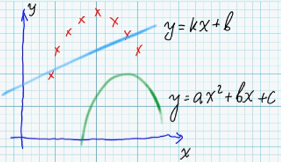 |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +Blue line has smaller value of mean squared error, but, actually - green parabola - would be a better candidate for the final solution. |
| 53 | + |
| 54 | +By this reason, current implementation of Symbolic Regression Solver - uses second pass of Genetic Algorithm - for optimizing of coefficients of each syntax tree. On the picture below - represented the way, how coefficients of each syntax tree - could be transformed to "chromosome": <br/> |
| 55 | +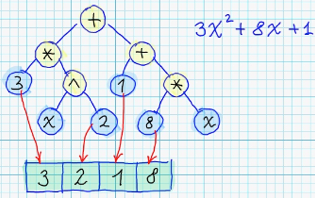 |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +More info in this [article](http://habrahabr.ru/post/163195/) (article is in Russian language). |
6 | 58 |
|
7 | 59 | This project depends on [Generic Genetic Algorithm project](https://github.com/lagodiuk/genetic-algorithm) (has a maven dependency) |
8 | 60 |
|
@@ -122,4 +174,4 @@ public class HelloSymbolicRegression { |
122 | 174 | return list; |
123 | 175 | } |
124 | 176 | } |
125 | | -``` |
| 177 | +``` |
0 commit comments