Network virtualization is the process of combining hardware and software network resources and network functionality into a single, software-based administrative entity, a virtual network.
A Virtual Network enables many types of Azure resources, such as Azure Virtual Machines (VM), to securely communicate with each other, the internet, and on-premises networks. A virtual network is scoped to a single region; however, multiple virtual networks from different regions can be connected together using Virtual Network Peering.
For each virtual network you can:
- Specify a custom private IP address space using public and private addresses.
- Segment the virtual network into one or more subnets.
- Use Azure-provided name resolution, or specify a DNS server.
-
Through a virtual network: deploy VMs, and other types.
-
Through a virtual network service endpoint: Extend vnet private address space and the identity to Azure service resources over a direct connection.
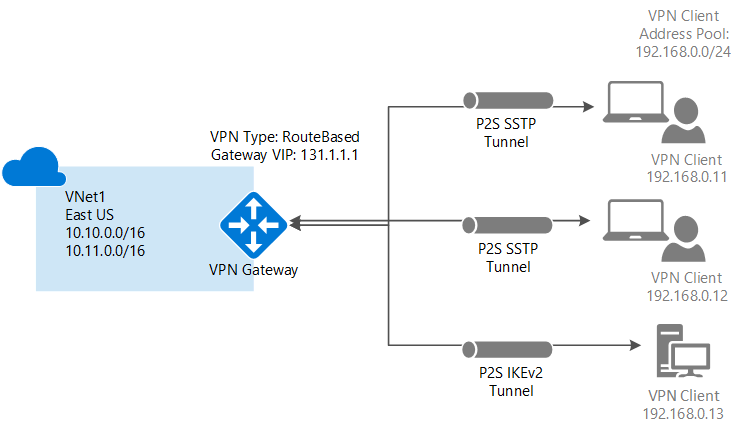
- Point-to-site VPN: Established between a virtual network and a single computer in your network.
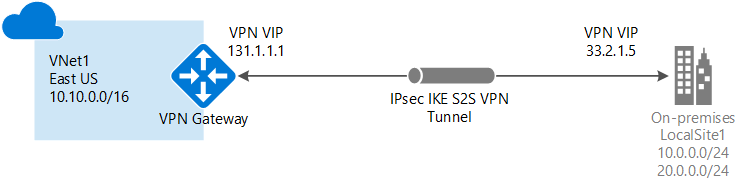
- Site-to-site VPN: Established between your on-premises VPN device and an Azure VPN Gateway that is deployed in a virtual network.
- Azure ExpressRoute: This connection is private and traffic does not go over the internet.
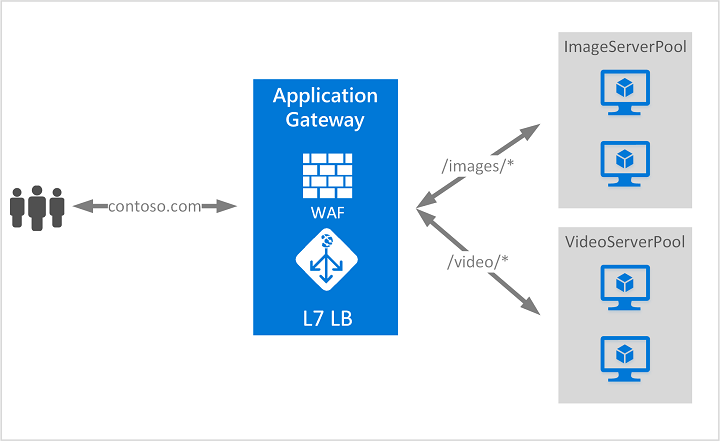
Azure Application Gateway is a web traffic load balancer that enables you to manage traffic to your web applications. Traditional load balancers operate at the transport layer, which is layer 4 in the OSI model for Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP), and route traffic based on the source IP address and port to a destination IP address and port. But with Application Gateway, you can be even more specific. Azure Application Gateway supports application layer (layer 7 in the OSI model) load balancing.
Application Gateway offers autoscaling and other critical performance enhancements.
- Autoscaling. scale up or down based on changing traffic load patterns.
- Zone redundancy. can span multiple Availability Zones
- Static VIP. supports the static VIP type exclusively
Application gateway supports SSL termination at the gateway.
Web application firewall (WAF) provides protection from the OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) core rule sets 3.0 or 2.2.9.
URL Path Based Routing allows you to route traffic to back-end server pools based on URL Paths of the request.
Multiple-site hosting enables you to configure up to 100 web sites to one application gateway.
Application Gateway is currently offered in three sizes. The following table shows an average performance throughput for each application gateway instance with SSL offload enabled:
| Average back-end page response size | Small | Medium | Large |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 KB | 7.5 Mbps | 13 Mbps | 50 Mbps |
| 100 KB | 35 Mbps | 100 Mbps | 200 Mbps |